以太坊-rpc原理及实现
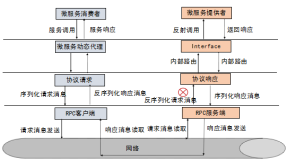
JSON-RPC是区块链外部调用的标配了。以太坊同样也实现了这个功能。底层支持四种协议:InProc,IPC,HTTP,WEBSOCKED。上层除了常规的方法调用之外还实现了Pub/Sub功能。本文主要分析以太坊是如何支持这些个功能的。
api发布
api接口分布在各个模块,主要分为两种
- 1:直接code再Node中的几个service(admin,web3j,debug etc)
- 2: 实现了Service接口的服务结构,已经注册的服务会调用APIs()方法获得其中的api。
//file go-ethereum/node/node.go
func (n *Node) startRPC(services map[reflect.Type]Service) error {
apis := n.apis()
for _, service := range services {
apis = append(apis, service.APIs()...)
}
}
node中写死的接口
// node中写死的接口
func (n *Node) apis() []rpc.API {
return []rpc.API{
{
Namespace: "admin",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPrivateAdminAPI(n),
}, {
Namespace: "admin",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPublicAdminAPI(n),
Public: true,
}, {
Namespace: "debug",
Version: "1.0",
Service: debug.Handler,
}, {
Namespace: "debug",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPublicDebugAPI(n),
Public: true,
}, {
Namespace: "web3",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPublicWeb3API(n),
Public: true,
},
}
}
Ethereum 服务实现的APIs()接口 类似的还有其他的服务(dashboard,ethstats)
//Ethereum 服务实现的APIs()接口
func (s *Ethereum) APIs() []rpc.API {
apis := ethapi.GetAPIs(s.ApiBackend)
// Append any APIs exposed explicitly by the consensus engine
apis = append(apis, s.engine.APIs(s.BlockChain())...)
// Append all the local APIs and return
return append(apis, []rpc.API{
{
Namespace: "eth",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPublicEthereumAPI(s),
Public: true,
}, {
Namespace: "eth",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPublicMinerAPI(s),
Public: true,
}, {
Namespace: "eth",
Version: "1.0",
Service: downloader.NewPublicDownloaderAPI(s.protocolManager.downloader, s.eventMux),
Public: true,
}, {
Namespace: "miner",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPrivateMinerAPI(s),
Public: false,
}, {
Namespace: "eth",
Version: "1.0",
Service: filters.NewPublicFilterAPI(s.ApiBackend, false),
Public: true,
}, {
Namespace: "admin",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPrivateAdminAPI(s),
}, {
Namespace: "debug",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPublicDebugAPI(s),
Public: true,
}, {
Namespace: "debug",
Version: "1.0",
Service: NewPrivateDebugAPI(s.chainConfig, s),
}, {
Namespace: "net",
Version: "1.0",
Service: s.netRPCService,
Public: true,
},
}...)
}
这里的Service只是类型,还要注册到Server里面,原理就是反射出结构体里的类型,解析出函数方法名称(转小写),参数名称,返回类型等信息,最终每个合格的方法都会生成service实例
type service struct {
name string // name for service
typ reflect.Type // receiver type
callbacks callbacks // registered handlers
subscriptions subscriptions // available subscriptions/notifications
}
//反射除Service Api的结构方法
//file go-ethereum/rpc/utils.go
func suitableCallbacks(rcvr reflect.Value, typ reflect.Type) (callbacks, subscriptions) {
callbacks := make(callbacks)
subscriptions := make(subscriptions)
METHODS:
for m := 0; m < typ.NumMethod(); m++ {
method := typ.Method(m)
mtype := method.Type
//转小写
mname := formatName(method.Name)
if method.PkgPath != "" { // method must be exported
continue
}
var h callback
//订阅事件类型判断 主要根据签名的入参第二位和返回参数第一位
h.isSubscribe = isPubSub(mtype)
h.rcvr = rcvr
h.method = method
h.errPos = -1
firstArg := 1
numIn := mtype.NumIn()
if numIn >= 2 && mtype.In(1) == contextType {
h.hasCtx = true
firstArg = 2
}
if h.isSubscribe {
//订阅类型
h.argTypes = make([]reflect.Type, numIn-firstArg) // skip rcvr type
for i := firstArg; i < numIn; i++ {
argType := mtype.In(i)
if isExportedOrBuiltinType(argType) {
h.argTypes[i-firstArg] = argType
} else {
continue METHODS
}
}
subscriptions[mname] = &h
continue METHODS
}
// determine method arguments, ignore first arg since it's the receiver type
// Arguments must be exported or builtin types
h.argTypes = make([]reflect.Type, numIn-firstArg)
for i := firstArg; i < numIn; i++ {
argType := mtype.In(i)
if !isExportedOrBuiltinType(argType) {
continue METHODS
}
h.argTypes[i-firstArg] = argType
}
// check that all returned values are exported or builtin types
for i := 0; i < mtype.NumOut(); i++ {
if !isExportedOrBuiltinType(mtype.Out(i)) {
continue METHODS
}
}
// when a method returns an error it must be the last returned value
h.errPos = -1
for i := 0; i < mtype.NumOut(); i++ {
if isErrorType(mtype.Out(i)) {
h.errPos = i
break
}
}
if h.errPos >= 0 && h.errPos != mtype.NumOut()-1 {
continue METHODS
}
switch mtype.NumOut() {
case 0, 1, 2:
if mtype.NumOut() == 2 && h.errPos == -1 { // method must one return value and 1 error
continue METHODS
}
callbacks[mname] = &h
}
}
return callbacks, subscriptions
}
底层协议
底层支持了InProc,IPC,HTTP,WEBSOCKED 四种传输协议
- 1 InProc 直接生成RPCService实例,挂在Node上面可以直接调用。
- 2 IPC 监听管道,收到消息后解析成ServerCodec对象,扔给Server的ServeCodec方法使用
//file ipc.go
func (srv *Server) ServeListener(l net.Listener) error {
for {
conn, err := l.Accept()
if netutil.IsTemporaryError(err) {
log.Warn("RPC accept error", "err", err)
continue
} else if err != nil {
return err
}
log.Trace("Accepted connection", "addr", conn.RemoteAddr())
go srv.ServeCodec(NewJSONCodec(conn), OptionMethodInvocation|OptionSubscriptions)
}
}
- 3 HTTP 生成两个中间件,第二个中间件接收消息生成ServerCOdec,扔给Server的ServeSingleRequest方法
//file http.go
func (srv *Server) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// Permit dumb empty requests for remote health-checks (AWS)
if r.Method == http.MethodGet && r.ContentLength == 0 && r.URL.RawQuery == "" {
return
}
if code, err := validateRequest(r); err != nil {
http.Error(w, err.Error(), code)
return
}
// All checks passed, create a codec that reads direct from the request body
// untilEOF and writes the response to w and order the server to process a
// single request.
ctx := context.Background()
ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, "remote", r.RemoteAddr)
ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, "scheme", r.Proto)
ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, "local", r.Host)
body := io.LimitReader(r.Body, maxRequestContentLength)
codec := NewJSONCodec(&httpReadWriteNopCloser{body, w})
defer codec.Close()
w.Header().Set("content-type", contentType)
srv.ServeSingleRequest(codec, OptionMethodInvocation, ctx)
}
- 1 WEBSOCKED 与Http类型生成WebsocketHandler中间件,到消息后解析成ServerCodec对象,扔给Server的ServeCodec方法使用
//websocked.go
func (srv *Server) WebsocketHandler(allowedOrigins []string) http.Handler {
return websocket.Server{
Handshake: wsHandshakeValidator(allowedOrigins),
Handler: func(conn *websocket.Conn) {
// Create a custom encode/decode pair to enforce payload size and number encoding
conn.MaxPayloadBytes = maxRequestContentLength
encoder := func(v interface{}) error {
return websocketJSONCodec.Send(conn, v)
}
decoder := func(v interface{}) error {
return websocketJSONCodec.Receive(conn, v)
}
srv.ServeCodec(NewCodec(conn, encoder, decoder), OptionMethodInvocation|OptionSubscriptions)
},
}
}
rpc响应
上面四种协议再拿到ServerCodec对象后,会把这个对象传递到service的响应请数里面去。最终都是调到handle函数里面,handle里面再根据不同的类型进行响应。
func (s *Server) handle(ctx context.Context, codec ServerCodec, req *serverRequest) (interface{}, func()) {
if req.err != nil {
return codec.CreateErrorResponse(&req.id, req.err), nil
}
if req.isUnsubscribe {
//取消订阅功能
if len(req.args) >= 1 && req.args[0].Kind() == reflect.String {
notifier, supported := NotifierFromContext(ctx) //获取notifier对象
if !supported { // interface doesn't support subscriptions (e.g. http)
return codec.CreateErrorResponse(&req.id, &callbackError{ErrNotificationsUnsupported.Error()}), nil
}
//取消订阅
subid := ID(req.args[0].String())
if err := notifier.unsubscribe(subid); err != nil {
return codec.CreateErrorResponse(&req.id, &callbackError{err.Error()}), nil
}
return codec.CreateResponse(req.id, true), nil
}
return codec.CreateErrorResponse(&req.id, &invalidParamsError{"Expected subscription id as first argument"}), nil
}
if req.callb.isSubscribe {
//订阅功能
subid, err := s.createSubscription(ctx, codec, req)
if err != nil {
return codec.CreateErrorResponse(&req.id, &callbackError{err.Error()}), nil
}
// active the subscription after the sub id was successfully sent to the client
activateSub := func() {
notifier, _ := NotifierFromContext(ctx) //获取notifier对象
notifier.activate(subid, req.svcname) //订阅事件
}
return codec.CreateResponse(req.id, subid), activateSub
}
// regular RPC call, prepare arguments
//参数生成
if len(req.args) != len(req.callb.argTypes) {
rpcErr := &invalidParamsError{fmt.Sprintf("%s%s%s expects %d parameters, got %d",
req.svcname, serviceMethodSeparator, req.callb.method.Name,
len(req.callb.argTypes), len(req.args))}
return codec.CreateErrorResponse(&req.id, rpcErr), nil
}
arguments := []reflect.Value{req.callb.rcvr}
if req.callb.hasCtx {
arguments = append(arguments, reflect.ValueOf(ctx))
}
if len(req.args) > 0 {
arguments = append(arguments, req.args...)
}
// execute RPC method and return result
//执行对应的函数
reply := req.callb.method.Func.Call(arguments)
if len(reply) == 0 {
return codec.CreateResponse(req.id, nil), nil
}
//校验结果
if req.callb.errPos >= 0 { // test if method returned an error
if !reply[req.callb.errPos].IsNil() {
e := reply[req.callb.errPos].Interface().(error)
res := codec.CreateErrorResponse(&req.id, &callbackError{e.Error()})
return res, nil
}
}
return codec.CreateResponse(req.id, reply[0].Interface()), nil
}
Pub/sub 实现
底层在context绑定一个notifier对象
if options&OptionSubscriptions == OptionSubscriptions {
ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, notifierKey{}, newNotifier(codec))
}
sub/unsub的时候会通过context.Value中拿notifier对象,调用上面的方法注册或者取消注册
func NotifierFromContext(ctx context.Context) (*Notifier, bool) {
n, ok := ctx.Value(notifierKey{}).(*Notifier)
return n, ok
}
注册
func (n *Notifier) activate(id ID, namespace string) {
n.subMu.Lock()
defer n.subMu.Unlock()
if sub, found := n.inactive[id]; found {
sub.namespace = namespace
n.active[id] = sub
delete(n.inactive, id)
}
}
注销
func (n *Notifier) unsubscribe(id ID) error {
n.subMu.Lock()
defer n.subMu.Unlock()
if s, found := n.active[id]; found {
close(s.err)
delete(n.active, id)
return nil
}
return ErrSubscriptionNotFound
}
消息事件触发
func (api *PrivateAdminAPI) PeerEvents(ctx context.Context) (*rpc.Subscription, error) {
// Make sure the server is running, fail otherwise
server := api.node.Server()
if server == nil {
return nil, ErrNodeStopped
}
// Create the subscription
//获取notifier对象
notifier, supported := rpc.NotifierFromContext(ctx)
if !supported {
return nil, rpc.ErrNotificationsUnsupported
}
//生成标识
rpcSub := notifier.CreateSubscription()
go func() {
events := make(chan *p2p.PeerEvent)
sub := server.SubscribeEvents(events)
defer sub.Unsubscribe()
for {
select {
case event := <-events:
//触发事件,发送通知消息
notifier.Notify(rpcSub.ID, event)
case <-sub.Err():
return
case <-rpcSub.Err():
return
case <-notifier.Closed():
return
}
}
}()
return rpcSub, nil
}
rpc client
对应实现的有一个rpcclient,提供了Rpc调用,事件订阅等功能 https://github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/tree/master/rpc/client.go
参考
json:http://json.org/
json-rpc :http://www.jsonrpc.org/specification
source code :https://github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/tree/master/rpc
转自:(魂祭心) https://my.oschina.net/hunjixin/blog/1803161
如果你希望高效的学习以太坊DApp开发,可以访问汇智网提供的最热门在线互动教程:
1.适合区块链新手的以太坊DApp实战入门教程
2.区块链+IPFS+Node.js+MongoDB+Express去中心化以太坊电商应用开发实战
其他更多内容也可以访问这个以太坊博客