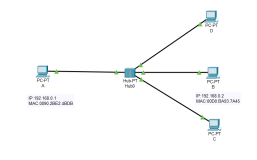
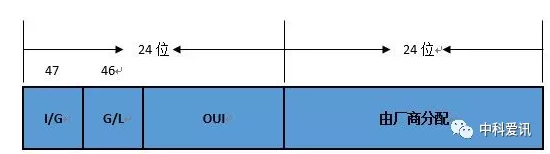
PS:这段时间好多人提到这个问题,我想都是被ARP给闹得!我在网上也找过资料,但是不多,昨天晚上在论坛里看到一篇关于这方面的资料与配置文档,感觉不错,发出来共享一下。
vmps server配置
To use VMPS, you first must create a VMPS database and store it on a TFTP server. The VMPS parser is line based. Start each entry in the file on a new line. The example at the end of this section corresponds to the information described below.
The VMPS database can have up to five sections:
Section 1, Global settings, lists the settings for the VMPS domain name, security mode, fallback VLAN, and the policy for VMPS and VTP domain name mismatches.
Begin the configuration file with the word "VMPS," to prevent other types of configuration files from incorrectly being read by the VMPS server.
Define the VMPS domain. The VMPS domain should correspond to the VTP domain name configured on the switch.
Define the security mode. VMPS can operate in open or secure mode. If you set it to open mode, VMPS returns an access denied response for an unauthorized MAC address and returns the fallback VLAN for a MAC address not listed in the VMPS database. In secure mode, VMPS shuts down the port for a MAC address that is unauthorized or that is not listed in the VMPS database.
(Optional) Define a fallback VLAN. Assign the fallback VLAN is assigned if the MAC addresses of the connected host is not defined in the database.
In the example at the end of this section, the VMPS domain name is WBU, the VMPS mode is set to open, the fallback VLAN is set to the VLAN default, and if the VTP domain name does match the VMPS domain name, then VMPS sends an access denied response message.
Section 2, MAC addresses, lists MAC addresses and authorized VLAN names for each MAC address.
Enter the MAC address of each host and the VLAN name to which each should belong.
Use the --NONE-- keyword as the VLAN name to deny the specified host network connectivity.
You can enter up to 21,051 MAC addresses in a VMPS database file for the Catalyst 2948G switch.
In the example at the end of this section, MAC addresses are listed in the MAC table. Notice that the MAC address fedc.ba98.7654 is set to --NONE--. This setting explicitly denies this MAC address from accessing the network.
Section 3, Port groups, lists groups of ports on various switches in your network that you want grouped together. You use these port groups when defining VLAN port policies.
Define a port group name for each port group; then list all ports you want included in the port group.
A port is identified by the IP address of the switch and the module/port number of the port in the form mod_num/port_num. Ranges are not allowed for the port numbers.
Use the all-ports keyword to specify all the ports in the specified switch.
The example at the end of this section has two port groups:
WiringCloset1 consists of the two ports: port 3/2 on the VMPS client 198.92.30.32 and port 2/8 on the VMPS client 172.20.26.141
Executive Row consists of three ports: port 1/2 and 1/3 on the VMPS client 198.4.254.222, and all ports on the VMPS client 198.4.254.223
Section 4, VLAN groups, lists groups of VLANs you want to associate together. You use these VLAN groups when defining VLAN port policies.
Define the VLAN group name; then list each VLAN name you want to include in the VLAN group.
You can enter a maximum of 256 VLANS in a VMPS database file for the Catalyst 2948G switch.
The example at the end of this section has the VLAN group Engineering, which consists of the VLANs hardware and software.
Section 5, VLAN port policies, lists the VLAN port policies, which use the port groups and VLAN groups to further restrict access to the network.
You can configure a restricted access using MAC addresses and the port groups or VLAN groups.
The example at the end of this section has three VLAN port policies specified.
In the first VLAN port policy, the VLAN hardware or software is restricted to port 3/2 on the VMPS client 198.92.30.32 and port 2/8 on the VMPS client 172.20.23.141.
In the second VLAN port policy, the devices specified in VLAN Green can connect only to port 4/8 on the VMPS client 198.92.30.32.
In the third VLAN port policy, the devices specified in VLAN Purple can connect to only port 1/2 on the VMPS client 198.4.254.22 and the ports specified in the port group Executive Row.
The following example shows a sample VMPS database configuration file.
!Section 1: GLOBAL SETTINGS
!VMPS File Format, version 1.1
! Always begin the configuration file with
! the word "VMPS"
!
!vmps domain
! The VMPS domain must be defined.
!vmps mode {open | secure}
! The default mode is open.
!vmps fallback
!vmps no-domain-req { allow | deny }
!
! The default value is allow.
vmps domain WBU
vmps mode open
vmps fallback default
vmps no-domain-req deny
!
!Section 2: MAC ADDRESSES
!MAC Addresses
vmps-mac-addrs
!
! address vlan-name
!
address 0012.2233.4455 vlan-name hardware
address 0000.6509.a080 vlan-name hardware
address aabb.ccdd.eeff vlan-name Green
address 1223.5678.9abc vlan-name ExecStaff
address fedc.ba98.7654 vlan-name --NONE--
address fedc.ba23.1245 vlan-name Purple
!
!Section 3: PORT GROUPS
!Port Groups
!vmps-port-group
! device { port | all-ports }
!
vmps-port-group WiringCloset1
device 198.92.30.32 port 3/2
device 172.20.26.141 port 2/8
vmps-port-group "Executive Row"
device 198.4.254.222 port 1/2
device 198.4.254.222 port 1/3
device 198.4.254.223 all-ports
!
!Section 4: VLAN GROUPS
!VLAN groups
!
!vmps-vlan-group
! vlan-name
!
vmps-vlan-group Engineering
vlan-name hardware
vlan-name software
!
!Section 5: VLAN PORT POLICIES
!VLAN port Policies
!
!vmps-port-policies {vlan-name | vlan-group }
! { port-group | device port }
!
vmps-port-policies vlan-group Engineering
ort-group WiringCloset1
vmps-port-policies vlan-name Green
device 198.92.30.32 port 4/8
vmps-port-policies vlan-name Purple
device 198.4.254.22 port 1/2
vmps server配置
To use VMPS, you first must create a VMPS database and store it on a TFTP server. The VMPS parser is line based. Start each entry in the file on a new line. The example at the end of this section corresponds to the information described below.
The VMPS database can have up to five sections:
Section 1, Global settings, lists the settings for the VMPS domain name, security mode, fallback VLAN, and the policy for VMPS and VTP domain name mismatches.
Begin the configuration file with the word "VMPS," to prevent other types of configuration files from incorrectly being read by the VMPS server.
Define the VMPS domain. The VMPS domain should correspond to the VTP domain name configured on the switch.
Define the security mode. VMPS can operate in open or secure mode. If you set it to open mode, VMPS returns an access denied response for an unauthorized MAC address and returns the fallback VLAN for a MAC address not listed in the VMPS database. In secure mode, VMPS shuts down the port for a MAC address that is unauthorized or that is not listed in the VMPS database.
(Optional) Define a fallback VLAN. Assign the fallback VLAN is assigned if the MAC addresses of the connected host is not defined in the database.
In the example at the end of this section, the VMPS domain name is WBU, the VMPS mode is set to open, the fallback VLAN is set to the VLAN default, and if the VTP domain name does match the VMPS domain name, then VMPS sends an access denied response message.
Section 2, MAC addresses, lists MAC addresses and authorized VLAN names for each MAC address.
Enter the MAC address of each host and the VLAN name to which each should belong.
Use the --NONE-- keyword as the VLAN name to deny the specified host network connectivity.
You can enter up to 21,051 MAC addresses in a VMPS database file for the Catalyst 2948G switch.
In the example at the end of this section, MAC addresses are listed in the MAC table. Notice that the MAC address fedc.ba98.7654 is set to --NONE--. This setting explicitly denies this MAC address from accessing the network.
Section 3, Port groups, lists groups of ports on various switches in your network that you want grouped together. You use these port groups when defining VLAN port policies.
Define a port group name for each port group; then list all ports you want included in the port group.
A port is identified by the IP address of the switch and the module/port number of the port in the form mod_num/port_num. Ranges are not allowed for the port numbers.
Use the all-ports keyword to specify all the ports in the specified switch.
The example at the end of this section has two port groups:
WiringCloset1 consists of the two ports: port 3/2 on the VMPS client 198.92.30.32 and port 2/8 on the VMPS client 172.20.26.141
Executive Row consists of three ports: port 1/2 and 1/3 on the VMPS client 198.4.254.222, and all ports on the VMPS client 198.4.254.223
Section 4, VLAN groups, lists groups of VLANs you want to associate together. You use these VLAN groups when defining VLAN port policies.
Define the VLAN group name; then list each VLAN name you want to include in the VLAN group.
You can enter a maximum of 256 VLANS in a VMPS database file for the Catalyst 2948G switch.
The example at the end of this section has the VLAN group Engineering, which consists of the VLANs hardware and software.
Section 5, VLAN port policies, lists the VLAN port policies, which use the port groups and VLAN groups to further restrict access to the network.
You can configure a restricted access using MAC addresses and the port groups or VLAN groups.
The example at the end of this section has three VLAN port policies specified.
In the first VLAN port policy, the VLAN hardware or software is restricted to port 3/2 on the VMPS client 198.92.30.32 and port 2/8 on the VMPS client 172.20.23.141.
In the second VLAN port policy, the devices specified in VLAN Green can connect only to port 4/8 on the VMPS client 198.92.30.32.
In the third VLAN port policy, the devices specified in VLAN Purple can connect to only port 1/2 on the VMPS client 198.4.254.22 and the ports specified in the port group Executive Row.
The following example shows a sample VMPS database configuration file.
!Section 1: GLOBAL SETTINGS
!VMPS File Format, version 1.1
! Always begin the configuration file with
! the word "VMPS"
!
!vmps domain
! The VMPS domain must be defined.
!vmps mode {open | secure}
! The default mode is open.
!vmps fallback
!vmps no-domain-req { allow | deny }
!
! The default value is allow.
vmps domain WBU
vmps mode open
vmps fallback default
vmps no-domain-req deny
!
!Section 2: MAC ADDRESSES
!MAC Addresses
vmps-mac-addrs
!
! address vlan-name
!
address 0012.2233.4455 vlan-name hardware
address 0000.6509.a080 vlan-name hardware
address aabb.ccdd.eeff vlan-name Green
address 1223.5678.9abc vlan-name ExecStaff
address fedc.ba98.7654 vlan-name --NONE--
address fedc.ba23.1245 vlan-name Purple
!
!Section 3: PORT GROUPS
!Port Groups
!vmps-port-group
! device { port | all-ports }
!
vmps-port-group WiringCloset1
device 198.92.30.32 port 3/2
device 172.20.26.141 port 2/8
vmps-port-group "Executive Row"
device 198.4.254.222 port 1/2
device 198.4.254.222 port 1/3
device 198.4.254.223 all-ports
!
!Section 4: VLAN GROUPS
!VLAN groups
!
!vmps-vlan-group
! vlan-name
!
vmps-vlan-group Engineering
vlan-name hardware
vlan-name software
!
!Section 5: VLAN PORT POLICIES
!VLAN port Policies
!
!vmps-port-policies {vlan-name | vlan-group }
! { port-group | device port }
!
vmps-port-policies vlan-group Engineering
ort-group WiringCloset1
vmps-port-policies vlan-name Green
device 198.92.30.32 port 4/8
vmps-port-policies vlan-name Purple
device 198.4.254.22 port 1/2
ort-group "Executive Row"
本文转自loveme2351CTO博客,原文链接: http://blog.51cto.com/loveme23/8011如需转载请自行联系原作者