Overview of Kotlin & Comparison Between Kotlin and Java
by Navdeep Singh Gill
What is Kotlin?
Kotlin is a new programming language from JetBrains. It first appeared in 2011 when JetBrains unveiled their project named “Kotlin”. Kotlin is an Open-Source Language.
Basically like Java, C and C++ - Kotlin is also “statically typed programming language”. Statically typed programming languages are those languages in which variables need not be defined before they are used. This means that static typing has to do with the explicit declaration or initialization of variables before they are employed.
As Earlier said that Java is an example of a statically typed language, similarly C and C++ are also statically typed languages.
Basically, Static typing does not mean that we have to declare all the variables first before we use them. Variables may be initialized anywhere in the program and we (developers) have to do so, to use those variables anywhere in the program when there is a need. Consider the following example
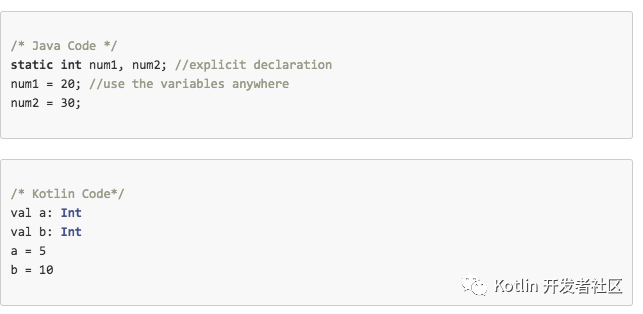
In addition to the classes and methods of object-oriented programming, Kotlin also supports procedural programming with the use of functions.
Like in Java, C and C++, the entry point to a Kotlin program is a function named “main”. Basically, it passed an array containing any command line arguments. Consider the following example -

Filename extensions of the Java are .java, .class, .jar but on the other hand filename extensions of the Kotlin are .kt and .kts.

Benefits of Kotlin Language
Kotlin compiles to JVM bytecode or JavaScript - Like Java, Bytecode is the compiled format for Kotlin programs also. Bytecode means Programming code that, once compiled, is run through a virtual machine instead of the computer’s processor. By using this approach, source code can be run on any platform once it has been compiled and run through the virtual machine. Once a kotlin program has been converted to bytecode, it can be transferred across a network and executed by JVM(Java Virtual Machine).
Kotlin programs can use all existing Java Frameworks and Libraries - Yes, it's true that Kotlin programs can use all existing java frameworks and libraries, even advanced frameworks that rely on annotation processing. The main important thing about kotlin language is that it can easily integrate with Maven, Gradle and other build systems.
Kotlin can be learned easily and it is approachable. It can be learned easily by simply reading the language reference.The syntax is clean and intuitive(easy to use and understand). Kotlin looks a lot like Scala but is simpler.
Kotlin is Open Source and it costs nothing to adopt.
Automatic conversion of Java to Kotlin - JetBrains integrated a new feature into IntelliJ which converts Java to Kotlin and saves a huge amount of time. And it also saves us to retype mundane code.
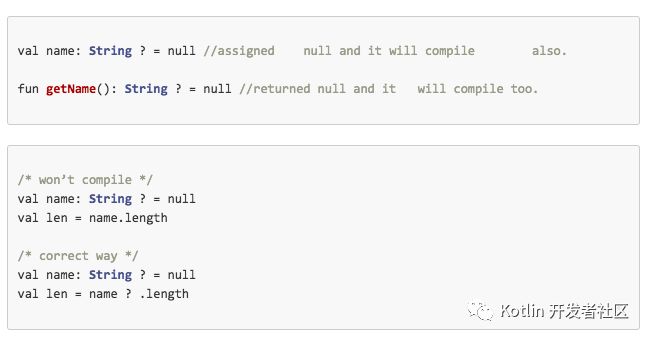
Kotlin’s null-safety is great - Now get rid of NullPointerExceptions. This type of system helps us to avoid null pointer exceptions. In Kotlin the system simply refuses to compile code that tries to assign or return null. Consider the following example
val name: String = null // tries to assign null, won’t compile.
fun getName(): String = null // tries to return null, won’t compile.
- Code reviews are not a problem - Kotlin is much more focuses on readable syntax so code reviews are not a problem, they can still be done by those team members who are not familiar with the language.
Features of Kotlin Language
- The billion dollar mistake made right. As already mentioned above that Kotlin avoids the null pointer exception. If we try to assign or return null to a variable or function respectively, then it won’t compile.
But in some special cases if we need nullability in our program then we have to ask Kotlin very nicely. Every Nullable type require some special care and treatment. We can’t treat them the same way as non-nullable types and this is a very good thing.
We have to add “?” after the variable type. Consider the following example - Kotlin also fails at compile-time whenever a NullPointerException may be thrown at run-time. Consider the following example -
- Versatile
- Lean Syntax and Concise - One liner functions take one line, simple structs/JavaBeans can also be declared in one line. Real properties generate getters and setters behind the scenes for Java interop. And Adding the data annotation to a class triggers autogeneration of boilerplate like equals, hashCode, toString and much more.
Consider the following example
/* Java program */
public class Address {
private String street;
private int streetNumber;
private String postCode;
private String city;
private Country country;
public Address(String street, int streetNumber, String postCode, String city, Country country) {
this.street = street;
this.streetNumber = streetNumber;
this.postCode = postCode;
this.city = city;
this.country = country;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Address address = (Address) o;
if (streetNumber != address.streetNumber) return false;
if (!street.equals(address.street)) return false;
if (!postCode.equals(address.postCode)) return false;
if (!city.equals(address.city)) return false;
return country == address.country;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = street.hashCode();
result = 31 * result + streetNumber;
result = 31 * result + postCode.hashCode();
result = 31 * result + city.hashCode();
result = 31 * result + (country != null ? country.hashCode() : 0);
return result;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Address{" +
"street='" + street + '\'' +
", streetNumber=" + streetNumber +
", postCode='" + postCode + '\'' +
", city='" + city + '\'' +
", country=" + country +
'}';
}
public String getStreet() {
return street;
}
public void setStreet(String street) {
this.street = street;
}
public int getStreetNumber() {
return streetNumber;
}
public void setStreetNumber(int streetNumber) {
this.streetNumber = streetNumber;
}
public String getPostCode() {
return postCode;
}
public void setPostCode(String postCode) {
this.postCode = postCode;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public Country getCountry() {
return country;
}
public void setCountry(Country country) {
this.country = country;
}
}

You May Also Love To Read Deploying Kotlin Application on Docker & Kubernetes
Compilation Speed Java vs Kotlin
We were actually very much interested in knowing the compilation speed of Kotlin as compared to Java.
Difference Between Kotlin And Java

Null Safety - As already mentioned in above section that Kotlin avoids NullPointerException. Kotlin fails at compile-time whenever a NullPointerException may be thrown.
-
Data Classes - In Kotlin there are Data Classes which leads to autogeneration of boilerplate like equals, hashCode, toString, getters/setters and much more. Consider the following example -
 image
image
But in Kotlin the above same class can define concisely in one line
/* kotlin Code */
data class Book(var title: Stri var author: Author)
It will also allow us to easily make copies of data classes with the help of copy()

- Extension Functions - Kotlin allows us to extend the functionality of existing classes without inheriting from them. Means to say that Kotlin provides the ability to extend a class with new functionality without having to inherit from the class. This is done by extension functions. To declare an extension function, we need to prefix its name with a receiver type, i.e. the type being extended. The following adds a swap function to MutableList<List>

The 'this' keyword inside an extension function corresponds to the receiver object, the one that is passed before the dot. Now we can call such a function on any MutableList<Int>

Smart Casts - When it comes to casts, Kotlin compiler is really intelligent. In many cases, one does not need to use explicit cast operators in kotlin, but in Kotlin there is “is-checks” for immutable values and inserts casts automatically when needed

-
Type Inference - In Kotlin, there is a great thing that you don’t have to specify the type of each variable explicitly(in clear and detailed manner). But if you want to define a data type explicitly, you can also do that. Consider the following example
 image
image Functional Programming - The main important thing is that Kotlin is a functional programming language. Basically Kotlin consist of many useful methods, which includes higher-order functions, lambda expressions, operator overloading, lazy evaluation, operator overloading and much more.
Functional Programing makes Kotlin much more handier when it comes to collections

Output - 15, 11
Higher - Order Functions
are those functions that take functions as a parameter and also returns a function. Consider the following code:
fun alphaNum(func: () -> Unit) {}
In the above code “func” is the name of the parameter and “ ( ) -> Unit ” is the function type. In this case, we are saying that func will be a function that does not receive any parameter and does not return any value also.
Lambda expression or an anonymous function is a “function literal”, i.e a function that is not declared, but passed immediately as an expression.
Lambda Expression
An Example of a Lambda Expression

In the above example, we simply declare a variable ‘sum’ that takes two integers and adds them together and returns total as an integer.
Then we just use ‘ sum(2,2) ’ in order to call it. Pretty cool huh?
Anonymous Function is a function which allows us to specify the return type and in this, the function name is omitted. Consider the following example:

Clean Builds Building your Codebase first time
When we compile our Kotlin code first time,then it takes more time than Java. Java compilation is almost around 15-20% faster than Kotlin.
Phases of Incremental Builds
But as we know that Most of the time we need incremental builds like we are doing some modifications in our existing code and then building them and doing continuous deployment
So in that perspective, Kotlin takes same amount of time to compile as compared to Java and even little bit faster than Java.
The Future of Kotlin language
Kotlin interwork with Java and provdes incremental change of code and superior type system to Java and provides the easy Migration path from Java with backward compatability.
With features Like more declarative, less code, mixed language database and more expressive than Java, Make Kotlin the future langauge for enterprises applications and Mobile.
Concluding Kotlin vs Java
We know that clean build is done only one time in our project and I think Incremental Builds Compilation time are more crucial for us than Clean Build. So Kotlin is almost same as Java and yes we can go with Kotlin without worrying about Compilation time.
Kotlin 开发者社区
国内第一Kotlin 开发者社区公众号,主要分享、交流 Kotlin 编程语言、Spring Boot、Android、React.js/Node.js、函数式编程、编程思想等相关主题。
