.net2.0开始就引入了泛型的机制,泛型有助于我们实现“算法重用”。
借助于泛型机制,我们可以少定义一些重载函数,同时还能保证类型安全性。泛型的语法非常简单,下面通过例子来演示泛型的一些应用。
主要内容:
- 减少装箱/拆箱(提高性能)
- 限制泛型参数的类型
- 节点类型不同的链表
1. 减少装箱/拆箱(提高性能)
我们都知道,.net中的额装箱/拆箱操作非常损害性能,通过使用泛型,可以有效的减少我们代码中的装箱拆箱操作,从而提高代码的性能。
实例代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
using
System;
using
System.Collections.Generic;
using
System.Collections;
class
CLRviaCSharp_13
{
static
void
Main(
string
[] args)
{
List<Int32> lst =
new
List<
int
>();
lst.Add(1);
Int32 i = lst[0];
ArrayList arr =
new
ArrayList();
arr.Add(1);
// 此处必须强制转型,否则报错,
// 因为ArrayList中的元素都是Object类型的。
i = (Int32) arr[0];
}
}
|
代码非常简单,分别用泛型List和ArrayList来存储值类型,然后在取出值类型。
使用泛型List的话,不会出现装箱/拆箱的操作。具体证据还是看下面的IL代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
.method private static hidebysig
void Main (
string[] args
) cil managed
{
// Method begins at RVA 0x217c
// Code size 56 (0x38)
.maxstack 2
.entrypoint
.locals init (
[0] class [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List`1<int32> lst
[1] int32 i
[2] class [mscorlib]System.Collections.ArrayList arr
)
IL_0000: nop
IL_0001: newobj instance void [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List`1<int32>::.ctor()
IL_0006: stloc.0
IL_0007: ldloc.0
IL_0008: ldc.i4.1
IL_0009: callvirt instance void [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List`1<int32>::Add(!!0)
IL_000e: nop
IL_000f: ldloc.0
IL_0010: ldc.i4.0
IL_0011: callvirt instance !!0 [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List`1<int32>::get_Item(int32)
IL_0016: stloc.1
IL_0017: newobj instance void [mscorlib]System.Collections.ArrayList::.ctor()
IL_001c: stloc.2
IL_001d: ldloc.2
IL_001e: ldc.i4.1
IL_001f: box int32
IL_0024: callvirt instance int32 [mscorlib]System.Collections.ArrayList::Add(object)
IL_0029: pop
IL_002a: ldloc.2
IL_002b: ldc.i4.0
IL_002c: callvirt instance object [mscorlib]System.Collections.ArrayList::get_Item(int32)
IL_0031: unbox.any int32
IL_0036: stloc.1
IL_0037: ret
} // End of method CLRviaCSharp_13.Main
|
其中IL_0001~IL_0016是泛型List的相关操作
IL_0017~IL_0036是ArrayList的操作,包含的损害性能的装箱(IL_001f: box int32)和拆箱(IL_0031: unbox.any int32)操作。
2. 限制泛型参数的类型
首先有一点需要说明,泛型类型和普通类型在静态构造函数上有一点不同。
对于普通类型,静态构造函数只在此类型第一次初始化的时候才会执行,
而泛型类型的静态构造函数会在 每种特定类型(即泛型参数T被替换为Int32或者String等等)的第一次初始化的时候执行。
描述的有些拗口,还是看代码吧:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
|
using
System;
using
System.Collections.Generic;
using
System.Collections;
using
System.Threading;
class
CLRviaCSharp_13
{
static
void
Main(
string
[] args)
{
/*
* 非泛型的类:虽然有3次初始化,但是静态构造函数只执行一次
*/
// 第一次初始化,会执行静态构造函数
NormalClass nc =
new
NormalClass();
// 第二次初始化,不会执行静态构造函数
NormalClass nc2 =
new
NormalClass();
// 第三次初始化,不会执行静态构造函数
NormalClass nc3 =
new
NormalClass();
/*
* 泛型的类:泛型参数类型改变的话,会再次执行静态构造函数
*/
// 对泛型参数(string)来说是第一次初始化,会执行静态构造函数
GenericClass<
string
> gc =
new
GenericClass<
string
>();
// 对泛型参数(string)来说是第二次初始化,不会执行静态构造函数
GenericClass<
string
> gc2 =
new
GenericClass<
string
>();
// 对泛型参数(Int32)来说是第一次初始化,会执行静态构造函数
GenericClass<Int32> gc3 =
new
GenericClass<Int32>();
Console.ReadKey(
true
);
}
}
public
class
GenericClass<T>
{
static
GenericClass()
{
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine(
"GenericClass<"
+
typeof
(T) +
"> is initialized at : "
+ DateTime.Now.ToString(
"yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss fff"
));
}
}
public
class
NormalClass
{
static
NormalClass()
{
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine(
"NormalClass is initialized at : "
+ DateTime.Now.ToString(
"yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss fff"
));
}
}
|
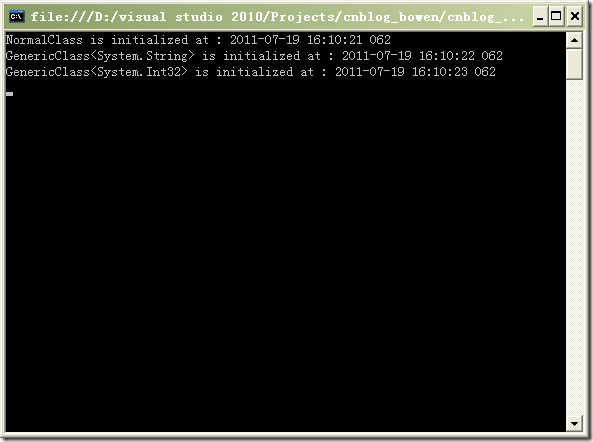
以上代码的执行结果为:
根据泛型类型的静态构造的特点,我们可以通过泛型类型的静态构造函数来限制泛型参数(T)的类型。
比如以下代码,通过泛型类型的静态构造函数来限制泛型参数(T)只能为值类型
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
using
System;
class
CLRviaCSharp_13
{
static
void
Main(
string
[] args)
{
// 对于引用类型的泛型参数,会抛出异常
GenericClass<
string
> gc =
new
GenericClass<
string
>();
// 对于值类型的泛型参数,都能正常初始化
GenericClass<Int32> gc2 =
new
GenericClass<Int32>();
GenericClass<Double> gc3 =
new
GenericClass<Double>();
GenericClass<DateTime> gc4 =
new
GenericClass<DateTime>();
Console.ReadKey(
true
);
}
}
public
class
GenericClass<T>
{
static
GenericClass()
{
if
(!
typeof
(T).IsValueType)
{
throw
new
ArgumentException(
"T must be a Enum type!"
);
}
Console.WriteLine(
"Type "
+
typeof
(T).ToString() +
" is initilized!"
);
}
}
|
注释掉 GenericClass<string> gc = new GenericClass<string>(); 就能正常执行。
关于泛型参数(T)的限制,将在下一篇 泛型高级 中有更进一步的阐释。
3. 节点类型不同的链表
链表是一种常用的数据结构,以往构造链表时,每个节点往往都是相同的类型,否则取出节点后我们无法还原其本身的类型。
但是现在借助于泛型,我们可以构造出节点类型不同的链表,而且链表中每个节点都是强类型(不是Object类型)的,从而满足日益复杂的需求。
代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
using
System;
class
CLRviaCSharp_13
{
static
void
Main(
string
[] args)
{
Node header =
new
TypedNode<Char>(
'.'
);
header =
new
TypedNode<
string
>(
"hello world"
, header);
header =
new
TypedNode<Int32>(100, header);
header =
new
TypedNode<DateTime>(DateTime.Now, header);
Console.WriteLine(header.ToString());
Console.ReadKey(
true
);
}
}
public
class
Node
{
protected
Node _next;
public
Node(Node next)
{
_next = next;
}
}
public
sealed
class
TypedNode<T> : Node
{
public
T _data;
public
TypedNode(T data) :
this
(data,
null
)
{}
public
TypedNode(T data, Node next) :
base
(next)
{
_data = data;
}
public
override
string
ToString()
{
return
_data.ToString() +
"\n"
+
((_next !=
null
) ? _next.ToString() :
null
);
}
}
|
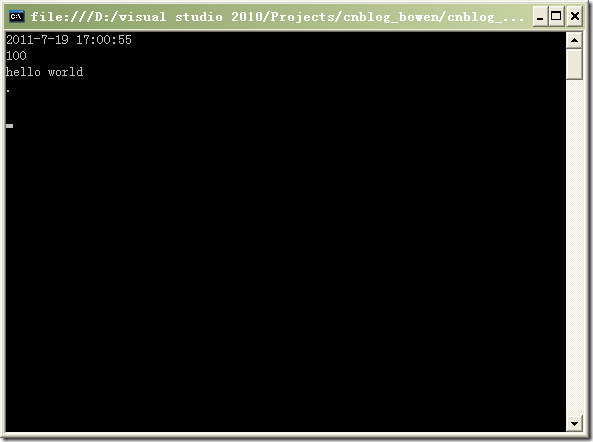
这个例子是《CLR via C#》上的,每次都是从链表头部增加一个节点。实际应用时也可以根据需求修改为从链表尾部追加节点。
执行结果如下: