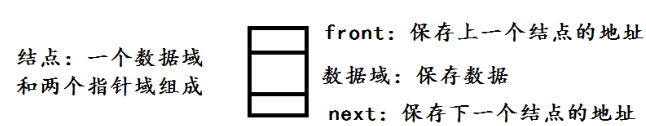
template<typename Type> class DoublyList;
template<typename Type> class ListNode{
private:
friend class DoublyList<Type>;
ListNode():m_pprior(NULL),m_pnext(NULL){}
ListNode(const Type item,ListNode<Type> *prior=NULL,ListNode<Type> *next=NULL)
:m_data(item),m_pprior(prior),m_pnext(next){}
~ListNode(){
m_pprior=NULL;
m_pnext=NULL;
}
public:
Type GetData();
private:
Type m_data;
ListNode *m_pprior;
ListNode *m_pnext;
};
template<typename Type> Type ListNode<Type>::GetData(){
return this->m_data;
}
#include "ListNode.h"
template<typename Type> class DoublyList{
public:
DoublyList():head(new ListNode<Type>()){ //the head node point to itself
head->m_pprior=head;
head->m_pnext=head;
}
~DoublyList(){
MakeEmpty();
delete head;
}
public:
void MakeEmpty(); //make the list empty
int Length(); //get the length of the list
ListNode<Type> *Find(int n=0); //find the nth data
ListNode<Type> * FindData(Type item); //find the data which is equal to item
bool Insert(Type item,int n=0); //insert item in the nth data
Type Remove(int n=0); //delete the nth data
Type Get(int n=0); //get the nth data
void Print(); //print the list
private:
ListNode<Type> *head;
};
template<typename Type> void DoublyList<Type>::MakeEmpty(){
ListNode<Type> *pmove=head->m_pnext,*pdel;
while(pmove!=head){
pdel=pmove;
pmove=pdel->m_pnext;
delete pdel;
}
head->m_pnext=head;
head->m_pprior=head;
}
template<typename Type> int DoublyList<Type>::Length(){
ListNode<Type> *pprior=head->m_pprior,*pnext=head->m_pnext;
int count=0;
while(1){
if(pprior->m_pnext==pnext){
break;
}
if(pprior==pnext&&pprior!=head){
count++;
break;
}
count+=2;
pprior=pprior->m_pprior;
pnext=pnext->m_pnext;
}
return count;
}
template<typename Type> ListNode<Type>* DoublyList<Type>::Find(int n = 0){
if(n<0){
cout<<"The n is out of boundary"<<endl;
return NULL;
}
ListNode<Type> *pmove=head->m_pnext;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
pmove=pmove->m_pnext;
if(pmove==head){
cout<<"The n is out of boundary"<<endl;
return NULL;
}
}
return pmove;
}
template<typename Type> bool DoublyList<Type>::Insert(Type item,int n){
if(n<0){
cout<<"The n is out of boundary"<<endl;
return 0;
}
ListNode<Type> *newnode=new ListNode<Type>(item),*pmove=head;
if(newnode==NULL){
cout<<"Application Erorr!"<<endl;
exit(1);
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ //find the position for insert
pmove=pmove->m_pnext;
if(pmove==head){
cout<<"The n is out of boundary"<<endl;
return 0;
}
}
//insert the data
newnode->m_pnext=pmove->m_pnext;
newnode->m_pprior=pmove;
pmove->m_pnext=newnode;
newnode->m_pnext->m_pprior=newnode;
return 1;
}
template<typename Type> Type DoublyList<Type>::Remove(int n = 0){
if(n<0){
cout<<"The n is out of boundary"<<endl;
exit(1);
}
ListNode<Type> *pmove=head,*pdel;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ //find the position for delete
pmove=pmove->m_pnext;
if(pmove==head){
cout<<"The n is out of boundary"<<endl;
exit(1);
}
}
//delete the data
pdel=pmove;
pmove->m_pprior->m_pnext=pdel->m_pnext;
pmove->m_pnext->m_pprior=pdel->m_pprior;
Type temp=pdel->m_data;
delete pdel;
return temp;
}
template<typename Type> Type DoublyList<Type>::Get(int n = 0){
if(n<0){
cout<<"The n is out of boundary"<<endl;
exit(1);
}
ListNode<Type> *pmove=head;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
pmove=pmove->m_pnext;
if(pmove==head){
cout<<"The n is out of boundary"<<endl;
exit(1);
}
}
return pmove->m_data;
}
template<typename Type> void DoublyList<Type>::Print(){
ListNode<Type> *pmove=head->m_pnext;
cout<<"head";
while(pmove!=head){
cout<<"--->"<<pmove->m_data;
pmove=pmove->m_pnext;
}
cout<<"--->over"<<endl<<endl<<endl;
}
template<typename Type> ListNode<Type>* DoublyList<Type>::FindData(Type item){
ListNode<Type> *pprior=head->m_pprior,*pnext=head->m_pnext;
while(pprior->m_pnext!=pnext && pprior!=pnext){ //find the data in the two direction
if(pprior->m_data==item){
return pprior;
}
if(pnext->m_data==item){
return pnext;
}
pprior=pprior->m_pprior;
pnext=pnext->m_pnext;
}
cout<<"can't find the element"<<endl;
return NULL;
}
#include <iostream>
#include "DoublyList.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
DoublyList<int> list;
for(int i=0;i<20;i++){
list.Insert(i*3,i);
}
cout<<"the Length of the list is "<<list.Length()<<endl;
list.Print();
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
list.Insert(3,i*3);
}
cout<<"the Length of the list is "<<list.Length()<<endl;
list.Print();
list.Remove(5);
cout<<"the Length of the list is "<<list.Length()<<endl;
list.Print();
cout<<list.FindData(54)->GetData()<<endl;
cout<<"The third element is "<<list.Get(3)<<endl;
list.MakeEmpty();
cout<<"the Length of the list is "<<list.Length()<<endl;
list.Print();
return 0;
}