一、Bean 生命周期
Spring bean的生命周期很容易理解。当bean被实例化时,可能需要执行一些初始化以使其进入可用状态。类似地,当不再需要bean并从容器中移除bean时,可能需要进行一些清理。
虽然,在bean实例化及其销毁之间存在幕后发生的活动列表,但本章仅讨论两个重要的bean生命周期回调方法,这些方法在bean初始化及其销毁时是必需的。
要定义bean的设置和拆卸,我们只需使用initmethod和/或destroy-method参数声明<bean> 。init-method属性指定在实例化时立即在bean上调用的方法。类似地,destroy-method指定在从容器中删除bean之前调用的方法。
示例如下:
(1)编写HelloWord.java
package com.tutorialspoint; public class HelloWorld { private String message; public void setMessage(String message){ this.message = message; } public void getMessage(){ System.out.println("Your Message : " + message); } public void init(){ System.out.println("Bean is going through init."); } public void destroy() { System.out.println("Bean will destroy now."); } }
(2)编写Beans.xml
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd"> <bean id = "helloWorld" class = "com.tutorialspoint.HelloWorld" init-method = "init" destroy-method = "destroy"> <property name = "message" value = "Hello World!"/> </bean> </beans>
(3)编写MainApp.java
package com.tutorialspoint; import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class MainApp { public static void main(String[] args) { AbstractApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml"); HelloWorld obj = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld"); obj.getMessage(); context.registerShutdownHook(); } }
二、Bean Post 处理器
该BeanPostProcessor接口定义,你可以实现提供自己的实例化逻辑,依赖解析逻辑等,您还可以实现一些自定义的逻辑Spring容器完成实例化,配置,并通过在一个或多个堵塞初始化Bean后回调方法BeanPostProcessor实现。
您可以配置多个BeanPostProcessor接口,并且您可以通过设置订单属性来控制这些BeanPostProcessor接口的执行顺序,前提是BeanPostProcessor实现了Ordered接口。
BeanPostProcessors在bean(或对象)实例上运行,这意味着Spring IoC容器实例化一个bean实例,然后BeanPostProcessor接口完成它们的工作。
一个ApplicationContext的自动检测与该执行中定义的任何Bean的BeanPostProcessor接口,并注册这些Bean类如后处理器,被通过在容器创建bean的适当调用。
示例如下:
(1)编写HelloWorld.java
package com.tutorialspoint; public class HelloWorld { private String message; public void setMessage(String message){ this.message = message; } public void getMessage(){ System.out.println("Your Message : " + message); } public void init(){ System.out.println("Bean is going through init."); } public void destroy(){ System.out.println("Bean will destroy now."); } }
(2)编写InitHelloWorld.java
package com.tutorialspoint; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; public class InitHelloWorld implements BeanPostProcessor { public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("BeforeInitialization : " + beanName); return bean; // you can return any other object as well } public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("AfterInitialization : " + beanName); return bean; // you can return any other object as well } }
(3)编写Beans.xml
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd"> <bean id = "helloWorld" class = "com.tutorialspoint.HelloWorld" init-method = "init" destroy-method = "destroy"> <property name = "message" value = "Hello World!"/> </bean> <bean class = "com.tutorialspoint.InitHelloWorld" /> </beans>
(4)编写MainApp.java
package com.tutorialspoint; import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class MainApp { public static void main(String[] args) { AbstractApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml"); HelloWorld obj = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld"); obj.getMessage(); context.registerShutdownHook(); } }
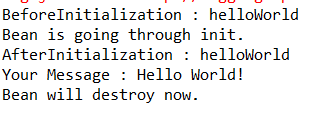
(5)运行MainApp.java中的main方法测试
结果如图: