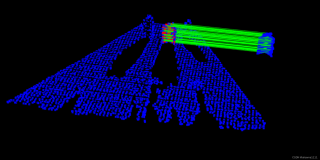
在逆向工程,计算机视觉,文物数字化等领域中,由于点云的不完整,旋转错位,平移错位等,使得要得到的完整的点云就需要对局部点云进行配准,为了得到被测物体的完整数据模型,需要确定一个合适的坐标系,将从各个视角得到的点集合并到统一的坐标系下形成一个完整的点云,然后就可以方便进行可视化的操作,这就是点云数据的配准。点云的配准有手动配准依赖仪器的配准,和自动配准,点云的自动配准技术是通过一定的算法或者统计学规律利用计算机计算两块点云之间错位,从而达到两块点云自动配准的效果,其实质就是把不同的坐标系中测得到的数据点云进行坐标系的变换,以得到整体的数据模型,问题的关键是如何让得到坐标变换的参数R(旋转矩阵)和T(平移向量),使得两视角下测得的三维数据经坐标变换后的距离最小,,目前配准算法按照过程可以分为整体配准和局部配准,。PCL中有单独的配准模块,实现了配准相关的基础数据结构,和经典的配准算法如ICP。
PCL中实现配准算法以及相关的概念
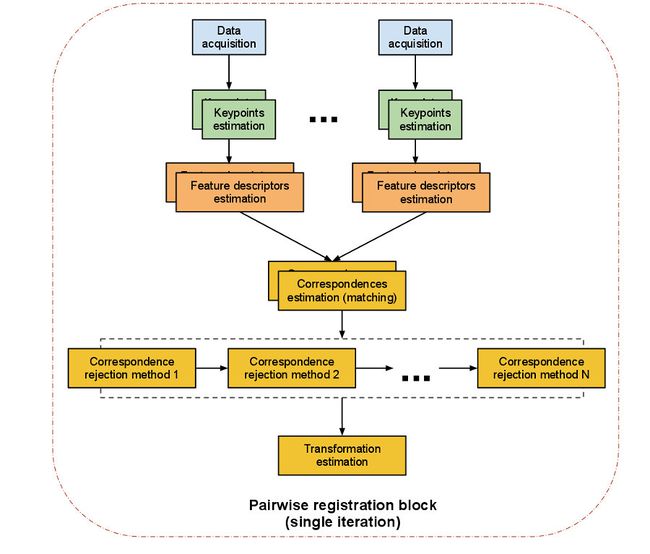
两两配准的简介:一对点云数据集的配准问题是两两配准(pairwise registration 或 pair-wise registration).通常通过应用一个估计得到的表示平移和选装的4*4缸体变换矩阵来使得一个点云的数据集精确的与另一个点云数据集(目标数据集)进行完美的配准
具体的实现步骤:
(1)首先从两个数据集中按照同样的关键点选取的标准,提取关键点
(2)对选择所有的关键点分别计算其特征描述子
(3)结合特征描述子在两个数据集中的坐标位置,以两者之间的特征和位置的相似度为基础,来估算它们的对应关系,初步的估计对应点对。
(4)假设数据是有噪声,出去对配准有影响的错误的对应点对
(5)利用剩余的正确的对应关系来估算刚体变换,完整配准。
对应估计(correspondences estimation):假设我们已经得到由来给你此扫描的点云数据获得的两组特征向量,在此基础基础上,我们必须找到,相似特征再确定数据的重叠部分,然后才能进行配准,根据特征的类型PCL使用不同的方法来搜索特征之间的对应关系
使用点匹配时,使用点的XYZ的坐标作为特征值,针对有序点云和无序点云数据的不同的处理策略:
(1)穷举配准(brute force matching)
(2)kd——数最近邻查询(FLANN)
(3)在有序点云数据的图像空间中查找
(4)在无序点云数据的索引空间中查找
(3)对应关系的去除(correspondence rejection)
由于噪声的影响,通常并不是所有估计的对应关系都是正确的,由于错误的对应关系对于最终的刚体变换矩阵的估算会产生负面的影响,所以必须去除它们,可以采用随机采样一致性估计,或者其他方法剔除错误的对应关系,最终使用对应关系数量只使用一定比例的对应关系,这样既能提高变换矩阵的估计京都也可以提高配准点的速度。
(4)变换矩阵的估算(transormation estimation)
估算对应矩阵的步骤如下
1. 在对应关系的基础上评估一些错误的度量标准
2.在摄像机位姿(运动估算)和最小化错误度量标准下估算一个刚体变换
3.优化点的结构
4使用刚体变换把源旋转/平移到与目标所在的同一坐标系下,用所有点,点的一个子集或者关键点运算一个内部的ICP循环
5,进行迭代,直到符合收敛性判断标准为止。
(5)迭代最近点算法(Iterative CLosest Point简称ICP算法)
ICP算法对待拼接的2片点云,首先根据一定的准则确立对应点集P与Q,其中对应点对的个数,然后通过最小乘法迭代计算最优的坐标变换,即旋转矩阵R和平移矢量t,使得误差函数最小,ICP处理流程分为四个主要的步骤:
1. 对原始点云数据进行采样
2.确定初始对应点集
3,去除错误对应点对
4.坐标变换的求解
PCL类的相关的介绍
| class | pcl::CorrespondenceGrouping< PointModelT, PointSceneT > |
| Abstract base class for Correspondence Grouping algorithms | |
| class | pcl::GeometricConsistencyGrouping< PointModelT, PointSceneT > |
| Class implementing a 3D correspondence grouping enforcing geometric consistency among feature correspondences. | |
| class | pcl::recognition::HoughSpace3D |
| HoughSpace3D is a 3D voting space. | |
| class | pcl::Hough3DGrouping< PointModelT, PointSceneT, PointModelRfT, PointSceneRfT > |
| Class implementing a 3D correspondence grouping algorithm that can deal with multiple instances of a model template found into a given scene. | |
| class | pcl::CRHAlignment< PointT, nbins_ > |
| CRHAlignment uses two Camera Roll Histograms (CRH) to find the roll rotation that aligns both views. | |
| class | pcl::recognition::ObjRecRANSAC::Output |
| This is an output item of the ObjRecRANSAC::recognize() method. More... | |
| class | pcl::recognition::ObjRecRANSAC::OrientedPointPair |
| class | pcl::recognition::ObjRecRANSAC::HypothesisCreator |
| class | pcl::recognition::ObjRecRANSAC |
| This is a RANSAC-based 3D object recognition method. | |
| class | pcl::recognition::ORROctree::Node::Data |
| class | pcl::recognition::ORROctree::Node |
| class | pcl::recognition::ORROctree |
| That's a very specialized and simple octree class. | |
| class | pcl::recognition::RotationSpace |
| This is a class for a discrete representation of the rotation space based on the axis-angle representation. |
实例分析:
(1)如何使用迭代最近点算法:在代码中使用ICP迭代最近点算法,程序随机生成一个点与作为源点云,并将其沿x轴平移后作为目标点云,然后利用ICP估计源到目标的刚体变换橘子,中间对所有信息都打印出来
新建文件
iterative_closest_point.cpp
#include <iostream> //标准输入输出头文件 #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> //I/O操作头文件 #include <pcl/point_types.h> //点类型定义头文件 #include <pcl/registration/icp.h> //ICP配准类相关头文件 int main (int argc, char** argv) { //创建两个pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>共享指针,并初始化它们 pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_in (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>); pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_out (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>); // 随机填充点云 cloud_in->width = 5; //设置点云宽度 cloud_in->height = 1; //设置点云为无序点 cloud_in->is_dense = false; cloud_in->points.resize (cloud_in->width * cloud_in->height); for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud_in->points.size (); ++i) { cloud_in->points[i].x = 1024 * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f); cloud_in->points[i].y = 1024 * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f); cloud_in->points[i].z = 1024 * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f); } std::cout << "Saved " << cloud_in->points.size () << " data points to input:"//打印处点云总数 << std::endl; for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud_in->points.size (); ++i) std::cout << " " << //打印处实际坐标 cloud_in->points[i].x << " " << cloud_in->points[i].y << " " << cloud_in->points[i].z << std::endl; *cloud_out = *cloud_in; std::cout << "size:" << cloud_out->points.size() << std::endl; //实现一个简单的点云刚体变换,以构造目标点云 for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud_in->points.size (); ++i) cloud_out->points[i].x = cloud_in->points[i].x + 0.7f; std::cout << "Transformed " << cloud_in->points.size () << " data points:" << std::endl; for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud_out->points.size (); ++i) //打印构造出来的目标点云 std::cout << " " << cloud_out->points[i].x << " " << cloud_out->points[i].y << " " << cloud_out->points[i].z << std::endl; pcl::IterativeClosestPoint<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::PointXYZ> icp; //创建IterativeClosestPoint的对象 icp.setInputCloud(cloud_in); //cloud_in设置为点云的源点 icp.setInputTarget(cloud_out); //cloud_out设置为与cloud_in对应的匹配目标 pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> Final; //存储经过配准变换点云后的点云 icp.align(Final); //打印配准相关输入信息 std::cout << "has converged:" << icp.hasConverged() << " score: " << icp.getFitnessScore() << std::endl; std::cout << icp.getFinalTransformation() << std::endl; return (0); }
编译运行的结果

可以有试验结果看得出变换后的点云只是在x轴的值增加了固定的值0.7,然后由这目标点云与源点云计算出它的旋转与平移,明显可以看出最后一行的x值为0.7
同时,我们可以自己更改程序,来观察不同的实验结果。
对于两幅图像通过ICP求它的变换:
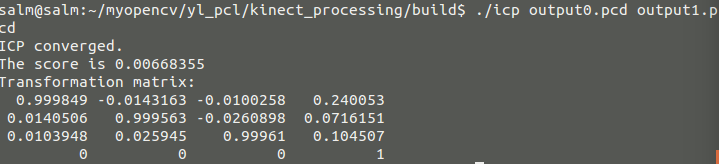
刚开始,如果直接通过通过kinect 得到数据运行会出现如下的错误,是因为该ICP 算法不能处理含有NaNs的点云数据,所以需要通过移除这些点,才能作为ICP算法的输入
错误的提示

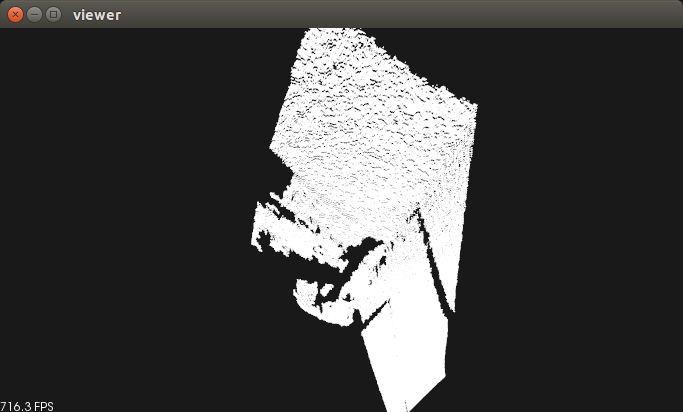
所以我们必须通过之前所学的代码把其中的无效的点云去除,然后作为输入,由于是我自己获得的点云数据,数据没有预处理,其中输入的两个点云后ICP后的结果及可视化为

(2)如何逐步匹配多幅点云
本实例是使用迭代最近点算法,逐步实现地对一系列点云进行两两匹配,他的思想是对所有的点云进行变换,使得都与第一个点云统一坐标系中,在每个连贯的有重叠的点云之间找出最佳的变换,并积累这些变换到全部的点云,能够进行ICP算法的点云需要粗略的预匹配(比如在一个机器人的量距内或者在地图的框架内),并且一个点云与另一个点云需要有重叠的部分。
新建文件pairwise_incremental_registration.cpp
#include <boost/make_shared.hpp> //boost指针相关头文件 #include <pcl/point_types.h> //点类型定义头文件 #include <pcl/point_cloud.h> //点云类定义头文件 #include <pcl/point_representation.h> //点表示相关的头文件 #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> //PCD文件打开存储类头文件 #include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h> //用于体素网格化的滤波类头文件 #include <pcl/filters/filter.h> //滤波相关头文件 #include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h> //法线特征头文件 #include <pcl/registration/icp.h> //ICP类相关头文件 #include <pcl/registration/icp_nl.h> //非线性ICP 相关头文件 #include <pcl/registration/transforms.h> //变换矩阵类头文件 #include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h> //可视化类头文件 using pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField; using pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom; //定义 typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointT; typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointT> PointCloud; //申明pcl::PointXYZ数据 typedef pcl::PointNormal PointNormalT; typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointNormalT> PointCloudWithNormals; // 申明一个全局可视化对象变量,定义左右视点分别显示配准前和配准后的结果点云 pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer *p; //创建可视化对象 int vp_1, vp_2; //定义存储 左 右视点的ID //申明一个结构体方便对点云以文件名和点云对象进行成对处理和管理点云,处理过程中可以同时接受多个点云文件的输入 struct PCD { PointCloud::Ptr cloud; //点云共享指针 std::string f_name; //文件名称 PCD() : cloud (new PointCloud) {}; }; struct PCDComparator //文件比较处理 { bool operator () (const PCD& p1, const PCD& p2) { return (p1.f_name < p2.f_name); } }; // 以< x, y, z, curvature >形式定义一个新的点表示 class MyPointRepresentation : public pcl::PointRepresentation <PointNormalT> { using pcl::PointRepresentation<PointNormalT>::nr_dimensions_; public: MyPointRepresentation () { nr_dimensions_ = 4; //定义点的维度 } // 重载copyToFloatArray方法将点转化为四维数组 virtual void copyToFloatArray (const PointNormalT &p, float * out) const { // < x, y, z, curvature > out[0] = p.x; out[1] = p.y; out[2] = p.z; out[3] = p.curvature; } }; /** \左视图用来显示未匹配的源和目标点云*/ void showCloudsLeft(const PointCloud::Ptr cloud_target, const PointCloud::Ptr cloud_source) { p->removePointCloud ("vp1_target"); p->removePointCloud ("vp1_source"); PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> tgt_h (cloud_target, 0, 255, 0); PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> src_h (cloud_source, 255, 0, 0); p->addPointCloud (cloud_target, tgt_h, "vp1_target", vp_1); p->addPointCloud (cloud_source, src_h, "vp1_source", vp_1); PCL_INFO ("Press q to begin the registration.\n"); p-> spin(); } /** \右边显示配准后的源和目标点云*/ void showCloudsRight(const PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr cloud_target, const PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr cloud_source) { p->removePointCloud ("source"); p->removePointCloud ("target"); PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField<PointNormalT> tgt_color_handler (cloud_target, "curvature"); if (!tgt_color_handler.isCapable ()) PCL_WARN ("Cannot create curvature color handler!"); PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField<PointNormalT> src_color_handler (cloud_source, "curvature"); if (!src_color_handler.isCapable ()) PCL_WARN ("Cannot create curvature color handler!"); p->addPointCloud (cloud_target, tgt_color_handler, "target", vp_2); p->addPointCloud (cloud_source, src_color_handler, "source", vp_2); p->spinOnce(); } //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// /** \brief Load a set of PCD files that we want to register together * \param argc the number of arguments (pass from main ()) * \param argv the actual command line arguments (pass from main ()) * \param models the resultant vector of point cloud datasets */ void loadData (int argc, char **argv, std::vector<PCD, Eigen::aligned_allocator<PCD> > &models) { std::string extension (".pcd"); // 第一个参数是命令本身,所以要从第二个参数开始解析 for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++) { std::string fname = std::string (argv[i]); // PCD文件名至少为5个字符大小字符串(因为后缀名.pcd就已经占了四个字符位置) if (fname.size () <= extension.size ()) continue; std::transform (fname.begin (), fname.end (), fname.begin (), (int(*)(int))tolower); //检查参数是否为一个pcd后缀的文件 if (fname.compare (fname.size () - extension.size (), extension.size (), extension) == 0) { //加载点云并保存在总体的点云列表中 PCD m; m.f_name = argv[i]; pcl::io::loadPCDFile (argv[i], *m.cloud); //从点云中移除NAN点也就是无效点 std::vector<int> indices; pcl::removeNaNFromPointCloud(*m.cloud,*m.cloud, indices); models.push_back (m); } } } //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// /** \brief Align a pair of PointCloud datasets and return the result * \param cloud_src the source PointCloud * \param cloud_tgt the target PointCloud * \param output the resultant aligned source PointCloud * \param final_transform the resultant transform between source and target *//
//实现匹配,其中参数有输入一组需要配准的点云,以及是否需要进行下采样,其他参数输出配准后的点云以及变换矩阵
void pairAlign (const PointCloud::Ptr cloud_src, const PointCloud::Ptr cloud_tgt, PointCloud::Ptr output, Eigen::Matrix4f &final_transform, bool downsample = false) { // // Downsample for consistency and speed // \note enable this for large datasets PointCloud::Ptr src (new PointCloud); //存储滤波后的源点云 PointCloud::Ptr tgt (new PointCloud); //存储滤波后的目标点云 pcl::VoxelGrid<PointT> grid; /////滤波处理对象 if (downsample) { grid.setLeafSize (0.05, 0.05, 0.05); //设置滤波时采用的体素大小 grid.setInputCloud (cloud_src); grid.filter (*src); grid.setInputCloud (cloud_tgt); grid.filter (*tgt); } else { src = cloud_src; tgt = cloud_tgt; } // 计算表面的法向量和曲率 PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr points_with_normals_src (new PointCloudWithNormals); PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr points_with_normals_tgt (new PointCloudWithNormals); pcl::NormalEstimation<PointT, PointNormalT> norm_est; //点云法线估计对象 pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree (new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ> ()); norm_est.setSearchMethod (tree); norm_est.setKSearch (30); norm_est.setInputCloud (src); norm_est.compute (*points_with_normals_src); pcl::copyPointCloud (*src, *points_with_normals_src); norm_est.setInputCloud (tgt); norm_est.compute (*points_with_normals_tgt); pcl::copyPointCloud (*tgt, *points_with_normals_tgt); // // Instantiate our custom point representation (defined above) ... MyPointRepresentation point_representation; // ... and weight the 'curvature' dimension so that it is balanced against x, y, and z float alpha[4] = {1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0}; point_representation.setRescaleValues (alpha); // // 配准 pcl::IterativeClosestPointNonLinear<PointNormalT, PointNormalT> reg; // 配准对象 reg.setTransformationEpsilon (1e-6); ///设置收敛判断条件,越小精度越大,收敛也越慢 // Set the maximum distance between two correspondences (src<->tgt) to 10cm大于此值的点对不考虑 // Note: adjust this based on the size of your datasets reg.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance (0.1); // 设置点表示 reg.setPointRepresentation (boost::make_shared<const MyPointRepresentation> (point_representation)); reg.setInputSource (points_with_normals_src); // 设置源点云 reg.setInputTarget (points_with_normals_tgt); // 设置目标点云 // // Run the same optimization in a loop and visualize the results Eigen::Matrix4f Ti = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity (), prev, targetToSource; PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr reg_result = points_with_normals_src; reg.setMaximumIterations (2);////设置最大的迭代次数,即每迭代两次就认为收敛,停止内部迭代 for (int i = 0; i < 30; ++i) ////手动迭代,每手动迭代一次,在配准结果视口对迭代的最新结果进行刷新显示 { PCL_INFO ("Iteration Nr. %d.\n", i); // 存储点云以便可视化 points_with_normals_src = reg_result; // Estimate reg.setInputSource (points_with_normals_src); reg.align (*reg_result); //accumulate transformation between each Iteration Ti = reg.getFinalTransformation () * Ti; //if the difference between this transformation and the previous one //is smaller than the threshold, refine the process by reducing //the maximal correspondence distance if (fabs ((reg.getLastIncrementalTransformation () - prev).sum ()) < reg.getTransformationEpsilon ()) reg.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance (reg.getMaxCorrespondenceDistance () - 0.001); prev = reg.getLastIncrementalTransformation (); // visualize current state showCloudsRight(points_with_normals_tgt, points_with_normals_src); } // // Get the transformation from target to source targetToSource = Ti.inverse();//deidao // // Transform target back in source frame pcl::transformPointCloud (*cloud_tgt, *output, targetToSource); p->removePointCloud ("source"); p->removePointCloud ("target"); PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> cloud_tgt_h (output, 0, 255, 0); PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> cloud_src_h (cloud_src, 255, 0, 0); p->addPointCloud (output, cloud_tgt_h, "target", vp_2); p->addPointCloud (cloud_src, cloud_src_h, "source", vp_2); PCL_INFO ("Press q to continue the registration.\n"); p->spin (); p->removePointCloud ("source"); p->removePointCloud ("target"); //add the source to the transformed target *output += *cloud_src; final_transform = targetToSource; } int main (int argc, char** argv) { // 存储管理所有打开的点云 std::vector<PCD, Eigen::aligned_allocator<PCD> > data; loadData (argc, argv, data); // 加载所有点云到data // 检查输入 if (data.empty ()) { PCL_ERROR ("Syntax is: %s <source.pcd> <target.pcd> [*]", argv[0]); PCL_ERROR ("[*] - multiple files can be added. The registration results of (i, i+1) will be registered against (i+2), etc"); return (-1); } PCL_INFO ("Loaded %d datasets.", (int)data.size ()); // 创建PCL可视化对象 p = new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer (argc, argv, "Pairwise Incremental Registration example"); p->createViewPort (0.0, 0, 0.5, 1.0, vp_1); //用左半窗口创建视口vp_1 p->createViewPort (0.5, 0, 1.0, 1.0, vp_2); //用右半窗口创建视口vp_2 PointCloud::Ptr result (new PointCloud), source, target; Eigen::Matrix4f GlobalTransform = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity (), pairTransform; for (size_t i = 1; i < data.size (); ++i) //循环处理所有点云 { source = data[i-1].cloud; //连续配准 target = data[i].cloud; // 相邻两组点云 showCloudsLeft(source, target); //可视化为配准的源和目标点云 //调用子函数完成一组点云的配准,temp返回配准后两组点云在第一组点云坐标下的点云 PointCloud::Ptr temp (new PointCloud); PCL_INFO ("Aligning %s (%d) with %s (%d).\n", data[i-1].f_name.c_str (), source->points.size (), data[i].f_name.c_str (), target->points.size ()); // pairTransform返回从目标点云target到source的变换矩阵 pairAlign (source, target, temp, pairTransform, true); //把当前两两配准后的点云temp转化到全局坐标系下返回result pcl::transformPointCloud (*temp, *result, GlobalTransform); //用当前的两组点云之间的变换更新全局变换 GlobalTransform = GlobalTransform * pairTransform; //保存转换到第一个点云坐标下的当前配准后的两组点云result到文件i.pcd std::stringstream ss; ss << i << ".pcd"; pcl::io::savePCDFile (ss.str (), *result, true); } } /* ]--- */
运行执行可执行文件
./pairwise_incremental_registration frame_00000.pcd capture0001.pcd capture0002.pcd capture0004.pcd capture0005.pcd
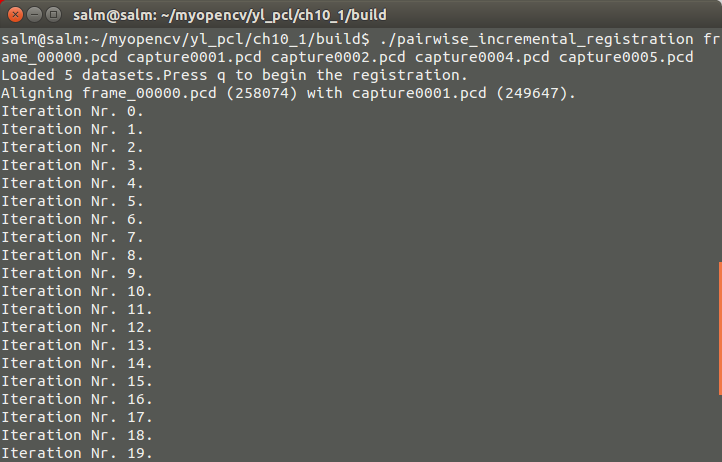
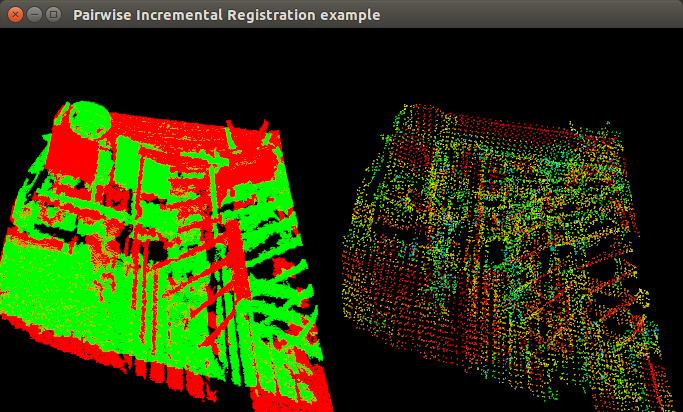
如果观察不到结果,就按键R来重设摄像头,调整角度可以观察到有红绿两组点云显示在窗口的左边,红色为源点云,将看到上面的类似结果,命令行提示需要执行配准按下Q,按下后可以发现左边的窗口不断的调整点云,其实是配准过程中的迭代中间结果的输出,在迭代次数小于设定的次数之前,右边会不断刷新最新的配准结果,直到收敛,迭代次数30次完成整个匹配的过程,再次按下Q后会看到存储的1.pcd文件,此文件为第一个和第二个点云配准后与第一个输入点云在同一个坐标系下的点云。
微信公众号号可扫描二维码一起共同学习交流

未完待续************************************8