Service是Android 系统中的四大组件之一,是在一段不定的时间运行在后台,不和用户交互应用组件。
service可以在很多场合的应用中使用,比如播放多媒体的时候用户启动了其他Activity这个时候程序要在后台继续播放,比如检测SD卡上文件的变化等等。
生命周期

context.startService() 启动流程:
context.startService() -> onCreate() -> onStart() -> Service running -> context.stopService() -> onDestroy() -> Service stop
如果Service还没有运行,则android先调用onCreate(),然后调用onStart();
如果Service已经运行,则只调用onStart(),所以一个Service的onStart方法可能会重复调用多次。
如果stopService的时候会直接onDestroy,如果是调用者自己直接退出而没有调用stopService的话,Service会一直在后台运行,该Service的调用者再启动起来后可以通过stopService关闭Service。
所以调用startService的生命周期为:onCreate --> onStart (可多次调用) --> onDestroy
context.bindService()启动流程:
context.bindService() -> onCreate() -> onBind() -> Service running -> onUnbind() -> onDestroy() -> Service stop
onBind()将返回给客户端一个IBind接口实例,IBind允许客户端回调服务的方法,比如得到Service的实例、运行状态或其他操作。这个时候把调用者(Context,例如Activity)会和Service绑定在一起,Context退出了,Srevice就会调用onUnbind->onDestroy相应退出。
所以调用bindService的生命周期为:onCreate --> onBind(只一次,不可多次绑定) --> onUnbind --> onDestory。
在Service每一次的开启关闭过程中,只有onStart可被多次调用(通过多次startService调用),其他onCreate,onBind,onUnbind,onDestory在一个生命周期中只能被调用一次。
开启关闭
Service的启动有两种方式:context.startService() 和 context.bindService()
Service的关闭有两种方式:context.stopService() 和 context.unbindService()
工程
<service android:name=".PhoneStatusService"></service>
Service的内容:
package com.yydcdut.servicestudy1; import java.io.IOException; import android.app.Service; import android.content.Intent; import android.media.MediaRecorder; import android.os.IBinder; import android.telephony.PhoneStateListener; import android.telephony.TelephonyManager; public class PhoneStatusService extends Service { @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { return null; } @Override public void onCreate() { System.out.println("onCreate"); super.onCreate(); } @Override public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) { System.out.println("onStart"); //监听电话状态的变化 TelephonyManager tm = (TelephonyManager) getSystemService(TELEPHONY_SERVICE); tm.listen(new MyPhoneStatusListener(), PhoneStateListener.LISTEN_CALL_STATE); super.onStart(intent, startId); } @Override public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) { System.out.println("onStartCommand"); return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId); } @Override public void onDestroy() { System.out.println("onDestroy"); super.onDestroy(); } } class MyPhoneStatusListener extends PhoneStateListener { private MediaRecorder recorder; @Override public void onCallStateChanged(int state, String incomingNumber) { switch (state) { case TelephonyManager.CALL_STATE_IDLE://空闲 if(recorder != null) { recorder.stop(); recorder.reset();recorder.release(); recorder = null; } break; case TelephonyManager.CALL_STATE_RINGING://响铃 System.out.println("发现来电!!!!!"); if("5556".equals(incomingNumber)) { System.out.println("挂断电话......"); } recorder = new MediaRecorder(); recorder.setAudioSource(MediaRecorder.AudioSource.MIC); recorder.setOutputFormat(MediaRecorder.OutputFormat.THREE_GPP); recorder.setAudioEncoder(MediaRecorder.AudioEncoder.AMR_NB); recorder.setOutputFile("/data/data/com.yydcdut.servicestudy1/"+System.currentTimeMillis()+".3gp"); try { recorder.prepare(); } catch (IllegalStateException e) { // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 e.printStackTrace(); } break; case TelephonyManager.CALL_STATE_OFFHOOK://通话状态 if(recorder != null) recorder.start(); break; default: break; } super.onCallStateChanged(state, incomingNumber); } }
主界面两个Button开启和关闭Service:
public void click(View view) { Intent intent = new Intent(getApplicationContext(),PhoneStatusService.class); startService(intent); } public void click2(View view) { Intent intent = new Intent(getApplicationContext(),PhoneStatusService.class); stopService(intent); }
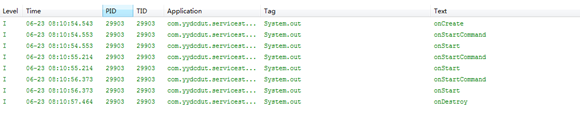
关于生命周期的截图:
我是天王盖地虎的分割线
源代码:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1dD1Qx01
service学习1.zip
本文转自我爱物联网博客园博客,原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/yydcdut/p/3804234.html,如需转载请自行联系原作者