为了在Kubernetes上搭建RabbitMQ3.7.X Cluster,踩爆无数坑,官方整合了第三方开源项目但没有完整demo,网上的post都是RabbitMQ 3.6.X旧版的部署方案,几经周折,最终弄明白在Kubernetes集群下,基于Kubernetes Discovery,使用hostname方式部署RabbitMQ3.7.X Cluster,总结如下:
1. IP模式
rabbitmq-peer-discovery-k8s是RabbitMQ官方基于第三方开源项目rabbitmq-autocluster开发,对3.7.X版本提供的Kubernetes下的同行发现插件,但官方只提供了一个基于IP模式的demo
kind: Service apiVersion: v1 metadata: namespace: test-rabbitmq name: rabbitmq labels: app: rabbitmq type: LoadBalancer spec: type: NodePort ports: - name: http protocol: TCP port: 15672 targetPort: 15672 nodePort: 31672 - name: amqp protocol: TCP port: 5672 targetPort: 5672 nodePort: 30672 selector: app: rabbitmq --- apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: rabbitmq-config namespace: test-rabbitmq data: enabled_plugins: | [rabbitmq_management,rabbitmq_peer_discovery_k8s]. rabbitmq.conf: | ## Cluster formation. See http://www.rabbitmq.com/cluster-formation.html to learn more. cluster_formation.peer_discovery_backend = rabbit_peer_discovery_k8s cluster_formation.k8s.host = kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local ## Should RabbitMQ node name be computed from the pod's hostname or IP address? ## IP addresses are not stable, so using [stable] hostnames is recommended when possible. ## Set to "hostname" to use pod hostnames. ## When this value is changed, so should the variable used to set the RABBITMQ_NODENAME ## environment variable. cluster_formation.k8s.address_type = ip ## How often should node cleanup checks run? cluster_formation.node_cleanup.interval = 30 ## Set to false if automatic removal of unknown/absent nodes ## is desired. This can be dangerous, see ## * http://www.rabbitmq.com/cluster-formation.html#node-health-checks-and-cleanup ## * https://groups.google.com/forum/#!msg/rabbitmq-users/wuOfzEywHXo/k8z_HWIkBgAJ cluster_formation.node_cleanup.only_log_warning = true cluster_partition_handling = autoheal ## See http://www.rabbitmq.com/ha.html#master-migration-data-locality queue_master_locator=min-masters ## See http://www.rabbitmq.com/access-control.html#loopback-users loopback_users.guest = false --- apiVersion: apps/v1beta1 kind: StatefulSet metadata: name: rabbitmq namespace: test-rabbitmq spec: serviceName: rabbitmq replicas: 3 template: metadata: labels: app: rabbitmq spec: serviceAccountName: rabbitmq terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 10 containers: - name: rabbitmq-k8s image: rabbitmq:3.7 volumeMounts: - name: config-volume mountPath: /etc/rabbitmq ports: - name: http protocol: TCP containerPort: 15672 - name: amqp protocol: TCP containerPort: 5672 livenessProbe: exec: command: ["rabbitmqctl", "status"] initialDelaySeconds: 60 periodSeconds: 60 timeoutSeconds: 10 readinessProbe: exec: command: ["rabbitmqctl", "status"] initialDelaySeconds: 20 periodSeconds: 60 timeoutSeconds: 10 imagePullPolicy: Always env: - name: MY_POD_IP valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: status.podIP - name: RABBITMQ_USE_LONGNAME value: "true" # See a note on cluster_formation.k8s.address_type in the config file section - name: RABBITMQ_NODENAME value: "rabbit@$(MY_POD_IP)" - name: K8S_SERVICE_NAME value: "rabbitmq" - name: RABBITMQ_ERLANG_COOKIE value: "mycookie" volumes: - name: config-volume configMap: name: rabbitmq-config items: - key: rabbitmq.conf path: rabbitmq.conf - key: enabled_plugins path: enabled_plugins
在ConfigMap配置项中,指明 cluster_formation.k8s.address_type = ip,也就是说RabbitMQ Node的命名和访问地址是以IP地址作为区分,如rabbit@172.0.5.1
但这样的配置会产生比较大的问题,如果我们使用pv和pvc去做数据的持久化,那么每个节点的配置和数据存储都会放在rabbit@172.0.5.1这样的文件夹下,而Kubernetes集群中,Pod的IP都是不稳定的,当有RabbitMQ Node的Pod挂掉后,重新创建的Pod IP可能会变,这就会使得节点的配置和数据全部丢失。
所以我们更希望RabbitMQ Node的命名是以一定规则编写的相对稳定的名称,如rabbit@rabbit-0,这就需要修改 cluster_formation.k8s.address_type = hostname,以启用hostname模式。
但直接修改address_type 并不能满足要求,注释部分也描述了“Set to hostname to use pod hostnames. When this value is changed, so should the variable used to set the RABBITMQ_NODENAME”。那么RABBITMQ_NODENAME该如何设置,就必须先要了解如何用hostname访问pod
2. Pod与Service的DNS
Kubernetes官方讲述了如何用hostname访问service和pod:dns-pod-service,
其中对于service,可以直接使用my-svc.my-namespace.svc.cluster.local进行访问;而对于pod,则需使用pod-ip-address.my-namespace.pod.cluster.local进行访问,但这里却仍显式的应用到了pod的ip。我们希望脱离ip对pod进行访问,很不幸的是,pod确实无法直接通过hostname访问,不过却有个曲线救国的方案。
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: default-subdomain # 和pod的subdomain相同 spec: selector: name: busybox clusterIP: None # clusterIP: None表示这是一个headless service ports: - name: foo # 没啥用 port: 1234 targetPort: 1234 --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: busybox1 labels: name: busybox spec: hostname: busybox-1 # 默认使用metadata.name作为hostname,也可指定设置 subdomain: default-subdomain containers: - image: busybox command: - sleep - "3600" name: busybox
如上面代码所示,我们需要一个headless service来作为中介,这样就可以使用busybox-1.default-subdomain.default.svc.cluster.local来访问pod了(hostname.subdomain.my-namespace.svc.cluster.local)
3. Statefulset 与Headless Service
了解了如何用hostname访问Pod还不足以解决问题,在RabbitMQ的配置中,我们使用的是StatefulSet,那么StatefulSet如何用Headless Service去做Pod的hostname访问呢?
Kubernetes(StatefulSets在1.9版本后已经是一个稳定功能)官方也给出了详细的说明:statefulset
Demo和注释如下:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: nginx labels: app: nginx spec: ports: - port: 80 name: web clusterIP: None # 是一个headless service selector: app: nginx --- apiVersion: apps/v1 # 需要注意如果是apps/v1,.spec.selector.matchLabels和.spec.template.metadata.labels要相同;如果是apps/v1beta,可以省略.spec.selector.matchLabels kind: StatefulSet metadata: name: web spec: selector: matchLabels: app: nginx # 需要与 .spec.template.metadata.labels 相同,但无需与headless service name相同 serviceName: "nginx" # 需要与headless service name相同 replicas: 3 template: metadata: labels: app: nginx # 需要与 .spec.selector.matchLabels 相同,但无需与headless service name相同 spec: terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 10 containers: - name: nginx image: k8s.gcr.io/nginx-slim:0.8 ports: - containerPort: 80 name: web
需要特别注意的是,网上很多例子的StatefulSet用的apps/v1beta
4. hostname模式
在我查找的众多资料中,在Kubernetes中
讲RabbitMQ 3.6.X部署的,https://www.kubernetes.org.cn/2629.html 这篇讲的比较清楚
讲RabbitMQ 3.7.X部署的,https://habr.com/company/eastbanctech/blog/419817 这篇俄文的Post讲的比较清楚,但它也是用的apps/v1beta,同时有大量的重复配置,不知道哪些可用哪些无用,还有一个最致命的问题是按照它的配置部署后,readinessProbe老报错,说DNS解析出现问题。几经折腾,才明白因为用Headless Service去做Pod的hostname访问,需要等Pod和Service都启动后才能访问,而readiness探针还没等DNS正常就去探查服务是否可用,所以才会误认为服务不可达,最终无法启动Pod。解决办法是给Headless Service设置publishNotReadyAddresses: true
我的配置文件如下所示:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: rabbitmq --- apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: rabbitmq namespace: rabbitmq --- kind: Role apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 metadata: name: endpoint-reader namespace: rabbitmq rules: - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["endpoints"] verbs: ["get"] --- kind: RoleBinding apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 metadata: name: endpoint-reader namespace: rabbitmq subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: rabbitmq roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: Role name: endpoint-reader --- apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolume metadata: name: rabbitmq-data labels: release: rabbitmq-data namespace: rabbitmq spec: capacity: storage: 10Gi accessModes: - ReadWriteMany persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain nfs: path: /rabbit server: xxxxx # nas地址 --- apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: rabbitmq-data-claim namespace: rabbitmq spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteMany resources: requests: storage: 10Gi selector: matchLabels: release: rabbitmq-data --- # headless service 用于使用hostname访问pod kind: Service apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: rabbitmq-headless namespace: rabbitmq spec: clusterIP: None # publishNotReadyAddresses, when set to true, indicates that DNS implementations must publish the notReadyAddresses of subsets for the Endpoints associated with the Service. The default value is false. The primary use case for setting this field is to use a StatefulSet's Headless Service to propagate SRV records for its Pods without respect to their readiness for purpose of peer discovery. This field will replace the service.alpha.kubernetes.io/tolerate-unready-endpoints when that annotation is deprecated and all clients have been converted to use this field. # 由于使用DNS访问Pod需Pod和Headless service启动之后才能访问,publishNotReadyAddresses设置成true,防止readinessProbe在服务没启动时找不到DNS publishNotReadyAddresses: true ports: - name: amqp port: 5672 - name: http port: 15672 selector: app: rabbitmq --- # 用于暴露dashboard到外网 kind: Service apiVersion: v1 metadata: namespace: rabbitmq name: rabbitmq-service spec: type: NodePort ports: - name: http protocol: TCP port: 15672 targetPort: 15672 nodePort: 15672 # 注意k8s默认情况下,nodeport要在30000~32767之间,可以自行修改 - name: amqp protocol: TCP port: 5672 targetPort: 5672 # 注意如果你想在外网下访问mq,需要增配nodeport selector: app: rabbitmq --- apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: rabbitmq-config namespace: rabbitmq data: enabled_plugins: | [rabbitmq_management,rabbitmq_peer_discovery_k8s]. rabbitmq.conf: | cluster_formation.peer_discovery_backend = rabbit_peer_discovery_k8s cluster_formation.k8s.host = kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local cluster_formation.k8s.address_type = hostname cluster_formation.node_cleanup.interval = 10 cluster_formation.node_cleanup.only_log_warning = true cluster_partition_handling = autoheal queue_master_locator=min-masters loopback_users.guest = false cluster_formation.randomized_startup_delay_range.min = 0 cluster_formation.randomized_startup_delay_range.max = 2 # 必须设置service_name,否则Pod无法正常启动,这里设置后可以不设置statefulset下env中的K8S_SERVICE_NAME变量 cluster_formation.k8s.service_name = rabbitmq-headless # 必须设置hostname_suffix,否则节点不能成为集群 cluster_formation.k8s.hostname_suffix = .rabbitmq-headless.rabbitmq.svc.cluster.local # 内存上限 vm_memory_high_watermark.absolute = 1.6GB # 硬盘上限 disk_free_limit.absolute = 2GB --- # 使用apps/v1版本代替apps/v1beta apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: StatefulSet metadata: name: rabbitmq namespace: rabbitmq spec: serviceName: rabbitmq-headless # 必须与headless service的name相同,用于hostname传播访问pod selector: matchLabels: app: rabbitmq # 在apps/v1中,需与 .spec.template.metadata.label 相同,用于hostname传播访问pod,而在apps/v1beta中无需这样做 replicas: 3 template: metadata: labels: app: rabbitmq # 在apps/v1中,需与 .spec.selector.matchLabels 相同 # 设置podAntiAffinity annotations: scheduler.alpha.kubernetes.io/affinity: > { "podAntiAffinity": { "requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution": [{ "labelSelector": { "matchExpressions": [{ "key": "app", "operator": "In", "values": ["rabbitmq"] }] }, "topologyKey": "kubernetes.io/hostname" }] } } spec: serviceAccountName: rabbitmq terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 10 containers: - name: rabbitmq image: registry-vpc.cn-shenzhen.aliyuncs.com/heygears/rabbitmq:3.7 resources: limits: cpu: 0.5 memory: 2Gi requests: cpu: 0.3 memory: 2Gi volumeMounts: - name: config-volume mountPath: /etc/rabbitmq - name: rabbitmq-data mountPath: /var/lib/rabbitmq/mnesia ports: - name: http protocol: TCP containerPort: 15672 - name: amqp protocol: TCP containerPort: 5672 livenessProbe: exec: command: ["rabbitmqctl", "status"] initialDelaySeconds: 60 periodSeconds: 60 timeoutSeconds: 5 readinessProbe: exec: command: ["rabbitmqctl", "status"] initialDelaySeconds: 20 periodSeconds: 60 timeoutSeconds: 5 imagePullPolicy: Always env: - name: HOSTNAME valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.name - name: RABBITMQ_USE_LONGNAME value: "true" - name: RABBITMQ_NODENAME value: "rabbit@$(HOSTNAME).rabbitmq-headless.rabbitmq.svc.cluster.local" # 若在ConfigMap中设置了service_name,则此处无需再次设置 # - name: K8S_SERVICE_NAME # value: "rabbitmq-headless" - name: RABBITMQ_ERLANG_COOKIE value: "mycookie" volumes: - name: config-volume configMap: name: rabbitmq-config items: - key: rabbitmq.conf path: rabbitmq.conf - key: enabled_plugins path: enabled_plugins - name: rabbitmq-data persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: rabbitmq-data-claim
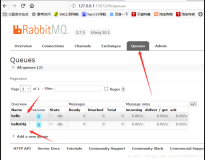
至此,终于在Kubernetes上部署完成RabbitMQ Cluster 3.7.X
本文转自中文社区-在Kubernetes上搭建RabbitMQ Cluster