都来自官网,请看官网 http://phoenix.apache.org/secondary_indexing.html
下边分析全局索引和本地索引
Global Indexing 全局索引
Global indexing targets read heavy,low write uses cases. With global indexes, all the performance penalties for indexes occur at write time. We intercept the data table updates on write (DELETE, UPSERT VALUES and UPSERT SELECT), build the index update and then sent any necessary updates to all interested index tables. At read time, Phoenix will select the index table to use that will produce the fastest query time and directly scan it just like any other HBase table. By default, unless hinted, an index will not be used for a query that references a column that isn’t part of the index.
Global indexing适用于多读少写的业务场景。使用Global indexing的话在写数据的时候会消耗大量开销,因为所有对数据表的更新操作(DELETE, UPSERT VALUES and UPSERT SELECT),会引起索引表的更新,而索引表是分布在不同的数据节点上的,跨节点的数据传输带来了较大的性能消耗。在读数据的时候Phoenix会选择索引表来降低查询消耗的时间。在默认情况下如果想查询的字段不是索引字段的话索引表不会被使用,也就是说不会带来查询速度的提升。
配置hbase-site.xml
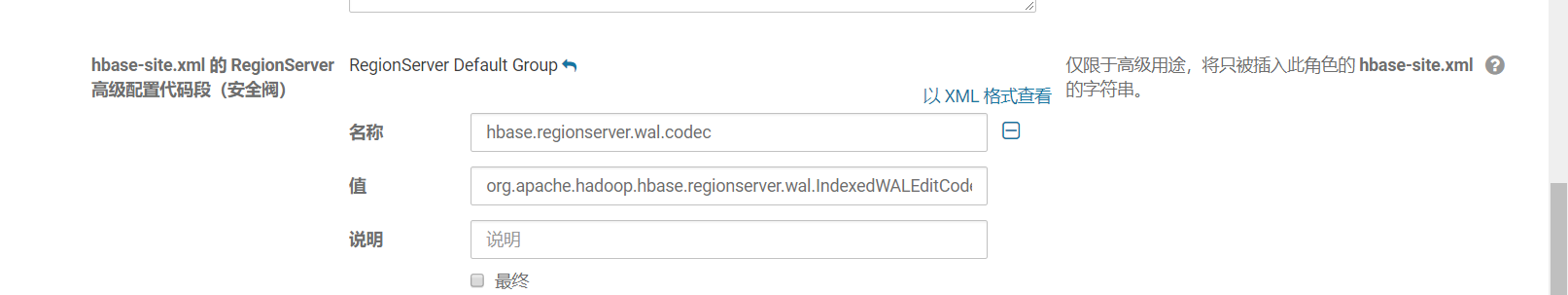
使用Global Indexing的话需要配置hbase-site.xml,在HBase集群的每个regionserver节点的hbase-site.xml中加入如下配置并重启HBase集群。
<property>
<name>hbase.regionserver.wal.codec</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.wal.IndexedWALEditCodec</value>
</property>
如果是CDH版本,要通过该cloudera manager配置
测试索引
-- 注意phoenix最好全大写字母,这里码字方便,我全小写了,请注意
-- 创建表
create table company(id varchar primary key, name varchar, address varchar);
--- 查看索引
!indexes company;
-- 创建索引
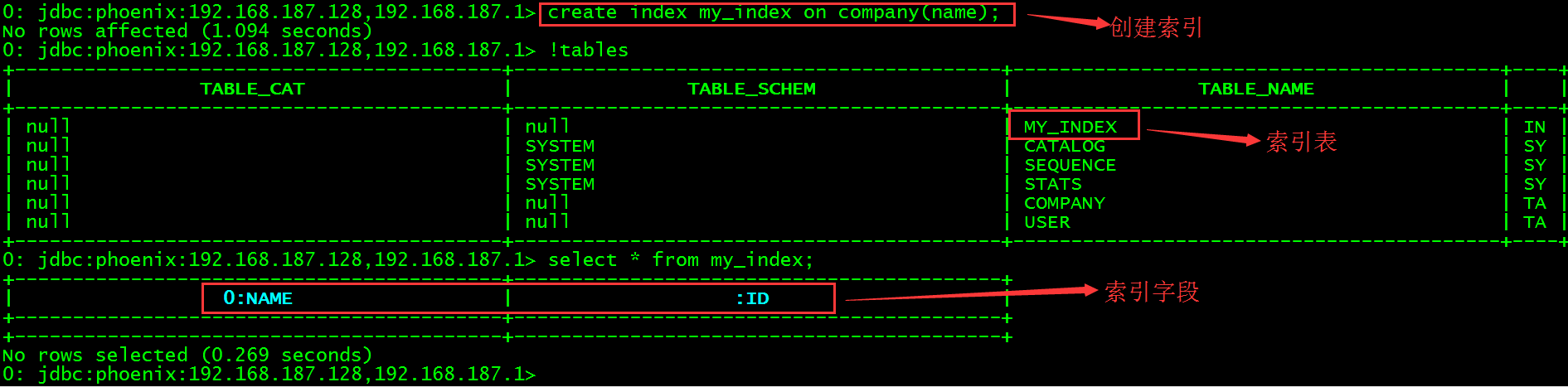
create index my_index on company(name);
--删除索引表
drop index my_index on company
-- 查看表就会发现多了一张索引表
!tables
SELET * FROM MY_INDEX
-- 插入数据
upsert into company(id, name, address) values('001', 'dimensoft', 'nanjing');
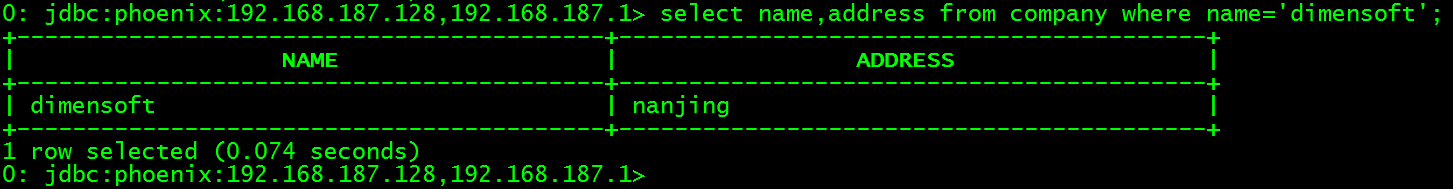
-- 查询数据
select name,address from company where name='dimensoft';
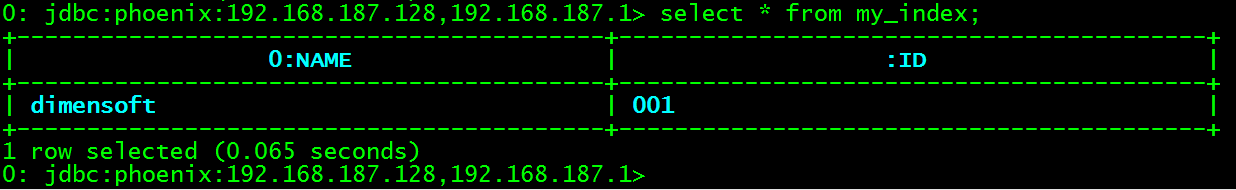
-- 查询索引表MY_INDEX
SELECT * FROM MY_INDEX
或者
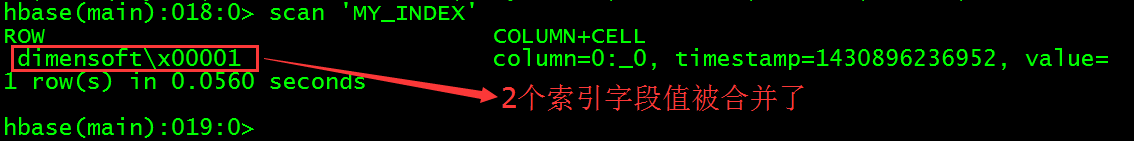
scan 'MY_INDEX'
高能预警
> select name,address from company where name='dimensoft';
这样的查询语句是不会用到索引表的
Global mutable index will not be used unless all of the columns referenced in the query are contained in the index.
name字段虽然是索引字段但是address字段并不是索引字段!也就是说需要查询出来的字段必须都是索引字段如:
> select name from company where name='dimensoft';
如果希望使用索引表进行查询的话可以使用以下三种方式来解决这个问题:
- 强制使用索引表
在进行查询的时候通过sql语句强制使用索引查询。
> SELECT /*+ INDEX(company my_index) */ name,address FROM company WHERE name = 'dimensoft';
This will cause each data row to be retrieved when the index is traversed to find the missing address column value. This hint should only be used if you know that the index has good selective (i.e. a small number of table rows have a value of ‘dimensoft’ in this example), as otherwise you’ll get better performance by the default behavior of doing a full table scan.
这样的查询语句会导致二次检索数据表,第一次检索是去索引表中查找符合name为dimensoft的数据,这时候发现address字段并不在索引字段中,会去company表中第二次扫描,因此只有当用户明确知道符合检索条件的数据较少的时候才适合使用,否则会造成全表扫描,对性能影响较大。
- 创建covered index
创建索引的时候指定一个covered字段,先删除my_index索引
> drop index my_index on company;
创建covered index
> create index my_index on company(name) include(address);
This will cause the address column value to be copied into the index and kept in synch as it changes. This will obviously increase the size of the index.
使用这种方式创建的所有会导致address字段的值被拷贝到索引中,缺点就是会导致索引表大小有一定的增加。
查询索引表my_index数据。
> select * from my_index;

这里的数据是自动同步过来的,可以发现address字段的值也被存储了。
从HBase的CLI中查看MY_INDEX表数据会发现比不使用include的时候多了一行数值,并且里面包含了address字段的值。
> scan 'MY_INDEX'
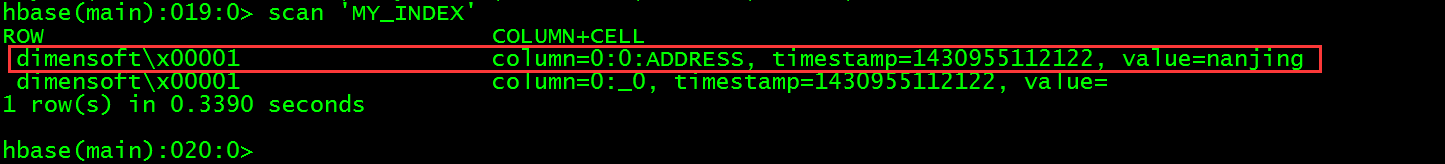
这个时候就再使用下面的查询语句就会使用到索引来进行查询了。
> select name,address from company where name='dimensoft';
- 使用Local Indexing创建索引
与Global Indexing不同,当使用Local Indexing的时候即使查询的所有字段都不在索引字段中时也会用到索引进行查询(这是由Local Indexing自动完成的)。这部分内容会放到后一篇文章详细介绍。
Local Indexing 本地索引
Local indexing targets write heavy, space constrained use cases. Just like with global indexes, Phoenix will automatically select whether or not to use a local index at query-time. With local indexes, index data and table data co-reside on same server preventing any network overhead during writes. Local indexes can be used even when the query isn’t fully covered (i.e. Phoenix automatically retrieve the columns not in the index through point gets against the data table). Unlike global indexes, all local indexes of a table are stored in a single, separate shared table.At read time when the local index is used, every region must be examined for the data as the exact region location of index data cannot be predetermined.Thus some overhead occurs at read-time.
Local indexing适用于写操作频繁的场景。与Global indexing一样,Phoenix会自动判定在进行查询的时候是否使用索引。使用Local indexing时,索引数据和数据表的数据是存放在相同的服务器中的避免了在写操作的时候往不同服务器的索引表中写索引带来的额外开销。使用Local indexing的时候即使查询的字段不是索引字段索引表也会被使用,这会带来查询速度的提升,这点跟Global indexing不同。一个数据表的所有索引数据都存储在一个单一的独立的可共享的表中。在读取数据的时候,标红的那句话不会翻译大意就是在读数据的时候因为存储数据的region的位置无法预测导致性能有一定损耗。
配置hbase-site.xml
使用Local Indexing的话需要配置hbase-site.xml,在HBase集群的master节点的hbase-site.xml中添加如下配置并重启HBase集群。
Local indexing also requires special configurations
in the master to ensure data table and local index regions co-location.
配置这个参数的目的是确保数据表与索引表协同定位。
<property>
<name>hbase.master.loadbalancer.class</name>
<value>org.apache.phoenix.hbase.index.balancer.IndexLoadBalancer</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hbase.coprocessor.master.classes</name>
<value>org.apache.phoenix.hbase.index.master.IndexMasterObserver</value>
</property>
高能预警:如果使用的是Phoenix 4.3+的版本的话
还需要在HBase集群的每个regionserver节点的
hbase-site.xml中添加如下配置并重启HBase集群。
To support local index regions merge on data
regions merge you will need to add the following
parameter to hbase-site.xml in all the region
servers and restart. (It’s applicable for Phoenix 4.3+ versions)
这个配置是为了支持在数据region合并之上进行
索引region合并(这句话感觉翻译的不太准确)。
<property>
<name>hbase.coprocessor.regionserver.classes</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.LocalIndexMerger</value>
</property>
注意: 同理使用CDH版的要通过cloudera manager页面管理配置
测试二级索引
进入phoenix的CLI的界面创建company表。
> create table company(id varchar primary key, name varchar, address varchar);
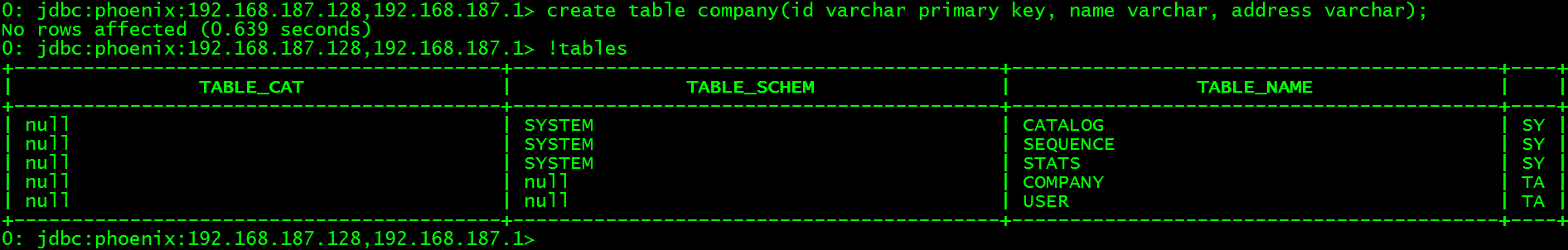
查看company表索引
> !indexes company

2.3 创建索引
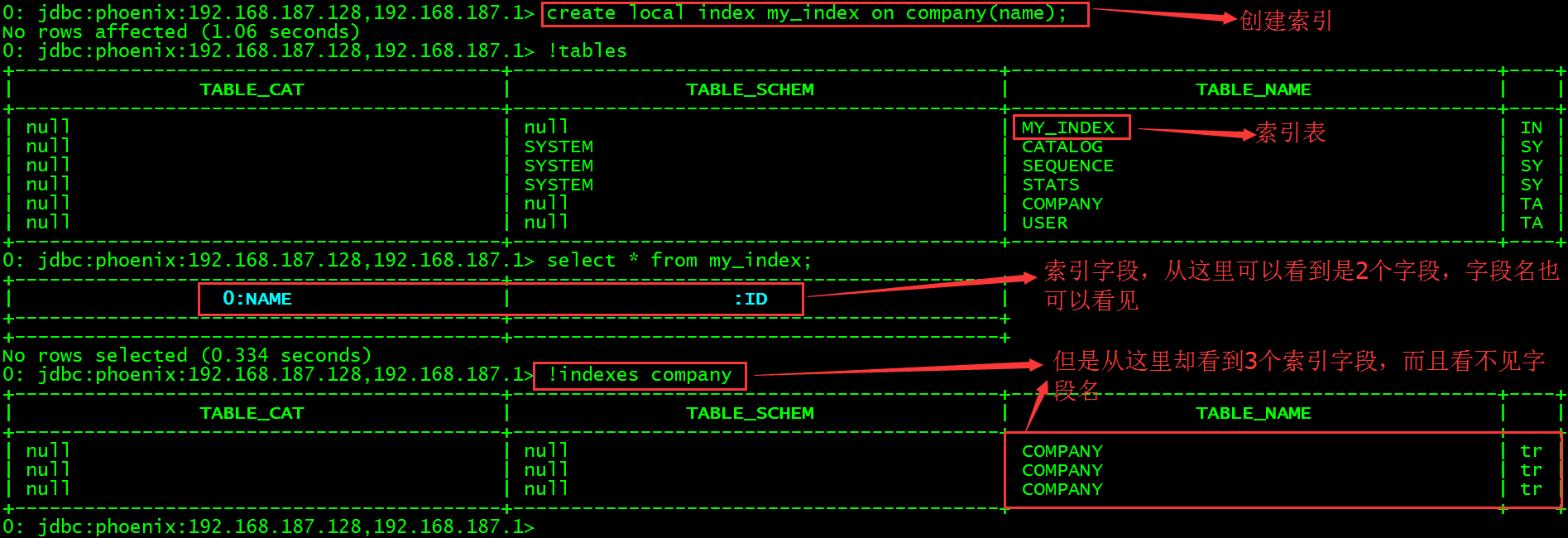
对company表的name字段创建索引,索引名为my_index。
> create local index my_index on company(name);
查看当前所有表会发现多一张MY_INDEX索引表,查询该表数据。
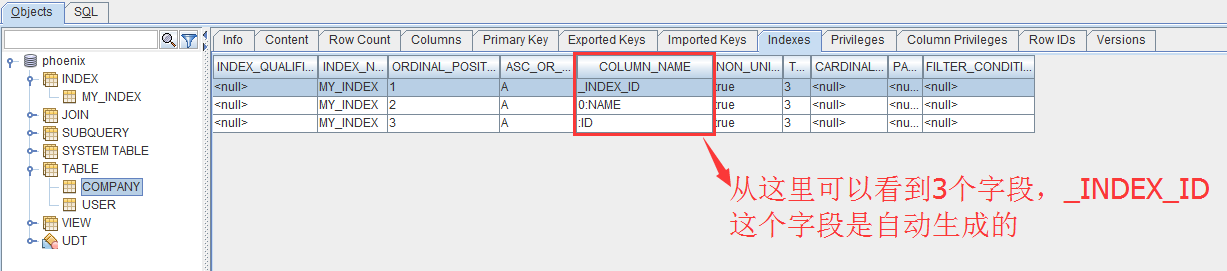
通过squirrel来查看company的索引字段。
从HBase的CLI界面查看当前所有表。
> list
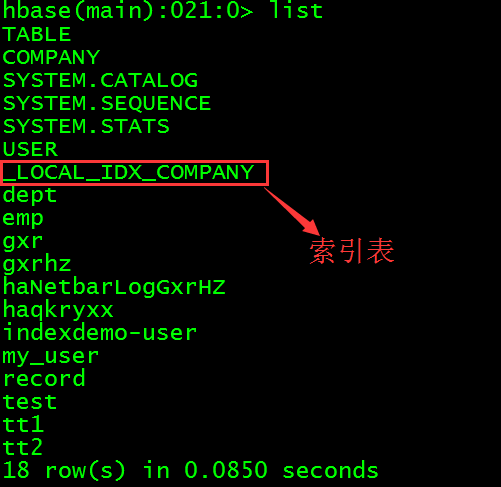
高能预警:这里的索引表并不叫MY_INDEX,而是叫_LOCAL_IDX_COMPANY,但是在Phoenix的CLI中进行数据查询的时候仍然是使用MY_INDEX进行查询,应该是做了映射。
2.4 插入数据
在company表中添加测试数据。
> upsert into company(id, name, address) values('001', 'dimensoft', 'nanjing');
2.5 查询数据
查看company表数据以及索引表my_index数据。
> select * from company;
> select * from my_index;
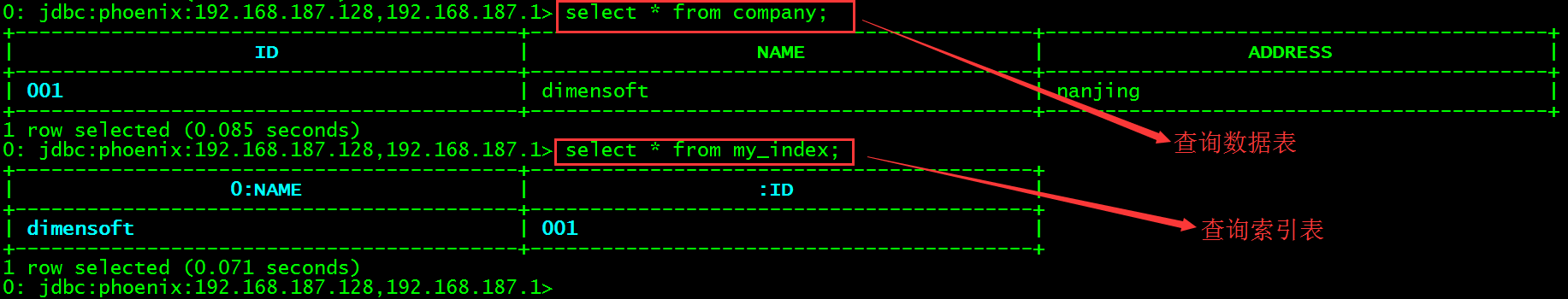
从HBase的CLI界面查看索引表_LOCAL_IDX_COMPANY。
> scan '_LOCAL_IDX_COMPANY'

3个索引字段_INDEX_ID、NAME和ID的值被合并为索引表的rowKey,其中_INDEX_ID并没有值(\x000是十六进制表示,转换为字符串是空格)。
函数索引 Functional Indexes
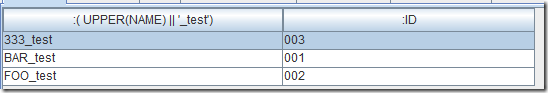
函数索引从4.3版本就有,这种索引的内容不局限于列,还能在表达式上建立索引。如果你使用的表达式正好就是索引的话,数据也可以直接从这个索引获取,而不需要从数据库获取。比如说,在一个表达式上建立索引,这个表达式是UPPER(name) || '_test':
<pre style="margin-top: 0px; margin-bottom: 0px; white-space: pre-wrap; word-wrap: break-word; box-sizing: border-box; font-family: "Courier New" !important; font-size: 12px !important;">CREATE INDEX index2_f ON hao1 (UPPER(name) || '_test');</pre>
同样的index2_f表会被建立,里面存储了表达式求值后的结果,和RowKey的关系。当然也可以添加INCLUDE作为覆盖索引,做了覆盖索引,就不需要再去原数据表中获取数据。但是数据会多很多。
在索引范围上,Phoenix的索引可以分为全局索引和本地索引,两种索引适合的场景不同。
创建异步索引
一般我们可以使用CREATE INDEX来创建一个索引,这是一种同步的方法。但是有时候我们创建索引的表非常大,我们需要等很长时间。Phoenix 4.5以后有一个异步创建索引的方式,使用关键字ASYNC来创建索引:
CREATE INDEX index1_c ON hao1 (age) INCLUDE(name) ASYNC;
这时候创建的索引表中不会有数据。你还必须要单独的使用命令行工具来执行数据的创建。当语句给执行的时候,后端会启动一个map reduce任务,只有等到这个任务结束,数据都被生成在索引表中后,这个索引才能被使用。启动工具的方法:
${HBASE_HOME}/bin/hbase org.apache.phoenix.mapreduce.index.IndexTool
--schema MY_SCHEMA --data-table MY_TABLE --index-table ASYNC_IDX
--output-path ASYNC_IDX_HFILES
这个任务不会因为客户端给关闭而结束,是在后台运行。你可以在指定的文件ASYNC_IDX_HFILES中找到最终实行的结果。