Spark2.4.0 Dataset head 源码分析
更多资源
视频
- Spark2.4.0 Dataset head 原理分析(bilibili视频): https://www.bilibili.com/video/av38193405/?p=6
- Spark2.4.0 Dataset head 源码分析(bilibili视频): https://www.bilibili.com/video/av38193405/?p=7
前置条件
- Hadoop版本: hadoop-2.9.2
- Spark版本: spark-2.4.0-bin-hadoop2.7
- JDK.1.8.0_191
- scala2.11.12
主要内容描述
- Dataset 如何转成RDD触发作业运行
- Dataset head 是如何读到HDFS上文件前n行数据
图解
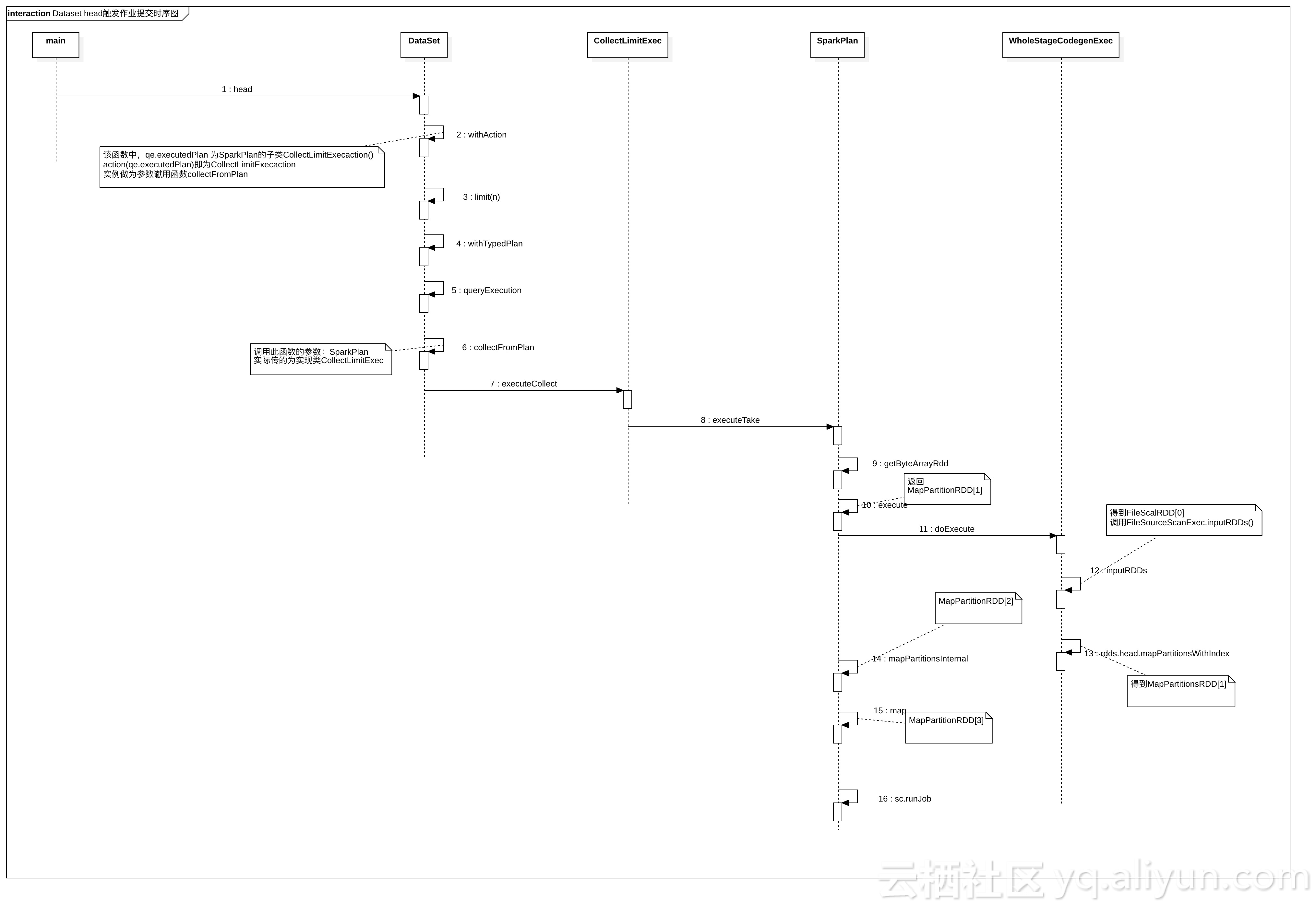

StartUML文件
源码分析
输入数据
第一行数据
第二行数据
第三行数据
第四行数据BaseSparkSession
package com.opensource.bigdata.spark.standalone.base
import java.io.File
import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession
/**
* 得到SparkSession
* 首先 extends BaseSparkSession
* 本地: val spark = sparkSession(true)
* 集群: val spark = sparkSession()
*/
class BaseSparkSession {
var appName = "sparkSession"
var master = "spark://standalone.com:7077" //本地模式:local standalone:spark://master:7077
def sparkSession(): SparkSession = {
val spark = SparkSession.builder
.master(master)
.appName(appName)
.config("spark.eventLog.enabled","true")
.config("spark.history.fs.logDirectory","hdfs://standalone.com:9000/spark/log/historyEventLog")
.config("spark.eventLog.dir","hdfs://standalone.com:9000/spark/log/historyEventLog")
.getOrCreate()
spark.sparkContext.addJar("/opt/n_001_workspaces/bigdata/spark-scala-maven-2.4.0/target/spark-scala-maven-2.4.0-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar")
//import spark.implicits._
spark
}
def sparkSession(isLocal:Boolean = false,isHiveSupport:Boolean = false,debug:Boolean=false): SparkSession = {
val warehouseLocation = new File("spark-warehouse").getAbsolutePath
if(isLocal){
master = "local"
var builder = SparkSession.builder
.master(master)
.appName(appName)
.config("spark.sql.warehouse.dir",warehouseLocation)
if(isHiveSupport){
builder = builder.enableHiveSupport()
//.config("spark.sql.hive.metastore.version","2.3.3")
}
val spark = builder.getOrCreate()
//spark.sparkContext.addJar("/opt/n_001_workspaces/bigdata/spark-scala-maven-2.4.0/target/spark-scala-maven-2.4.0-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar")
//import spark.implicits._
spark
}else{
var builder = SparkSession.builder
.master(master)
.appName(appName)
.config("spark.sql.warehouse.dir",warehouseLocation)
.config("spark.eventLog.enabled","true")
.config("spark.eventLog.compress","true")
.config("spark.history.fs.logDirectory","hdfs://standalone.com:9000/spark/log/historyEventLog")
.config("spark.eventLog.dir","hdfs://standalone.com:9000/spark/log/historyEventLog")
//executor debug,是在提交作的地方读取
if(debug){
builder.config("spark.executor.extraJavaOptions","-Xdebug -Xrunjdwp:transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=y,address=10002")
}
if(isHiveSupport){
builder = builder.enableHiveSupport()
//.config("spark.sql.hive.metastore.version","2.3.3")
}
val spark = builder.getOrCreate()
//需要有jar才可以在远程执行
spark.sparkContext.addJar("/opt/n_001_workspaces/bigdata/spark-scala-maven-2.4.0/target/spark-scala-maven-2.4.0-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar")
spark
}
}
/**
* 得到当前工程的路径
* @return
*/
def getProjectPath:String=System.getProperty("user.dir")
}
客户端程序
- 功能:读取HDFS上文件前3行的数据
object Run extends BaseSparkSession{
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val spark = sparkSession(false,false,false)
//返回dataFrame
val df = spark.read.textFile("data/text/line.txt")
//调用Dataset.head(n) 函数,该方法返回读取到的数据,并按行的数组返回
val result = df.head(3)
println(s"运行结果: ${result.mkString("\n")}")
spark.stop()
}
}df.head
- 调用Dataset.head(n) 函数,该方法返回读取到的数据,并按行的数组返回
- 函数 collectFromPlan 的参数SparkPlan,是在函数withAction中赋值的
/**
* Returns the first `n` rows.
*
* @note this method should only be used if the resulting array is expected to be small, as
* all the data is loaded into the driver's memory.
*
* @group action
* @since 1.6.0
*/
def head(n: Int): Array[T] = withAction("head", limit(n).queryExecution)(collectFromPlan)Dataset.withAction
- qe.executedPlan 返回的对象是CollectLimitExec
- CollectLimitExec extends UnaryExecNode extends SparkPlan
- 也说是说函数collectFromPlan的参数是CollectLimitExec实例
/**
* Wrap a Dataset action to track the QueryExecution and time cost, then report to the
* user-registered callback functions.
*/
private def withAction[U](name: String, qe: QueryExecution)(action: SparkPlan => U) = {
try {
qe.executedPlan.foreach { plan =>
plan.resetMetrics()
}
val start = System.nanoTime()
val result = SQLExecution.withNewExecutionId(sparkSession, qe) {
action(qe.executedPlan)
}
val end = System.nanoTime()
sparkSession.listenerManager.onSuccess(name, qe, end - start)
// result就是结果,文件的前n行数据做为一个数组
result
} catch {
case e: Exception =>
sparkSession.listenerManager.onFailure(name, qe, e)
throw e
}
}Dataset.collectFromPlan
- 从SparkPlan中收集元素
- plan.executeCollect()拿到文件前n行数据,每行数据的对象是UnsafeRow,所以还需要进行转换才变成字符串格式
- plan.executeCollect() 等于是调用CollectLimitExec.executeCollect()
/**
* Collect all elements from a spark plan.
*/
private def collectFromPlan(plan: SparkPlan): Array[T] = {
// This projection writes output to a `InternalRow`, which means applying this projection is not
// thread-safe. Here we create the projection inside this method to make `Dataset` thread-safe.
val objProj = GenerateSafeProjection.generate(deserializer :: Nil)
plan.executeCollect().map { row =>
// The row returned by SafeProjection is `SpecificInternalRow`, which ignore the data type
// parameter of its `get` method, so it's safe to use null here.
objProj(row).get(0, null).asInstanceOf[T]
}
}
CollectLimitExec.executeCollect()
- child为SparkPlan,所以是调用SparkPlan.executeTake(limit)
override def executeCollect(): Array[InternalRow] = child.executeTake(limit)
SparkPlan.executeTake(limit)
- 最关键的方法
- getByteArrayRdd(n) 得到RDD
- sc.runJob 触发作业提交
/**
* Runs this query returning the first `n` rows as an array.
*
* This is modeled after `RDD.take` but never runs any job locally on the driver.
*/
def executeTake(n: Int): Array[InternalRow] = {
if (n == 0) {
return new Array[InternalRow](0)
}
//得到RDD MapPartitionsRDD[3]
val childRDD = getByteArrayRdd(n).map(_._2)
val buf = new ArrayBuffer[InternalRow]
val totalParts = childRDD.partitions.length
var partsScanned = 0
//按rdd partition 来提交作业
while (buf.size < n && partsScanned < totalParts) {
// The number of partitions to try in this iteration. It is ok for this number to be
// greater than totalParts because we actually cap it at totalParts in runJob.
var numPartsToTry = 1L
if (partsScanned > 0) {
// If we didn't find any rows after the previous iteration, quadruple and retry.
// Otherwise, interpolate the number of partitions we need to try, but overestimate
// it by 50%. We also cap the estimation in the end.
val limitScaleUpFactor = Math.max(sqlContext.conf.limitScaleUpFactor, 2)
if (buf.isEmpty) {
numPartsToTry = partsScanned * limitScaleUpFactor
} else {
val left = n - buf.size
// As left > 0, numPartsToTry is always >= 1
numPartsToTry = Math.ceil(1.5 * left * partsScanned / buf.size).toInt
numPartsToTry = Math.min(numPartsToTry, partsScanned * limitScaleUpFactor)
}
}
val p = partsScanned.until(math.min(partsScanned + numPartsToTry, totalParts).toInt)
val sc = sqlContext.sparkContext
//提交作业
val res = sc.runJob(childRDD,
(it: Iterator[Array[Byte]]) => if (it.hasNext) it.next() else Array.empty[Byte], p)
buf ++= res.flatMap(decodeUnsafeRows)
partsScanned += p.size
}
if (buf.size > n) {
buf.take(n).toArray
} else {
buf.toArray
}
}SparkPlan.getByteArrayRdd()得到RDD的方法
- 调用函数 execute() 得到RDD,调用的是WholeStageCodegenExec.doExecute()函数
- rdd.mapPartitionsInternal() 调用函数得到新的rdd MapPartitionsRDD
/**
* Packing the UnsafeRows into byte array for faster serialization.
* The byte arrays are in the following format:
* [size] [bytes of UnsafeRow] [size] [bytes of UnsafeRow] ... [-1]
*
* UnsafeRow is highly compressible (at least 8 bytes for any column), the byte array is also
* compressed.
*/
private def getByteArrayRdd(n: Int = -1): RDD[(Long, Array[Byte])] = {
//MapPartitionsRDD[2]
execute().mapPartitionsInternal { iter =>
var count = 0
val buffer = new Array[Byte](4 << 10) // 4K
val codec = CompressionCodec.createCodec(SparkEnv.get.conf)
val bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream()
val out = new DataOutputStream(codec.compressedOutputStream(bos))
// `iter.hasNext` may produce one row and buffer it, we should only call it when the limit is
// not hit.
while ((n < 0 || count < n) && iter.hasNext) {
val row = iter.next().asInstanceOf[UnsafeRow]
out.writeInt(row.getSizeInBytes)
row.writeToStream(out, buffer)
count += 1
}
out.writeInt(-1)
out.flush()
out.close()
Iterator((count, bos.toByteArray))
}
}WholeStageCodegenExec.doExecute()
- child.asInstanceOf[CodegenSupport].inputRDDs() 得到RDD
override def doExecute(): RDD[InternalRow] = {
val (ctx, cleanedSource) = doCodeGen()
// try to compile and fallback if it failed
val (_, maxCodeSize) = try {
CodeGenerator.compile(cleanedSource)
} catch {
case NonFatal(_) if !Utils.isTesting && sqlContext.conf.codegenFallback =>
// We should already saw the error message
logWarning(s"Whole-stage codegen disabled for plan (id=$codegenStageId):\n $treeString")
return child.execute()
}
// Check if compiled code has a too large function
if (maxCodeSize > sqlContext.conf.hugeMethodLimit) {
logInfo(s"Found too long generated codes and JIT optimization might not work: " +
s"the bytecode size ($maxCodeSize) is above the limit " +
s"${sqlContext.conf.hugeMethodLimit}, and the whole-stage codegen was disabled " +
s"for this plan (id=$codegenStageId). To avoid this, you can raise the limit " +
s"`${SQLConf.WHOLESTAGE_HUGE_METHOD_LIMIT.key}`:\n$treeString")
child match {
// The fallback solution of batch file source scan still uses WholeStageCodegenExec
case f: FileSourceScanExec if f.supportsBatch => // do nothing
case _ => return child.execute()
}
}
val references = ctx.references.toArray
val durationMs = longMetric("pipelineTime")
//得到RDD,调用FileSourceScanExec.inputRDDs()
val rdds = child.asInstanceOf[CodegenSupport].inputRDDs()
assert(rdds.size <= 2, "Up to two input RDDs can be supported")
if (rdds.length == 1) {
//MapPartitionsRDD[1]
rdds.head.mapPartitionsWithIndex { (index, iter) =>
val (clazz, _) = CodeGenerator.compile(cleanedSource)
val buffer = clazz.generate(references).asInstanceOf[BufferedRowIterator]
buffer.init(index, Array(iter))
new Iterator[InternalRow] {
override def hasNext: Boolean = {
val v = buffer.hasNext
if (!v) durationMs += buffer.durationMs()
v
}
override def next: InternalRow = buffer.next()
}
}
} else {
// Right now, we support up to two input RDDs.
rdds.head.zipPartitions(rdds(1)) { (leftIter, rightIter) =>
Iterator((leftIter, rightIter))
// a small hack to obtain the correct partition index
}.mapPartitionsWithIndex { (index, zippedIter) =>
val (leftIter, rightIter) = zippedIter.next()
val (clazz, _) = CodeGenerator.compile(cleanedSource)
val buffer = clazz.generate(references).asInstanceOf[BufferedRowIterator]
buffer.init(index, Array(leftIter, rightIter))
new Iterator[InternalRow] {
override def hasNext: Boolean = {
val v = buffer.hasNext
if (!v) durationMs += buffer.durationMs()
v
}
override def next: InternalRow = buffer.next()
}
}
}
}
FileSourceScanExec.inputRDDs()
- 调用 inputRDD函数
override def inputRDDs(): Seq[RDD[InternalRow]] = {
inputRDD :: Nil
}
FileSourceScanExec.inputRDD()
- 定义函数 readFile,返回值为 PartitionedFile 文件,是一个可迭代对象Iterator[InternalRow]
- 调用函数 createNonBucketedReadRDD(readFile, selectedPartitions, relation)
private lazy val inputRDD: RDD[InternalRow] = {
val readFile: (PartitionedFile) => Iterator[InternalRow] =
relation.fileFormat.buildReaderWithPartitionValues(
sparkSession = relation.sparkSession,
dataSchema = relation.dataSchema,
partitionSchema = relation.partitionSchema,
requiredSchema = requiredSchema,
filters = pushedDownFilters,
options = relation.options,
hadoopConf = relation.sparkSession.sessionState.newHadoopConfWithOptions(relation.options))
relation.bucketSpec match {
case Some(bucketing) if relation.sparkSession.sessionState.conf.bucketingEnabled =>
createBucketedReadRDD(bucketing, readFile, selectedPartitions, relation)
case _ =>
createNonBucketedReadRDD(readFile, selectedPartitions, relation)
}
}FileSourceScanExec.createNonBucketedReadRDD()
- 返回 FileScanRDD, FileScanRDD[0],以上三个RDD全部找到
- MapPartitionsRDD[3],MapPartitionsRDD[2],MapPartitionsRDD[1],FileScanRDD[0]
/**
* Create an RDD for non-bucketed reads.
* The bucketed variant of this function is [[createBucketedReadRDD]].
*
* @param readFile a function to read each (part of a) file.
* @param selectedPartitions Hive-style partition that are part of the read.
* @param fsRelation [[HadoopFsRelation]] associated with the read.
*/
private def createNonBucketedReadRDD(
readFile: (PartitionedFile) => Iterator[InternalRow],
selectedPartitions: Seq[PartitionDirectory],
fsRelation: HadoopFsRelation): RDD[InternalRow] = {
val defaultMaxSplitBytes =
fsRelation.sparkSession.sessionState.conf.filesMaxPartitionBytes
val openCostInBytes = fsRelation.sparkSession.sessionState.conf.filesOpenCostInBytes
val defaultParallelism = fsRelation.sparkSession.sparkContext.defaultParallelism
val totalBytes = selectedPartitions.flatMap(_.files.map(_.getLen + openCostInBytes)).sum
val bytesPerCore = totalBytes / defaultParallelism
val maxSplitBytes = Math.min(defaultMaxSplitBytes, Math.max(openCostInBytes, bytesPerCore))
logInfo(s"Planning scan with bin packing, max size: $maxSplitBytes bytes, " +
s"open cost is considered as scanning $openCostInBytes bytes.")
val splitFiles = selectedPartitions.flatMap { partition =>
partition.files.flatMap { file =>
val blockLocations = getBlockLocations(file)
if (fsRelation.fileFormat.isSplitable(
fsRelation.sparkSession, fsRelation.options, file.getPath)) {
(0L until file.getLen by maxSplitBytes).map { offset =>
val remaining = file.getLen - offset
val size = if (remaining > maxSplitBytes) maxSplitBytes else remaining
val hosts = getBlockHosts(blockLocations, offset, size)
PartitionedFile(
partition.values, file.getPath.toUri.toString, offset, size, hosts)
}
} else {
val hosts = getBlockHosts(blockLocations, 0, file.getLen)
Seq(PartitionedFile(
partition.values, file.getPath.toUri.toString, 0, file.getLen, hosts))
}
}
}.toArray.sortBy(_.length)(implicitly[Ordering[Long]].reverse)
val partitions = new ArrayBuffer[FilePartition]
val currentFiles = new ArrayBuffer[PartitionedFile]
var currentSize = 0L
/** Close the current partition and move to the next. */
def closePartition(): Unit = {
if (currentFiles.nonEmpty) {
val newPartition =
FilePartition(
partitions.size,
currentFiles.toArray.toSeq) // Copy to a new Array.
partitions += newPartition
}
currentFiles.clear()
currentSize = 0
}
// Assign files to partitions using "Next Fit Decreasing"
splitFiles.foreach { file =>
if (currentSize + file.length > maxSplitBytes) {
closePartition()
}
// Add the given file to the current partition.
currentSize += file.length + openCostInBytes
currentFiles += file
}
closePartition()
new FileScanRDD(fsRelation.sparkSession, readFile, partitions)
}
输出结果数据
第一行数据
第二行数据
第三行数据end



