环境
- python 3.6(推荐使用anaconda)
- django 1.11(pip install django)
- scrapy 1.3.3 (pip install scrapy)
- mysql 5.7.17
- mac os 10.11.6
- chrome 57.0.2987.133 (64-bit)
概述
利用scrapy的css选择器和xpath选择器解析网页,利用django的orm保存数据到mysql,项目github地址:https://github.com/zhujiajunup/Jpider
点评爬虫
先创建django项目和scrapy项目
项目结构如下所示: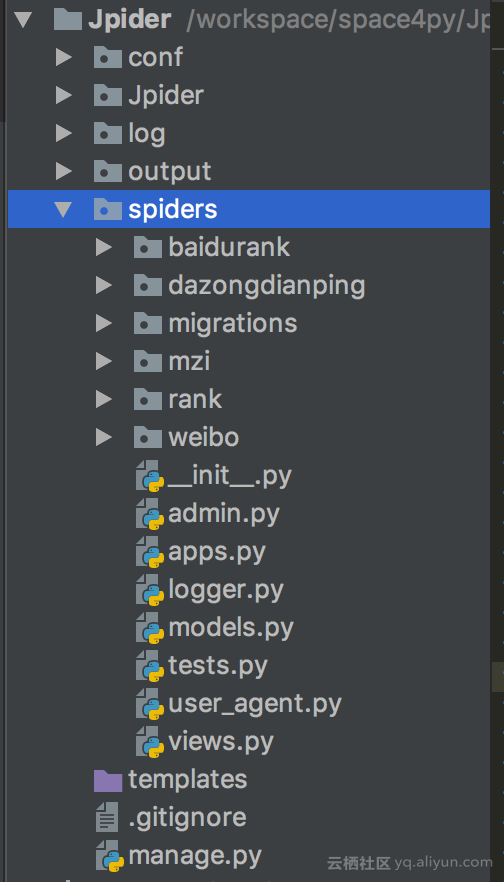
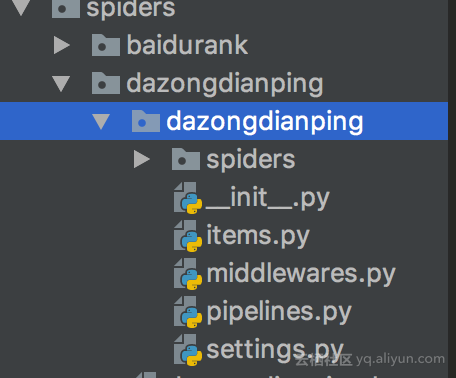
在django app spiders包下的models.py 创建shop信息对应的model
class ShopInfo(models.Model):
shop_id = models.CharField(max_length=20, primary_key=True)
shop_name = models.CharField(max_length=200, default='')
review_count = models.CharField(max_length=20, default='')
avg_price = models.CharField(max_length=20, default='')
taste = models.CharField(max_length=10, default='')
env = models.CharField(max_length=10, default='')
service = models.CharField(max_length=10, default='')
address = models.CharField(max_length=200, default='')
open_time = models.CharField(max_length=200, default='')
rank_star = models.CharField(max_length=20, default='')
place = models.CharField(max_length=20, default='')
classify = models.CharField(max_length=20, default='')
star_all = models.CharField(max_length=20, default='')
star_5 = models.CharField(max_length=20, default='')
star_4 = models.CharField(max_length=20, default='')
star_3 = models.CharField(max_length=20, default='')
star_2 = models.CharField(max_length=20, default='')
star_1 = models.CharField(max_length=20, default='')
feature = models.BooleanField(default=False)
feature2 = models.CharField(max_length=200, default='')在Jpider包下的setting.py配置mysql数据库相关信息
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql',
# 'NAME': os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'db.sqlite3'),
'NAME': 'spider',
'USER': 'root',
'HOST': '127.0.0.1',
'PASSWORD': '1234',
'PORT': 3306,
'OPTIONS': {'charset':'utf8mb4'},
}
}执行如下命令初始化mysql数据库表
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate如果要使用django的orm来与mysql交互,需要在爬虫项目的items.py里配置一下,需要scrapy_djangoitem包,通过如下命令安装
pip install scrapy_djangoitem并定义item
import scrapy
from spiders.models import ShopInfo, ReviewDedail, ShopId
from scrapy_djangoitem import DjangoItem
class DazongdianpingItem(scrapy.Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
# name = scrapy.Field()
pass
class ShopInfoItem(DjangoItem):
django_model = ShopInfo
class ReviewDetailItem(DjangoItem):
django_model = ReviewDedail
class ShopIdItem(DjangoItem):
django_model = ShopId还需要注意的是,在不启动django项目的时候要使用django的模块,需要手动启动,在scrapy的__init__.py里加入如下代码:
import sys
import os
import django
sys.path.append('../../../Jpider') # 具体路径
os.environ['DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE'] = 'Jpider.settings'
django.setup()写爬虫之前,需要了解一下要爬的网站的url组成规则,打开www.dianping.com,打开chrom的调试模式(option+command+i),由于朋友需要美食类下的餐厅信息,
self.start_urls = [
'http://www.dianping.com/search/category/2/10/g110', # 北京火锅
'http://www.dianping.com/search/category/2/10/g107', # 北京台湾菜
'http://www.dianping.com/search/category/2/10/g112', # 北京小吃快餐
'http://www.dianping.com/search/category/2/10/g250', # 北京创意菜
'http://www.dianping.com/search/category/2/10/g116', # 北京西餐
'http://www.dianping.com/search/category/2/10/g113', # 北京日本菜
'http://www.dianping.com/search/category/2/10/g103', # 北京粤菜
'http://www.dianping.com/search/category/2/10/g115', # 北京东南亚菜
'http://www.dianping.com/search/category/2/10/g102', # 北京川菜
'http://www.dianping.com/search/category/1/10/g113', # 上海日本菜???
'http://www.dianping.com/search/category/1/10/g110', # 上海火锅
'http://www.dianping.com/search/category/1/10/g107', # 上海台湾菜
'http://www.dianping.com/search/category/1/10/g103', # 上海粤菜
'http://www.dianping.com/search/category/1/10/g102', # 上海川菜
'http://www.dianping.com/search/category/1/10/g112', # 上海小吃快餐
'http://www.dianping.com/search/category/1/10/g115', # 上海东南亚菜
'http://www.dianping.com/search/category/1/10/g116', # 上海西餐
]那就上海火锅http://www.dianping.com/search/category/1/10/g110 为例
在调试模式下,可以发现,当前页的餐厅信息是在<div calss='shop-list ...'>的li标签下,而餐厅的url包含在a标签的href下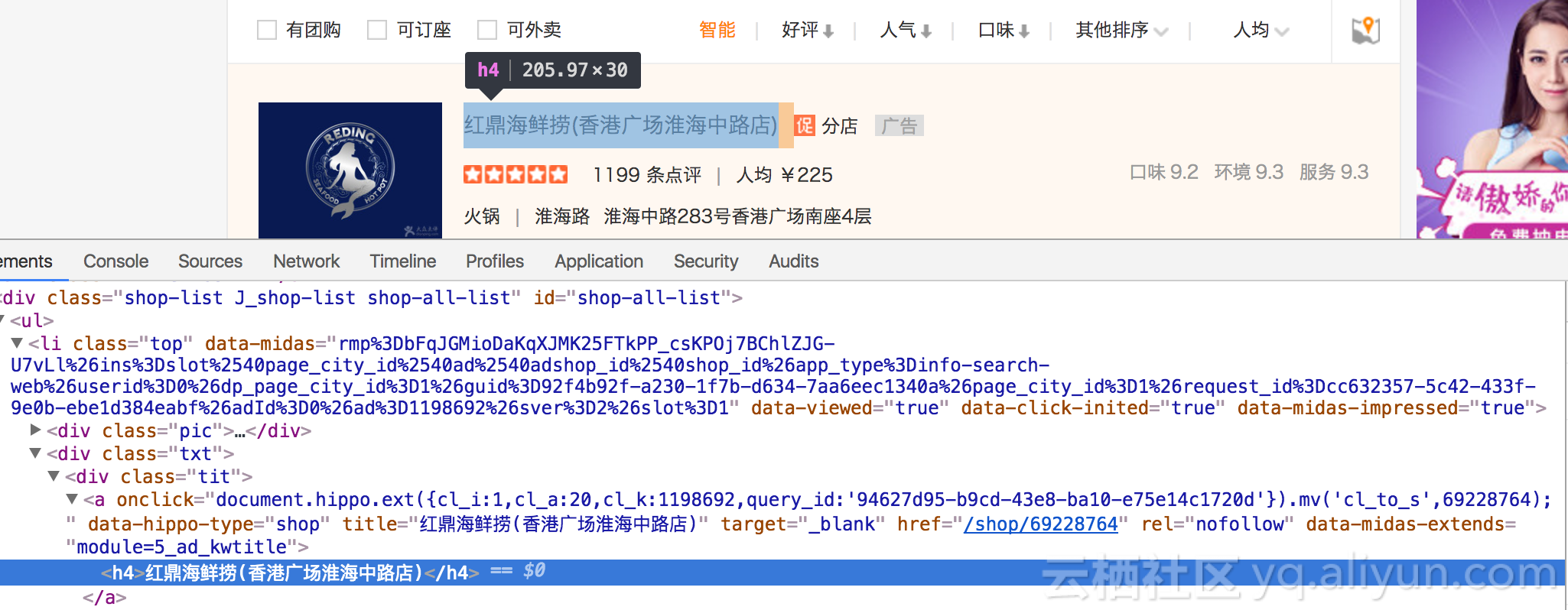
一个
所以就可以先取出li标签,再取出a下的href,处理函数如下:
def parse_pg(self, response):
print(response.url)
shops = response.css('div.content div.shop-list li')
for s in shops:
shop_id_item = ShopIdItem()
short_url = s.css('div.tit a::attr(href)').extract()[0].strip()
shop_url = self.root_url+short_url
shop_id = short_url.split('/')[2]
shop_id_item['shop_id'] = shop_id
shop_id_item.save()
self.count += 1
yield scrapy.Request(shop_url, callback=self.parse_detail)
self.logger.error('total count %d' % self.count)当然需要处理分页问题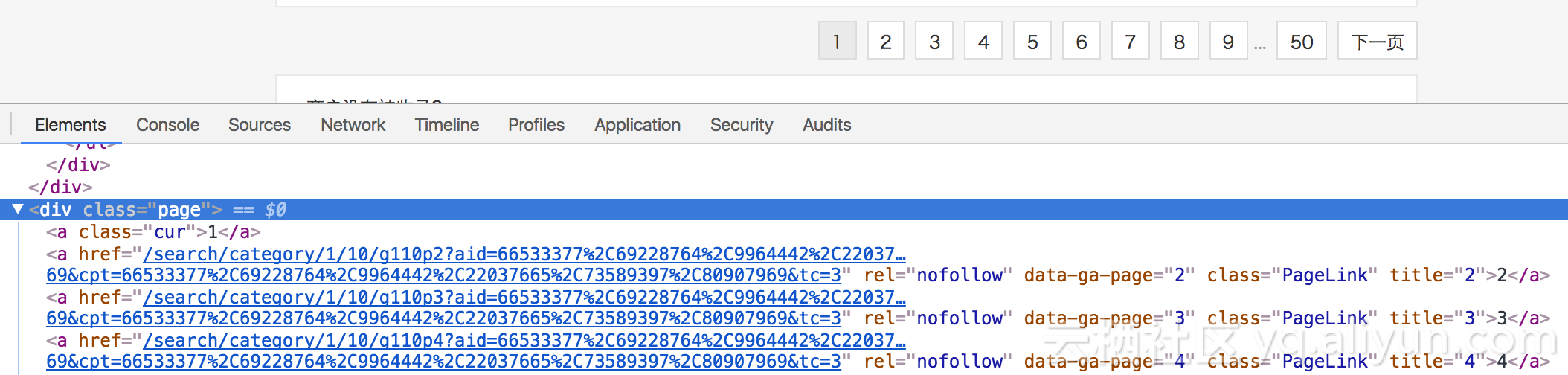
同理,通过scrapy的css+xpath很容易定位
def parse(self, response):
yield scrapy.Request(response.url, callback=self.parse_pg)
pages = int(response.css('div.page a::text').extract()[-2])
for pg in range(1, pages+1):
print(response.url + 'p' + str(pg))
yield scrapy.Request(response.url + 'p' + str(pg), callback=self.parse_pg)现在就可以提取餐厅的具体信息了
def parse_detail(self, response):
print(response.url)
shop_id = response.url[response.url.rindex('/')+1:]
basic_info = response.css('div.basic-info')
closed_class = basic_info.css('p.shop-closed').extract()
if closed_class != []: # 未营业
shop_info = ShopInfoItem()
shop_info['shop_id'] = shop_id
shop_name = basic_info.css('h1.shop-name::text').extract()[0].strip()
shop_info['shop_name'] = shop_name
shop_info.save()
self.logger.error('%s 未营业' % response.url)
return None
try:
rank_star = basic_info.css('div.brief-info span.mid-rank-stars::attr(title)').extract()[0].strip()
shop_name = basic_info.css('h1.shop-name::text').extract()[0].strip()
review_count = basic_info.css('div.brief-info').xpath('./span/text()').extract()[0].strip()
avg_price = basic_info.css('div.brief-info').xpath('./span[@id="avgPriceTitle"]/text()').extract()[0].strip()
comment_score = basic_info.css('div.brief-info').xpath('./span[@id="comment_score"]').css('span.item::text').extract()
address = basic_info.css('div.address').xpath('./span[@itemprop="street-address"]/text()').extract()[0].strip()
info_indent = basic_info.css('div.other p.info')
print(basic_info.css('div.promosearch-wrapper').extract())
tuan = basic_info.css('div.promosearch-wrapper p.expand-info').css('span.info-name::text').extract()
print('-'*10+str(tuan)+'-'*10)
breadcrumb = response.css('div.breadcrumb')
bars = breadcrumb.css('a::text').extract()
if len(bars) >= 3:
place = bars[1].strip()
classify = bars[2].strip()
else:
place = ''
classify = ''
open_time = ''
for ind in info_indent:
# print(ind.css('span.info-name::text').extract())
if ind.css('span.info-name::text').extract()[0].strip().startswith('营业时间'):
open_time = ind.css('span.item::text').extract()[0].strip()
break
# print(shop_id+'\t'+shop_name+'\t'+review_count+'\t'+avg_price+'\t'+str(comment_score)+'\t'+str(address)+'\t'+open_time)
shop_info = ShopInfoItem()
shop_info['shop_id'] = shop_id
shop_info['shop_name'] = shop_name
shop_info['review_count'] = review_count
shop_info['avg_price'] = avg_price
shop_info['address'] = address
shop_info['open_time'] = open_time
shop_info['taste'] = comment_score[0]
shop_info['env'] = comment_score[1]
shop_info['service'] = comment_score[2]
shop_info['rank_star'] = rank_star
shop_info['place'] = place
shop_info['classify'] = classify
shop_file = open(self.save_dir + 'shop/' + str(shop_id) + '.html', 'w')
shop_file.write(response.body.decode('utf-8'))
shop_info.save()
yield scrapy.Request(response.url+'/review_more_newest', callback=self.parse_review)
except Exception:
self.logger.error(response.url+' exception')
self.logger.error(traceback.format_exc())启动scrapy
scrapy crawl dazongdianping查看数据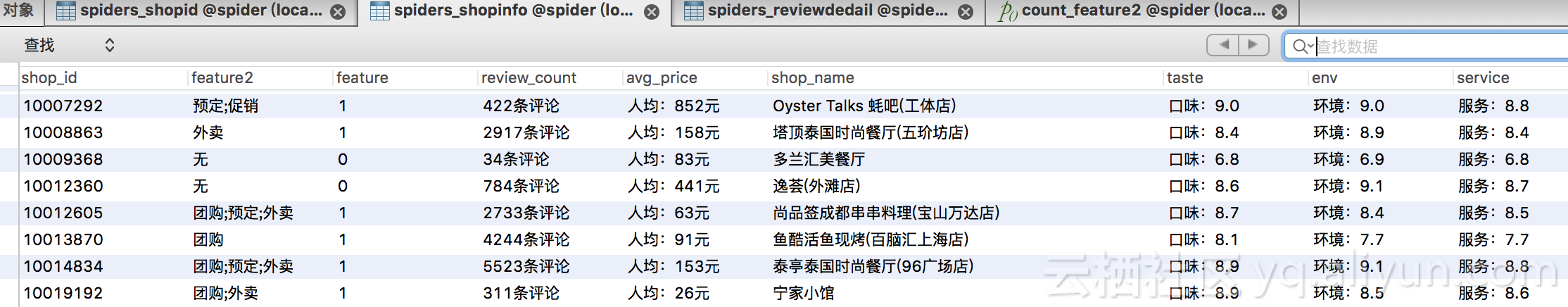
导出数据到excel
import sys
import os
import django
import django.db.models
sys.path.append('../Jpider')
os.environ['DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE'] = 'Jpider.settings'
django.setup()
from spiders.models import ShopInfo, ReviewDedail, ShopId
import xlwt
category_dict = {'g110':'火锅', 'g107':'台湾菜', 'g112':'小吃快餐', 'g250': '创意菜',
'g116': '西餐', 'g113': '日本菜', 'g103': '粤菜', 'g115': '东南亚菜', 'g102': '川菜'}
rank_star_dict = {
'五星商户': 5,
'准五星商户':4.5,
'四星商户': 4,
'准四星商户': 3.5,
'三星商户': 3,
'准三星商户': 2.5,
'二星商户': 2,
'准二星商户': 1.5,
'一星商户': 1,
'准一星商户': 0.5,
'该商户暂无星级': 0,
'': '无'
}
workbook = xlwt.Workbook()
sheet = workbook.add_sheet('dazongdianping',cell_overwrite_ok=True)
title = ['餐厅id','城市', '餐厅名称', '餐厅地点', '餐厅地址', '餐厅类别', '人均价格', '是否参加营销活动', '营业时间', '点评数量',
'总体评分', '口味评分', '环境评分', '服务评分', '五星', '四星', '三星', '二星', '一星', '第一条评论时间']
for i in range(len(title)):
sheet.write(0, i, title[i] )
shops = ShopInfo.objects.all()
result_dic = {}
for j in range(1, len(shops)+1):
shop = shops[j-1]
info_list = []
info_list.append(str(shop.shop_id)) # id
print(shop.shop_id)
try:
url = ShopId.objects.get(pk=shop.shop_id).from_url
except ShopId.DoesNotExist:
continue
if url is None:
continue
city_no = url.split('/')[-3]
city = '北京' if city_no == '2' else '上海'
info_list.append(city)
category = category_dict[url.split('/')[-1][:4]]
info_list.append(shop.shop_name)
info_list.append(shop.place if shop.place is not None else '')
info_list.append(shop.address if shop.address is not None else '')
info_list.append(category)
avg_price = shop.avg_price.split(':')[1]
if len(avg_price) != 1:
avg_price = avg_price[:-1]
info_list.append(avg_price )
features = shop.feature2.split(';')
print(features)
f_l = []
for f in features:
if f == 'huo':
print('活动')
f_l.append('活动')
elif f == 'ka':
print('会员卡')
f_l.append('会员卡')
else:
f_l.append(f)
info_list.append(';'.join(f_l))
f_l.clear()
info_list.append(shop.open_time.replace('\t', ' ').replace('\r','').replace('\n', ';') if shop.open_time is not None else '')
info_list.append(shop.review_count[:-3])
info_list.append(rank_star_dict[shop.rank_star])
info_list.append(shop.taste.split(':')[1])
info_list.append(shop.env.split(':')[1])
info_list.append(shop.service.split(':')[1])
review = ReviewDedail.objects.get(pk=shop.shop_id)
info_list.append(review.star_5)
info_list.append(review.star_4)
info_list.append(review.star_3)
info_list.append(review.star_2)
info_list.append(review.star_1)
info_list.append(review.first_review_time)
for i in range(len(info_list)):
if info_list[i] is None:
info_list[i] = ' '
li = result_dic.get(city+'_'+category, [])
li.append(info_list.copy())
result_dic[city+'_'+category] = li
info_list.clear()
book = xlwt.Workbook()
for city_cate, infos in result_dic.items():
sheet = book.add_sheet(city_cate)
for i in range(len(title)):
sheet.write(0, i, title[i])
for i in range(1, len(infos)):
for j in range(len(infos[i])):
sheet.write(i, j, infos[i][j])
book.save('./all-data.xls')
