分区只是内核的概念,就是说A~B地址放内核,C~D地址放文件系统,(也就是规定哪个地址区间放内核或者文件系统)等等。
1:在内核MTD中可以定义分区A~B,C~D。。。。。。并予以绝对的地址赋值给每个分区。我们可以来看看在内核中是怎样来对MTD进行分区的:arch\arm\plat-s3c24xx\common-smdk.c
static struct mtd_partition smdk_default_nand_part[] = {
[0] = {
.name = "Boot",
.size = SZ_16K,
.offset = 0,
},
[1] = {
.name = "S3C2410 flash partition 1",
.offset = 0,
.size = SZ_2M,
},
[2] = {
.name = "S3C2410 flash partition 2",
.offset = SZ_4M,
.size = SZ_4M,
},
[3] = {
.name = "S3C2410 flash partition 3",
.offset = SZ_8M,
.size = SZ_2M,
},
[4] = {
.name = "S3C2410 flash partition 4",
.offset = SZ_1M * 10,
.size = SZ_4M,
},
......
};
一般我们只需要分3-4个区,第一个为boot区,一个为boot参数区(传递给内核的参数),一个为内核区,一个为文件系统区。
而对于bootloader中只要能将内核下载到A~B区的A地址开始处就可以,C~D区的C起始地址下载文件系统。。。这些起始地址在MTD的分区信息中能找到。所以bootloader对分区的概念不重要,只要它能把内核烧到A位置,把文件系统烧到C位置。
所以,在bootloader对Flash进行操作时,哪块区域放什么是以内核为主。
而为了方便操作,bootloader类似也引入分区的概念,如,可以使用“nand write 0x3000000 kernel 200000”命令将uImage烧到kernel分区,而不必写那么长:nand write 3000000 A 200000,也就是用分区名来代替具体的地址。
这要对bootloader对内核重新分区:这需要重新设置一下bootloader环境参数,就可以同步更新内核分区信息
如:
setenv bootargs 'noinitrd console=ttySAC0 root=/dev/mtdblock3 rootfstype=jffs2
mtdparts=nand_flash:128k(u-boot)ro,64k(u-boot envs),3m(kernel),30m(root.jffs2),30m(root.yaffs)'
内核配置时选上Device Drivers ---> Memory Technology Device (MTD) support ---> Command line partition table parsing
在设置了mtdparts变量之后,就可以在nand read/write/erase命令中直接使用分区的名字而不必指定分区的偏移位置.而这需要内核MTD最好没有规划分区。
如果你是通过uboot的内核命令行给MTD层传递MTD分区信息,这种情况下,内核读取到的分区信息始终和u-boot中的保持一致(推荐的做法)
如果你是把分区信息写在内核源代码MTD里定义好的方法,那最好保证它和u-boot中的保持一致,即同步修改uboot及内核的相关部分。
2:
内核通过bootargs找到文件系统,bootargs中的mtdblockx即代表分区,block1,2,3代表哪个分区。
事实上,bootargs中的"root=/dev/mtdblockx"只是告诉内核,root fs从第x个(x=0,1,2...)MTD分区挂载,mtdblock0对应第一个分区,mtdblock1对应第二个分区,以此类推.
3:分区方法
1) MTD层的分区
2) 通过U-boot传递给内核的命令行中的mtdparts=...
3) 其他可以让内核知道分区信息的任何办法,(内核默认的命令参数)
下面说到mtdparts,及它的用法:
mtdparts
mtdparts=fc000000.nor_flash:1920k(linux),128k(fdt),20M(ramdisk),4M(jffs2),38272k(user),256k(env),384k(uboot)
要想这个参数起作用,内核中的mtd驱动必须要支持,即内核配置时需要选上Device Drivers ---> Memory Technology Device (MTD) support ---> Command line partition table parsing
mtdparts的格式如下:
mtdparts=[;
:= :[,]
:= [@offset][][ro]
:= unique id used in mapping driver/device
:= standard linux memsize OR "-" to denote all remaining space
:= (NAME)
因此你在使用的时候需要按照下面的格式来设置:
mtdparts=mtd-id:@(),@()
这里面有几个必须要注意的:
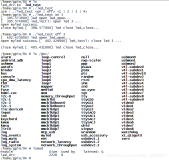
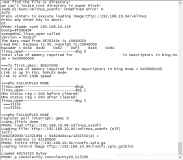
a. mtd-id 必须要跟你当前平台的flash的mtd-id一致,不然整个mtdparts会失效 怎样获取到当前平台的flash的mtd-id?
在bootargs参数列表中可以指定当前flash的mtd-id,如指定 mtdids:nand0=gen_nand.1,前面的nand0则表示第一个flash
b. size在设置的时候可以为实际的size(xxM,xxk,xx),也可以为'-'这表示剩余的所有空间。
相关信息可以查看drivers/mtd/cmdlinepart.c中的注释找到相关描述。
U-boot的环境变量值得注意的有两个: bootcmd 和bootargs。
引用:
u bootcmd
前面有说过bootcmd是自动启动时默认执行的一些命令,因此你可以在当前环境中定义各种不同配置,不同环境的参数设置,然后设置bootcmd为你经常使用的那种参数。
u bootargs
bootargs是环境变量中的重中之重,甚至可以说整个环境变量都是围绕着bootargs来设置的。bootargs的种类非常非常的多,我们平常只是使用了几种而已,感兴趣的可以看看这篇文章说的很全:http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2011-03/33599p4.htm。bootargs非常的灵活,内核和文件系统的不同搭配就会有不同的设置方法,甚至你也可以不设置bootargs,而直接将其写到内核中去(在配置内核的选项中可以进行这样的设置),正是这些原因导致了bootargs使用上的困难。
下面介绍一下bootargs常用参数,bootargs的种类非常的多,而且随着kernel的发展会出现一些新的参数,使得设置会更加灵活多样。
A. root
用来指定rootfs的位置, 常见的情况有:
root=/dev/ram rw
root=/dev/ram0 rw
请注意上面的这两种设置情况是通用的,我做过测试甚至root=/dev/ram1 rw和root=/dev/ram2 rw也是可以的,网上有人说在某些情况下是不通用的,即必须设置成ram或者ram0,但是目前还没有遇到,还需要进一步确认,遇到不行的时候可以逐一尝试。
root=/dev/mtdx rw
root=/dev/mtdblockx rw
root=/dev/mtdblock/x rw
root=31:0x
上面的这几个在一定情况下是通用的,当然这要看你当前的系统是否支持,不过mtd是字符设备,而mtdblock是块设备,有时候你的挨个的试到底当前的系统支持上面那种情况下,不过root=/dev/mtdblockx rw比较通用。此外,如果直接指定设备名可以的话,那么使用此设备的设备号也是可以的。
root=/dev/nfs
在文件系统为基于nfs的文件系统的时候使用。当然指定root=/dev/nfs之后,还需要指定nfsroot=serverip:nfs_dir,即指明文件系统存在那个主机的那个目录下面。
B. rootfstype
这个选项需要跟root一起配合使用,一般如果根文件系统是ext2的话,有没有这个选项是无所谓的,但是如果是jffs2,squashfs等文件系统的话,就需要rootfstype指明文件系统的类型,不然会无法挂载根分区.
C. console
console=tty 使用虚拟串口终端设备 .
console=ttyS[,options] 使用特定的串口,options可以是这样的形式bbbbpnx,这里bbbb是指串口的波特率,p是奇偶校验位,n是指的bits。
console=ttySAC[,options] 同上面。
看你当前的环境,有时用ttyS,有时用ttySAC,网上有人说,这是跟内核的版本有关,2.4用ttyS,2.6用ttySAC,但实际情况是官方文档中也是使用ttyS,所以应该是跟内核版本没有关联的。可以查看Documentation/serial-console.txt找到相关描述。
D. mem
mem=xxM 指定内存的大小,不是必须的
E. ramdisk_size
ramdisk=xxxxx 不推荐
ramdisk_size=xxxxx 推荐
上面这两个都可以告诉ramdisk 驱动,创建的ramdisk的size,默认情况下是4m(s390默认8M),你可以查看Documentation/ramdisk.txt找到相关的描述,不过ramdisk=xxxxx在新版的内核都已经没有提了,不推荐使用。
F. initrd, noinitrd
当你没有使用ramdisk启动系统的时候,你需要使用noinitrd这个参数,但是如果使用了的话,就需要指定initrd=r_addr,size, r_addr表示initrd在内存中的位置,size表示initrd的大小。
G. init
init指定的是内核启起来后,进入系统中运行的第一个脚本,一般init=/linuxrc, 或者init=/etc/preinit,preinit的内容一般是创建console,null设备节点,运行init程序,挂载一些文件系统等等操作。请注意,很多初学者以为init=/linuxrc是固定写法,其实不然,/linuxrc指的是/目录下面的linuxrc脚本,一般是一个连接罢了。
H. ip
指定系统启动之后网卡的ip地址,如果你使用基于nfs的文件系统,那么必须要有这个参数,其他的情况下就看你自己的喜好了。设置ip有两种方法:
ip = ip addr
ip=ip addr:server ip addr:gateway:netmask::which netcard:off
这两种方法可以用,不过很明显第二种要详细很多,请注意第二种中which netcard 是指开发板上的网卡,而不是主机上的网卡。
说完常见的几种bootargs,那么我们来讨论平常我经常使用的几种组合:
1). 假设文件系统是ramdisk,且直接就在内存中,bootargs的设置应该如下:
setenv bootargs ‘initrd=0x32000000,0xa00000 root=/dev/ram0 console=ttySAC0 mem=64M init=/linuxrc’
2). 假设文件系统是ramdisk,且在flash中,bootargs的设置应该如下:
setenv bootargs ‘mem=32M console=ttyS0,115200 root=/dev/ram rw init=/linuxrc’
注意这种情况下你应该要在bootm命令中指定ramdisk在flash中的地址,如bootm kernel_addr ramdisk_addr (fdt_addr)
3). 假设文件系统是jffs2类型的,且在flash中,bootargs的设置应该如下
setenv bootargs ‘mem=32M console=ttyS0,115200 noinitrd root=/dev/mtdblock2 rw rootfstype=jffs2 init=/linuxrc’
4). 假设文件系统是基于nfs的,bootargs的设置应该如下
setenv bootargs ‘noinitrd mem=64M console=ttySAC0 root=/dev/nfs nfsroot=192.168.0.3:/nfs ip=192.168.0.5:192.168.0.3:192.168.0.3:255.255.255.0::eth0:off’
或者
setenv bootargs ‘noinitrd mem=64M console=ttySAC0 root=/dev/nfs nfsroot=192.168.0.3:/nfs ip=192.168.0.5’
linux kernel boot arguments
The following is a consolidated list of the kernel parameters as implemented (mostly) by the __setup() macro and sorted into English Dictionary order (defined as ignoring all punctuation and sorting digits before letters in a case insensitive manner), and with descriptions where known.
Module parameters for loadable modules are specified only as the parameter name with optional '=' and value as appropriate, such as:
modprobe usbcore blinkenlights=1
Module parameters for modules that are built into the kernel image are specified on the kernel command line with the module name plus '.' plus parameter name, with '=' and value if appropriate, such as:
usbcore.blinkenlights=1
The text in square brackets at the beginning of the description states the restrictions on the kernel for the said kernel parameter to be valid. The restrictions referred to are that the relevant option is valid if:
ACPI ACPI support is enabled.ALSA ALSA sound support is enabled.
APIC APIC support is enabled.
APM Advanced Power Management support is enabled.
AX25 Appropriate AX.25 support is enabled.
CD Appropriate CD support is enabled.
DEVFS devfs support is enabled.
DRM Direct Rendering Management support is enabled.
EDD BIOS Enhanced Disk Drive Services (EDD) is enabled
EFI EFI Partitioning (GPT) is enabled
EIDE EIDE/ATAPI support is enabled.
FB The frame buffer device is enabled.
HW Appropriate hardware is enabled.
IA-32 IA-32 aka i386 architecture is enabled.
IA-64 IA-64 architecture is enabled.
IOSCHED More than one I/O scheduler is enabled.
IP_PNP IP DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP is enabled.
ISAPNP ISA PnP code is enabled.
ISDN Appropriate ISDN support is enabled.
JOY Appropriate joystick support is enabled.
LP Printer support is enabled.
LOOP Loopback device support is enabled.
M68k M68k architecture is enabled.
These options have more detailed description inside of
Documentation/m68k/kernel-options.txt.
MCA MCA bus support is enabled.
MDA MDA console support is enabled.
MOUSE Appropriate mouse support is enabled.
MTD MTD support is enabled.
NET Appropriate network support is enabled.
NUMA NUMA support is enabled.
NFS Appropriate NFS support is enabled.
OSS OSS sound support is enabled.
PARIDE The ParIDE subsystem is enabled.
PARISC The PA-RISC architecture is enabled.
PCI PCI bus support is enabled.
PCMCIA The PCMCIA subsystem is enabled.
PNP Plug & Play support is enabled.
PPC PowerPC architecture is enabled.
PPT Parallel port support is enabled.
PS2 Appropriate PS/2 support is enabled.
RAM RAM disk support is enabled.
S390 S390 architecture is enabled.
SCSI Appropriate SCSI support is enabled.
A lot of drivers has their options described inside of
Documentation/scsi/.
SELINUX SELinux support is enabled.
SERIAL Serial support is enabled.
SMP The kernel is an SMP kernel.
SPARC Sparc architecture is enabled.
SWSUSP Software suspend is enabled.
TS Appropriate touchscreen support is enabled.
USB USB support is enabled.
USBHID USB Human Interface Device support is enabled.
V4L Video For Linux support is enabled.
VGA The VGA console has been enabled.
VT Virtual terminal support is enabled.
WDT Watchdog support is enabled.
XT IBM PC/XT MFM hard disk support is enabled.
X86-64 X86-64 architecture is enabled.
More X86-64 boot options can be found in
Documentation/x86_64/boot-options.txt .
In addition, the following text indicates that the option:
BUGS= Relates to possible processor bugs on the said processor.KNL Is a kernel start-up parameter.
BOOT Is a boot loader parameter.
Parameters denoted with BOOT are actually interpreted by the boot loader, and have no meaning to the kernel directly. Do not modify the syntax of boot loader parameters without extreme need or coordination with .
Note that ALL kernel parameters listed below are CASE SENSITIVE, and that a trailing = on the name of any parameter states that that parameter will be entered as an environment variable, whereas its absence indicates that it will appear as a kernel argument readable via /proc/cmdline by programs running once the system is up.
53c7xx= [HW,SCSI] Amiga SCSI controllersSee header of drivers/scsi/53c7xx.c.
See also Documentation/scsi/ncr53c7xx.txt.
acpi= [HW,ACPI] Advanced Configuration and Power Interface
Format: { force | off | ht | strict | noirq }
force -- enable ACPI if default was off
off -- disable ACPI if default was on
noirq -- do not use ACPI for IRQ routing
ht -- run only enough ACPI to enable Hyper Threading
strict -- Be less tolerant of platforms that are not
strictly ACPI specification compliant.
See also Documentation/pm.txt, pci=noacpi
acpi_sleep= [HW,ACPI] Sleep options
Format: { s3_bios, s3_mode }
See Documentation/power/video.txt
acpi_sci= [HW,ACPI] ACPI System Control Interrupt trigger mode
Format: { level | edge | high | low }
acpi_irq_balance [HW,ACPI]
ACPI will balance active IRQs
default in APIC mode
acpi_irq_nobalance [HW,ACPI]
ACPI will not move active IRQs (default)
default in PIC mode
acpi_irq_pci= [HW,ACPI] If irq_balance, clear listed IRQs for
use by PCI
Format: ,...
acpi_irq_isa= [HW,ACPI] If irq_balance, mark listed IRQs used by ISA
Format: ,...
acpi_osi= [HW,ACPI] empty param disables _OSI
acpi_serialize [HW,ACPI] force serialization of AML methods
acpi_skip_timer_override [HW,ACPI]
Recognize and ignore IRQ0/pin2 Interrupt Override.
For broken nForce2 BIOS resulting in XT-PIC timer.
acpi_dbg_layer= [HW,ACPI]
Format:
Each bit of the indicates an ACPI debug layer,
1: enable, 0: disable. It is useful for boot time
debugging. After system has booted up, it can be set
via /proc/acpi/debug_layer.
acpi_dbg_level= [HW,ACPI]
Format:
Each bit of the indicates an ACPI debug level,
1: enable, 0: disable. It is useful for boot time
debugging. After system has booted up, it can be set
via /proc/acpi/debug_level.
acpi_fake_ecdt [HW,ACPI] Workaround failure due to BIOS lacking ECDT
acpi_generic_hotkey [HW,ACPI]
Allow consolidated generic hotkey driver to
override platform specific driver.
See also Documentation/acpi-hotkey.txt.
enable_timer_pin_1 [i386,x86-64]
Enable PIN 1 of APIC timer
Can be useful to work around chipset bugs
(in particular on some ATI chipsets).
The kernel tries to set a reasonable default.
disable_timer_pin_1 [i386,x86-64]
Disable PIN 1 of APIC timer
Can be useful to work around chipset bugs.
ad1816= [HW,OSS]
Format: ,,,
See also Documentation/sound/oss/AD1816.
ad1848= [HW,OSS]
Format: ,,,,
adlib= [HW,OSS]
Format:
advansys= [HW,SCSI]
See header of drivers/scsi/advansys.c.
advwdt= [HW,WDT] Advantech WDT
Format: ,
aedsp16= [HW,OSS] Audio Excel DSP 16
Format: ,,,,,
See also header of sound/oss/aedsp16.c.
aha152x= [HW,SCSI]
See Documentation/scsi/aha152x.txt.
aha1542= [HW,SCSI]
Format: [,,[,]]
aic7xxx= [HW,SCSI]
See Documentation/scsi/aic7xxx.txt.
aic79xx= [HW,SCSI]
See Documentation/scsi/aic79xx.txt.
amijoy.map= [HW,JOY] Amiga joystick support
Map of devices attached to JOY0DAT and JOY1DAT
Format: ,
See also Documentation/kernel/input/joystick.txt
analog.map= [HW,JOY] Analog joystick and gamepad support
Specifies type or capabilities of an analog joystick
connected to one of 16 gameports
Format: ,,..
apc= [HW,SPARC]
Power management functions (SPARCstation-4/5 + deriv.)
Format: noidle
Disable APC CPU standby support. SPARCstation-Fox does
not play well with APC CPU idle - disable it if you have
APC and your system crashes randomly.
apic= [APIC,i386] Change the output verbosity whilst booting
Format: { quiet (default) | verbose | debug }
Change the amount of debugging information output
when initialising the APIC and IO-APIC components.
apm= [APM] Advanced Power Management
See header of arch/i386/kernel/apm.c.
applicom= [HW]
Format: ,
arcrimi= [HW,NET] ARCnet - "RIM I" (entirely mem-mapped) cards
Format: ,,
ataflop= [HW,M68k]
atarimouse= [HW,MOUSE] Atari Mouse
atascsi= [HW,SCSI] Atari SCSI
atkbd.extra= [HW] Enable extra LEDs and keys on IBM RapidAccess,
EzKey and similar keyboards
atkbd.reset= [HW] Reset keyboard during initialization
atkbd.set= [HW] Select keyboard code set
Format: (2 = AT (default), 3 = PS/2)
atkbd.scroll= [HW] Enable scroll wheel on MS Office and similar
keyboards
atkbd.softraw= [HW] Choose between synthetic and real raw mode
Format: (0 = real, 1 = synthetic (default))
atkbd.softrepeat= [HW]
Use software keyboard repeat
autotest [IA64]
awe= [HW,OSS] AWE32/SB32/AWE64 wave table synth
Format: ,,
aztcd= [HW,CD] Aztech CD268 CDROM driver
Format: ,0x79 (?)
baycom_epp= [HW,AX25]
Format: ,
baycom_par= [HW,AX25] BayCom Parallel Port AX.25 Modem
Format: ,
See header of drivers/net/hamradio/baycom_par.c.
baycom_ser_fdx= [HW,AX25]
BayCom Serial Port AX.25 Modem (Full Duplex Mode)
Format: ,,[,]
See header of drivers/net/hamradio/baycom_ser_fdx.c.
baycom_ser_hdx= [HW,AX25]
BayCom Serial Port AX.25 Modem (Half Duplex Mode)
Format: ,,
See header of drivers/net/hamradio/baycom_ser_hdx.c.
blkmtd_device= [HW,MTD]
blkmtd_erasesz=
blkmtd_ro=
blkmtd_bs=
blkmtd_count=
bttv.card= [HW,V4L] bttv (bt848 + bt878 based grabber cards)
bttv.radio= Most important insmod options are available as
kernel args too.
bttv.pll= See Documentation/video4linux/bttv/Insmod-options
bttv.tuner= and Documentation/video4linux/bttv/CARDLIST
BusLogic= [HW,SCSI]
See drivers/scsi/BusLogic.c, comment before function
BusLogic_ParseDriverOptions().
c101= [NET] Moxa C101 synchronous serial card
cachesize= [BUGS=IA-32] Override level 2 CPU cache size detection.
Sometimes CPU hardware bugs make them report the cache
size incorrectly. The kernel will attempt work arounds
to fix known problems, but for some CPUs it is not
possible to determine what the correct size should be.
This option provides an override for these situations.
cdu31a= [HW,CD]
Format: ,[,PAS]
See header of drivers/cdrom/cdu31a.c.
chandev= [HW,NET] Generic channel device initialisation
checkreqprot [SELINUX] Set initial checkreqprot flag value.
Format: { "0" | "1" }
See security/selinux/Kconfig help text.
0 -- check protection applied by kernel (includes
any implied execute protection).
1 -- check protection requested by application.
Default value is set via a kernel config option.
Value can be changed at runtime via
/selinux/checkreqprot.
clock= [BUGS=IA-32,HW] gettimeofday timesource override.
Forces specified timesource (if avaliable) to be used
when calculating gettimeofday(). If specicified
timesource is not avalible, it defaults to PIT.
Format: { pit | tsc | cyclone | pmtmr }
hpet= [IA-32,HPET] option to disable HPET and use PIT.
Format: disable
cm206= [HW,CD]
Format: { auto | [,][] }
com20020= [HW,NET] ARCnet - COM20020 chipset
Format:
[,[,[,[,[,]]]]]
com90io= [HW,NET] ARCnet - COM90xx chipset (IO-mapped buffers)
Format: [,]
com90xx= [HW,NET]
ARCnet - COM90xx chipset (memory-mapped buffers)
Format: [,[,]]
condev= [HW,S390] console device
conmode=
console= [KNL] Output console device and options.
tty Use the virtual console device .
ttyS[,options]
Use the specified serial port. The options are of
the form "bbbbpn", where "bbbb" is the baud rate,
"p" is parity ("n", "o", or "e"), and "n" is bits.
Default is "9600n8".
See also Documentation/serial-console.txt.
uart,io,[,options]
uart,mmio,[,options]
Start an early, polled-mode console on the 8250/16550
UART at the specified I/O port or MMIO address,
switching to the matching ttyS device later. The
options are the same as for ttyS, above.
cpcihp_generic= [HW,PCI] Generic port I/O CompactPCI driver
Format:
,,,[,]
cpia_pp= [HW,PPT]
Format: { parport | auto | none }
crashkernel=nn[KMG]@ss[KMG]
[KNL] Reserve a chunk of physical memory to
hold a kernel to switch to with kexec on panic.
cs4232= [HW,OSS]
Format: ,,,,,
cs89x0_dma= [HW,NET]
Format:
cs89x0_media= [HW,NET]
Format: { rj45 | aui | bnc }
cyclades= [HW,SERIAL] Cyclades multi-serial port adapter.
dasd= [HW,NET]
See header of drivers/s390/block/dasd_devmap.c.
db9.dev[2|3]= [HW,JOY] Multisystem joystick support via parallel port
(one device per port)
Format: ,
See also Documentation/input/joystick-parport.txt
debug [KNL] Enable kernel debugging (events log level).
decnet= [HW,NET]
Format: [,]
See also Documentation/networking/decnet.txt.
devfs= [DEVFS]
See Documentation/filesystems/devfs/boot-options.
dhash_entries= [KNL]
Set number of hash buckets for dentry cache.
digi= [HW,SERIAL]
IO parameters + enable/disable command.
digiepca= [HW,SERIAL]
See drivers/char/README.epca and
Documentation/digiepca.txt.
dmascc= [HW,AX25,SERIAL] AX.25 Z80SCC driver with DMA
support available.
Format: [,[,..]]
dmasound= [HW,OSS] Sound subsystem buffers
dscc4.setup= [NET]
dtc3181e= [HW,SCSI]
earlyprintk= [IA-32,X86-64]
earlyprintk=vga
earlyprintk=serial[,ttySn[,baudrate]]
Append ",keep" to not disable it when the real console
takes over.
Only vga or serial at a time, not both.
Currently only ttyS0 and ttyS1 are supported.
Interaction with the standard serial driver is not
very good.
The VGA output is eventually overwritten by the real
console.
eata= [HW,SCSI]
eda= [HW,PS2]
edb= [HW,PS2]
edd= [EDD]
Format: {"of[f]" | "sk[ipmbr]"}
See comment in arch/i386/boot/edd.S
eicon= [HW,ISDN]
Format: ,,
eisa_irq_edge= [PARISC,HW]
See header of drivers/parisc/eisa.c.
elanfreq= [IA-32]
See comment before function elanfreq_setup() in
arch/i386/kernel/cpu/cpufreq/elanfreq.c.
elevator= [IOSCHED]
Format: {"as" | "cfq" | "deadline" | "noop"}
See Documentation/block/as-iosched.txt and
Documentation/block/deadline-iosched.txt for details.
elfcorehdr= [IA-32]
Specifies physical address of start of kernel core
image elf header.
See Documentation/kdump.txt for details.
enforcing [SELINUX] Set initial enforcing status.
Format: {"0" | "1"}
See security/selinux/Kconfig help text.
0 -- permissive (log only, no denials).
1 -- enforcing (deny and log).
Default value is 0.
Value can be changed at runtime via /selinux/enforce.
es1370= [HW,OSS]
Format: [,]
See also header of sound/oss/es1370.c.
es1371= [HW,OSS]
Format: ,[,[]]
See also header of sound/oss/es1371.c.
ether= [HW,NET] Ethernet cards parameters
This option is obsoleted by the "netdev=" option, which
has equivalent usage. See its documentation for details.
eurwdt= [HW,WDT] Eurotech CPU-1220/1410 onboard watchdog.
Format: [,]
fd_mcs= [HW,SCSI]
See header of drivers/scsi/fd_mcs.c.
fdomain= [HW,SCSI]
See header of drivers/scsi/fdomain.c.
floppy= [HW]
See Documentation/floppy.txt.
ftape= [HW] Floppy Tape subsystem debugging options.
See Documentation/ftape.txt.
gamecon.map[2|3]=
[HW,JOY] Multisystem joystick and NES/SNES/PSX pad
support via parallel port (up to 5 devices per port)
Format: ,,,,,
See also Documentation/input/joystick-parport.txt
gamma= [HW,DRM]
gdth= [HW,SCSI]
See header of drivers/scsi/gdth.c.
gpt [EFI] Forces disk with valid GPT signature but
invalid Protective MBR to be treated as GPT.
gscd= [HW,CD]
Format:
gt96100eth= [NET] MIPS GT96100 Advanced Communication Controller
gus= [HW,OSS]
Format: ,,,
gvp11= [HW,SCSI]
hashdist= [KNL,NUMA] Large hashes allocated during boot
are distributed across NUMA nodes. Defaults on
for IA-64, off otherwise.
Format: 0 | 1 (for off | on)
hcl= [IA-64] SGI's Hardware Graph compatibility layer
hd= [EIDE] (E)IDE hard drive subsystem geometry
Format: ,,
hd?= [HW] (E)IDE subsystem
hd?lun= See Documentation/ide.txt.
highmem=nn[KMG] [KNL,BOOT] forces the highmem zone to have an exact
size of . This works even on boxes that have no
highmem otherwise. This also works to reduce highmem
size on bigger boxes.
hisax= [HW,ISDN]
See Documentation/isdn/README.HiSax.
hugepages= [HW,IA-32,IA-64] Maximal number of HugeTLB pages.
noirqbalance [IA-32,SMP,KNL] Disable kernel irq balancing
i8042.direct [HW] Put keyboard port into non-translated mode
i8042.dumbkbd [HW] Pretend that controlled can only read data from
keyboard and can not control its state
(Don't attempt to blink the leds)
i8042.noaux [HW] Don't check for auxiliary (== mouse) port
i8042.nokbd [HW] Don't check/create keyboard port
i8042.nomux [HW] Don't check presence of an active multiplexing
controller
i8042.nopnp [HW] Don't use ACPIPnP / PnPBIOS to discover KBD/AUX
controllers
i8042.panicblink=
[HW] Frequency with which keyboard LEDs should blink
when kernel panics (default is 0.5 sec)
i8042.reset [HW] Reset the controller during init and cleanup
i8042.unlock [HW] Unlock (ignore) the keylock
i810= [HW,DRM]
i8k.ignore_dmi [HW] Continue probing hardware even if DMI data
indicates that the driver is running on unsupported
hardware.
i8k.force [HW] Activate i8k driver even if SMM BIOS signature
does not match list of supported models.
i8k.power_status
[HW] Report power status in /proc/i8k
(disabled by default)
i8k.restricted [HW] Allow controlling fans only if SYS_ADMIN
capability is set.
ibmmcascsi= [HW,MCA,SCSI] IBM MicroChannel SCSI adapter
See Documentation/mca.txt.
icn= [HW,ISDN]
Format: [,[,[,]]]
ide= [HW] (E)IDE subsystem
Format: ide=nodma or ide=doubler or ide=reverse
See Documentation/ide.txt.
ide?= [HW] (E)IDE subsystem
Format: ide?=noprobe or chipset specific parameters.
See Documentation/ide.txt.
idebus= [HW] (E)IDE subsystem - VLB/PCI bus speed
See Documentation/ide.txt.
idle= [HW]
Format: idle=poll or idle=halt
ihash_entries= [KNL]
Set number of hash buckets for inode cache.
in2000= [HW,SCSI]
See header of drivers/scsi/in2000.c.
init= [KNL]
Format:
Run specified binary instead of /sbin/init as init
process.
initcall_debug [KNL] Trace initcalls as they are executed. Useful
for working out where the kernel is dying during
startup.
initrd= [BOOT] Specify the location of the initial ramdisk
inport.irq= [HW] Inport (ATI XL and Microsoft) busmouse driver
Format:
inttest= [IA64]
io7= [HW] IO7 for Marvel based alpha systems
See comment before marvel_specify_io7 in
arch/alpha/kernel/core_marvel.c.
ip= [IP_PNP]
See Documentation/nfsroot.txt.
ip2= [HW] Set IO/IRQ pairs for up to 4 IntelliPort boards
See comment before ip2_setup() in drivers/char/ip2.c.
ips= [HW,SCSI] Adaptec / IBM ServeRAID controller
See header of drivers/scsi/ips.c.
irqfixup [HW]
When an interrupt is not handled search all handlers
for it. Intended to get systems with badly broken
firmware running.
irqpoll [HW]
When an interrupt is not handled search all handlers
for it. Also check all handlers each timer
interrupt. Intended to get systems with badly broken
firmware running.
isapnp= [ISAPNP]
Format: ,,,
isolcpus= [KNL,SMP] Isolate CPUs from the general scheduler.
Format: ,...,
This option can be used to specify one or more CPUs
to isolate from the general SMP balancing and scheduling
algorithms. The only way to move a process onto or off
an "isolated" CPU is via the CPU affinity syscalls.
begins at 0 and the maximum value is
"number of CPUs in system - 1".
This option is the preferred way to isolate CPUs. The
alternative -- manually setting the CPU mask of all
tasks in the system -- can cause problems and
suboptimal load balancer performance.
isp16= [HW,CD]
Format: ,,,
iucv= [HW,NET]
js= [HW,JOY] Analog joystick
See Documentation/input/joystick.txt.
keepinitrd [HW,ARM]
kstack=N [IA-32,X86-64] Print N words from the kernel stack
in oops dumps.
l2cr= [PPC]
lapic [IA-32,APIC] Enable the local APIC even if BIOS
disabled it.
lasi= [HW,SCSI] PARISC LASI driver for the 53c700 chip
Format: addr:,irq:
llsc*= [IA64] See function print_params() in
arch/ia64/sn/kernel/llsc4.c.
load_ramdisk= [RAM] List of ramdisks to load from floppy
See Documentation/ramdisk.txt.
lockd.udpport= [NFS]
lockd.tcpport= [NFS]
logibm.irq= [HW,MOUSE] Logitech Bus Mouse Driver
Format:
loglevel= All Kernel Messages with a loglevel smaller than the
console loglevel will be printed to the console. It can
also be changed with klogd or other programs. The
loglevels are defined as follows:
0 (KERN_EMERG) system is unusable
1 (KERN_ALERT) action must be taken immediately
2 (KERN_CRIT) critical conditions
3 (KERN_ERR) error conditions
4 (KERN_WARNING) warning conditions
5 (KERN_NOTICE) normal but significant condition
6 (KERN_INFO) informational
7 (KERN_DEBUG) debug-level messages
log_buf_len=n Sets the size of the printk ring buffer, in bytes.
Format: { n | nk | nM }
n must be a power of two. The default size
is set in the kernel config file.
lp=0 [LP] Specify parallel ports to use, e.g,
lp=port[,port...] lp=none,parport0 (lp0 not configured, lp1 uses
lp=reset first parallel port). 'lp=0' disables the
lp=auto printer driver. 'lp=reset' (which can be
specified in addition to the ports) causes
attached printers to be reset. Using
lp=port1,port2,... specifies the parallel ports
to associate lp devices with, starting with
lp0. A port specification may be 'none' to skip
that lp device, or a parport name such as
'parport0'. Specifying 'lp=auto' instead of a
port specification list means that device IDs
from each port should be examined, to see if
an IEEE 1284-compliant printer is attached; if
so, the driver will manage that printer.
See also header of drivers/char/lp.c.
lpj=n [KNL]
Sets loops_per_jiffy to given constant, thus avoiding
time-consuming boot-time autodetection (up to 250 ms per
CPU). 0 enables autodetection (default). To determine
the correct value for your kernel, boot with normal
autodetection and see what value is printed. Note that
on SMP systems the preset will be applied to all CPUs,
which is likely to cause problems if your CPUs need
significantly divergent settings. An incorrect value
will cause delays in the kernel to be wrong, leading to
unpredictable I/O errors and other breakage. Although
unlikely, in the extreme case this might damage your
hardware.
ltpc= [NET]
Format: ,,
mac5380= [HW,SCSI] Format:
,,,,
mac53c9x= [HW,SCSI] Format:
,,,,,,,
machvec= [IA64] Force the use of a particular machine-vector
(machvec) in a generic kernel.
Example: machvec=hpzx1_swiotlb
mad16= [HW,OSS] Format:
,,,,,,
maui= [HW,OSS]
Format: ,
max_loop= [LOOP] Maximum number of loopback devices that can
be mounted
Format:
maxcpus= [SMP] Maximum number of processors that an SMP kernel
should make use of
max_addr=[KMG] [KNL,BOOT,ia64] All physical memory greater than or
equal to this physical address is ignored.
max_luns= [SCSI] Maximum number of LUNs to probe.
Should be between 1 and 2^32-1.
max_report_luns=
[SCSI] Maximum number of LUNs received.
Should be between 1 and 16384.
mca-pentium [BUGS=IA-32]
mcatest= [IA-64]
mcd= [HW,CD]
Format: ,,
mcdx= [HW,CD]
mce [IA-32] Machine Check Exception
md= [HW] RAID subsystems devices and level
See Documentation/md.txt.
mdacon= [MDA]
Format: ,
Specifies range of consoles to be captured by the MDA.
mem=nn[KMG] [KNL,BOOT] Force usage of a specific amount of memory
Amount of memory to be used when the kernel is not able
to see the whole system memory or for test.
[IA-32] Use together with memmap= to avoid physical
address space collisions. Without memmap= PCI devices
could be placed at addresses belonging to unused RAM.
mem=nopentium [BUGS=IA-32] Disable usage of 4MB pages for kernel
memory.
memmap=exactmap [KNL,IA-32] Enable setting of an exact
E820 memory map, as specified by the user.
Such memmap=exactmap lines can be constructed based on
BIOS output or other requirements. See the memmap=nn@ss
option description.
memmap=nn[KMG]@ss[KMG]
[KNL] Force usage of a specific region of memory
Region of memory to be used, from ss to ss+nn.
memmap=nn[KMG]#ss[KMG]
[KNL,ACPI] Mark specific memory as ACPI data.
Region of memory to be used, from ss to ss+nn.
memmap=nn[KMG]$ss[KMG]
[KNL,ACPI] Mark specific memory as reserved.
Region of memory to be used, from ss to ss+nn.
meye.*= [HW] Set MotionEye Camera parameters
See Documentation/video4linux/meye.txt.
mga= [HW,DRM]
mousedev.tap_time=
[MOUSE] Maximum time between finger touching and
leaving touchpad surface for touch to be considered
a tap and be reported as a left button click (for
touchpads working in absolute mode only).
Format:
mousedev.xres= [MOUSE] Horizontal screen resolution, used for devices
reporting absolute coordinates, such as tablets
mousedev.yres= [MOUSE] Vertical screen resolution, used for devices
reporting absolute coordinates, such as tablets
mpu401= [HW,OSS]
Format: ,
MTD_Partition= [MTD]
Format: ,,,
MTD_Region= [MTD] Format:
,[,,,,]
mtdparts= [MTD]
See drivers/mtd/cmdline.c.
mtouchusb.raw_coordinates=
[HW] Make the MicroTouch USB driver use raw coordinates
('y', default) or cooked coordinates ('n')
n2= [NET] SDL Inc. RISCom/N2 synchronous serial card
NCR_D700= [HW,SCSI]
See header of drivers/scsi/NCR_D700.c.
ncr5380= [HW,SCSI]
ncr53c400= [HW,SCSI]
ncr53c400a= [HW,SCSI]
ncr53c406a= [HW,SCSI]
ncr53c8xx= [HW,SCSI]
netdev= [NET] Network devices parameters
Format: ,,,,
Note that mem_start is often overloaded to mean
something different and driver-specific.
This usage is only documented in each driver source
file if at all.
nfsaddrs= [NFS]
See Documentation/nfsroot.txt.
nfsroot= [NFS] nfs root filesystem for disk-less boxes.
See Documentation/nfsroot.txt.
nmi_watchdog= [KNL,BUGS=IA-32] Debugging features for SMP kernels
no387 [BUGS=IA-32] Tells the kernel to use the 387 maths
emulation library even if a 387 maths coprocessor
is present.
noalign [KNL,ARM]
noapic [SMP,APIC] Tells the kernel to not make use of any
IOAPICs that may be present in the system.
noasync [HW,M68K] Disables async and sync negotiation for
all devices.
nobats [PPC] Do not use BATs for mapping kernel lowmem
on "Classic" PPC cores.
nocache [ARM]
nodisconnect [HW,SCSI,M68K] Disables SCSI disconnects.
noexec [IA-64]
noexec [IA-32,X86-64]
noexec=on: enable non-executable mappings (default)
noexec=off: disable nn-executable mappings
nofxsr [BUGS=IA-32]
nohlt [BUGS=ARM]
no-hlt [BUGS=IA-32] Tells the kernel that the hlt
instruction doesn't work correctly and not to
use it.
nohalt [IA-64] Tells the kernel not to use the power saving
function PAL_HALT_LIGHT when idle. This increases
power-consumption. On the positive side, it reduces
interrupt wake-up latency, which may improve performance
in certain environments such as networked servers or
real-time systems.
noirqdebug [IA-32] Disables the code which attempts to detect and
disable unhandled interrupt sources.
noisapnp [ISAPNP] Disables ISA PnP code.
noinitrd [RAM] Tells the kernel not to load any configured
initial RAM disk.
nointroute [IA-64]
nolapic [IA-32,APIC] Do not enable or use the local APIC.
noltlbs [PPC] Do not use large page/tlb entries for kernel
lowmem mapping on PPC40x.
nomce [IA-32] Machine Check Exception
noresidual [PPC] Don't use residual data on PReP machines.
noresume [SWSUSP] Disables resume and restores original swap
space.
no-scroll [VGA] Disables scrollback.
This is required for the Braillex ib80-piezo Braille
reader made by F.H. Papenmeier (Germany).
nosbagart [IA-64]
nosmp [SMP] Tells an SMP kernel to act as a UP kernel.
nosync [HW,M68K] Disables sync negotiation for all devices.
notsc [BUGS=IA-32] Disable Time Stamp Counter
nousb [USB] Disable the USB subsystem
nowb [ARM]
opl3= [HW,OSS]
Format:
opl3sa= [HW,OSS]
Format: ,,,,,
opl3sa2= [HW,OSS] Format:
,,,,,,,[,,
oprofile.timer= [HW]
Use timer interrupt instead of performance counters
optcd= [HW,CD]
Format:
osst= [HW,SCSI] SCSI Tape Driver
Format: ,
See also Documentation/scsi/st.txt.
panic= [KNL] Kernel behaviour on panic
Format:
parkbd.port= [HW] Parallel port number the keyboard adapter is
connected to, default is 0.
Format:
parkbd.mode= [HW] Parallel port keyboard adapter mode of operation,
0 for XT, 1 for AT (default is AT).
Format:
parport= [HW,PPT] Specify parallel ports. 0 disables.
Format: { 0 | auto | 0xBBB[,IRQ[,DMA]] }
Use 'auto' to force the driver to use any
IRQ/DMA settings detected (the default is to
ignore detected IRQ/DMA settings because of
possible conflicts). You can specify the base
address, IRQ, and DMA settings; IRQ and DMA
should be numbers, or 'auto' (for using detected
settings on that particular port), or 'nofifo'
(to avoid using a FIFO even if it is detected).
Parallel ports are assigned in the order they
are specified on the command line, starting
with parport0.
parport_init_mode= [HW,PPT]
Configure VIA parallel port to operate in
a specific mode. This is necessary on Pegasos
computer where firmware has no options for setting
up parallel port mode and sets it to spp.
Currently this function knows 686a and 8231 chips.
Format: [spp|ps2|epp|ecp|ecpepp]
pas2= [HW,OSS] Format:
,,,,,,,
pas16= [HW,SCSI]
See header of drivers/scsi/pas16.c.
pcbit= [HW,ISDN]
pcd. [PARIDE]
See header of drivers/block/paride/pcd.c.
See also Documentation/paride.txt.
pci=option[,option...] [PCI] various PCI subsystem options:
off [IA-32] don't probe for the PCI bus
bios [IA-32] force use of PCI BIOS, don't access
the hardware directly. Use this if your machine
has a non-standard PCI host bridge.
nobios [IA-32] disallow use of PCI BIOS, only direct
hardware access methods are allowed. Use this
if you experience crashes upon bootup and you
suspect they are caused by the BIOS.
conf1 [IA-32] Force use of PCI Configuration
Mechanism 1.
conf2 [IA-32] Force use of PCI Configuration
Mechanism 2.
nosort [IA-32] Don't sort PCI devices according to
order given by the PCI BIOS. This sorting is
done to get a device order compatible with
older kernels.
biosirq [IA-32] Use PCI BIOS calls to get the interrupt
routing table. These calls are known to be buggy
on several machines and they hang the machine
when used, but on other computers it's the only
way to get the interrupt routing table. Try
this option if the kernel is unable to allocate
IRQs or discover secondary PCI buses on your
motherboard.
rom [IA-32] Assign address space to expansion ROMs.
Use with caution as certain devices share
address decoders between ROMs and other
resources.
irqmask=0xMMMM [IA-32] Set a bit mask of IRQs allowed to be
assigned automatically to PCI devices. You can
make the kernel exclude IRQs of your ISA cards
this way.
pirqaddr=0xAAAAA [IA-32] Specify the physical address
of the PIRQ table (normally generated
by the BIOS) if it is outside the
F0000h-100000h range.
lastbus=N [IA-32] Scan all buses thru bus #N. Can be
useful if the kernel is unable to find your
secondary buses and you want to tell it
explicitly which ones they are.
assign-busses [IA-32] Always assign all PCI bus
numbers ourselves, overriding
whatever the firmware may have done.
usepirqmask [IA-32] Honor the possible IRQ mask stored
in the BIOS $PIR table. This is needed on
some systems with broken BIOSes, notably
some HP Pavilion N5400 and Omnibook XE3
notebooks. This will have no effect if ACPI
IRQ routing is enabled.
noacpi [IA-32] Do not use ACPI for IRQ routing
or for PCI scanning.
routeirq Do IRQ routing for all PCI devices.
This is normally done in pci_enable_device(),
so this option is a temporary workaround
for broken drivers that don't call it.
firmware [ARM] Do not re-enumerate the bus but instead
just use the configuration from the
bootloader. This is currently used on
IXP2000 systems where the bus has to be
configured a certain way for adjunct CPUs.
pcmv= [HW,PCMCIA] BadgePAD 4
pd. [PARIDE]
See Documentation/paride.txt.
pdcchassis= [PARISC,HW] Disable/Enable PDC Chassis Status codes at
boot time.
Format: { 0 | 1 }
See arch/parisc/kernel/pdc_chassis.c
pf. [PARIDE]
See Documentation/paride.txt.
pg. [PARIDE]
See Documentation/paride.txt.
pirq= [SMP,APIC] Manual mp-table setup
See Documentation/i386/IO-APIC.txt.
plip= [PPT,NET] Parallel port network link
Format: { parport | timid | 0 }
See also Documentation/parport.txt.
pnpacpi= [ACPI]
{ off }
pnpbios= [ISAPNP]
{ on | off | curr | res | no-curr | no-res }
pnp_reserve_irq=
[ISAPNP] Exclude IRQs for the autoconfiguration
pnp_reserve_dma=
[ISAPNP] Exclude DMAs for the autoconfiguration
pnp_reserve_io= [ISAPNP] Exclude I/O ports for the autoconfiguration
Ranges are in pairs (I/O port base and size).
pnp_reserve_mem=
[ISAPNP] Exclude memory regions for the
autoconfiguration.
Ranges are in pairs (memory base and size).
profile= [KNL] Enable kernel profiling via /proc/profile
Format: [schedule,]
Param: "schedule" - profile schedule points.
Param: - step/bucket size as a power of 2 for
statistical time based profiling.
processor.max_cstate= [HW,ACPI]
Limit processor to maximum C-state
max_cstate=9 overrides any DMI blacklist limit.
prompt_ramdisk= [RAM] List of RAM disks to prompt for floppy disk
before loading.
See Documentation/ramdisk.txt.
psmouse.proto= [HW,MOUSE] Highest PS2 mouse protocol extension to
probe for; one of (bare|imps|exps|lifebook|any).
psmouse.rate= [HW,MOUSE] Set desired mouse report rate, in reports
per second.
psmouse.resetafter= [HW,MOUSE]
Try to reset the device after so many bad packets
(0 = never).
psmouse.resolution=
[HW,MOUSE] Set desired mouse resolution, in dpi.
psmouse.smartscroll=
[HW,MOUSE] Controls Logitech smartscroll autorepeat.
0 = disabled, 1 = enabled (default).
pss= [HW,OSS] Personal Sound System (ECHO ESC614)
Format:
,,,,,
pt. [PARIDE]
See Documentation/paride.txt.
quiet= [KNL] Disable log messages
r128= [HW,DRM]
raid= [HW,RAID]
See Documentation/md.txt.
ramdisk= [RAM] Sizes of RAM disks in kilobytes [deprecated]
See Documentation/ramdisk.txt.
ramdisk_blocksize= [RAM]
See Documentation/ramdisk.txt.
ramdisk_size= [RAM] Sizes of RAM disks in kilobytes
New name for the ramdisk parameter.
See Documentation/ramdisk.txt.
rdinit= [KNL]
Format:
Run specified binary instead of /init from the ramdisk,
used for early userspace startup. See initrd.
reboot= [BUGS=IA-32,BUGS=ARM,BUGS=IA-64] Rebooting mode
Format: [,[,...]]
See arch/*/kernel/reboot.c.
reserve= [KNL,BUGS] Force the kernel to ignore some iomem area
resume= [SWSUSP]
Specify the partition device for software suspend
rhash_entries= [KNL,NET]
Set number of hash buckets for route cache
riscom8= [HW,SERIAL]
Format: [,[,...]]
ro [KNL] Mount root device read-only on boot
root= [KNL] Root filesystem
rootdelay= [KNL] Delay (in seconds) to pause before attempting to
mount the root filesystem
rootflags= [KNL] Set root filesystem mount option string
rootfstype= [KNL] Set root filesystem type
rw [KNL] Mount root device read-write on boot
S [KNL] Run init in single mode
sa1100ir [NET]
See drivers/net/irda/sa1100_ir.c.
sb= [HW,OSS]
Format: ,,,
sbni= [NET] Granch SBNI12 leased line adapter
sbpcd= [HW,CD] Soundblaster CD adapter
Format: ,
See a comment before function sbpcd_setup() in
drivers/cdrom/sbpcd.c.
sc1200wdt= [HW,WDT] SC1200 WDT (watchdog) driver
Format: [,[,]]
scsi_debug_*= [SCSI]
See drivers/scsi/scsi_debug.c.
scsi_default_dev_flags=
[SCSI] SCSI default device flags
Format:
scsi_dev_flags= [SCSI] Black/white list entry for vendor and model
Format: ::
(flags are integer value)
scsi_logging= [SCSI]
selinux [SELINUX] Disable or enable SELinux at boot time.
Format: { "0" | "1" }
See security/selinux/Kconfig help text.
0 -- disable.
1 -- enable.
Default value is set via kernel config option.
If enabled at boot time, /selinux/disable can be used
later to disable prior to initial policy load.
serialnumber [BUGS=IA-32]
sg_def_reserved_size= [SCSI]
sgalaxy= [HW,OSS]
Format: ,,,,
shapers= [NET]
Maximal number of shapers.
sim710= [SCSI,HW]
See header of drivers/scsi/sim710.c.
simeth= [IA-64]
simscsi=
sjcd= [HW,CD]
Format: ,,
See header of drivers/cdrom/sjcd.c.
slram= [HW,MTD]
smart2= [HW]
Format: [,[,...,]]
snd-ad1816a= [HW,ALSA]
snd-ad1848= [HW,ALSA]
snd-ali5451= [HW,ALSA]
snd-als100= [HW,ALSA]
snd-als4000= [HW,ALSA]
snd-azt2320= [HW,ALSA]
snd-cmi8330= [HW,ALSA]
snd-cmipci= [HW,ALSA]
snd-cs4231= [HW,ALSA]
snd-cs4232= [HW,ALSA]
snd-cs4236= [HW,ALSA]
snd-cs4281= [HW,ALSA]
snd-cs46xx= [HW,ALSA]
snd-dt019x= [HW,ALSA]
snd-dummy= [HW,ALSA]
snd-emu10k1= [HW,ALSA]
snd-ens1370= [HW,ALSA]
snd-ens1371= [HW,ALSA]
snd-es968= [HW,ALSA]
snd-es1688= [HW,ALSA]
snd-es18xx= [HW,ALSA]
snd-es1938= [HW,ALSA]
snd-es1968= [HW,ALSA]
snd-fm801= [HW,ALSA]
snd-gusclassic= [HW,ALSA]
snd-gu***treme= [HW,ALSA]
snd-gusmax= [HW,ALSA]
snd-hdsp= [HW,ALSA]
snd-ice1712= [HW,ALSA]
snd-intel8x0= [HW,ALSA]
snd-interwave= [HW,ALSA]
snd-interwave-stb=
[HW,ALSA]
snd-korg1212= [HW,ALSA]
snd-maestro3= [HW,ALSA]
snd-mpu401= [HW,ALSA]
snd-mtpav= [HW,ALSA]
snd-nm256= [HW,ALSA]
snd-opl3sa2= [HW,ALSA]
snd-opti92x-ad1848=
[HW,ALSA]
snd-opti92x-cs4231=
[HW,ALSA]
snd-opti93x= [HW,ALSA]
snd-pmac= [HW,ALSA]
snd-rme32= [HW,ALSA]
snd-rme96= [HW,ALSA]
snd-rme9652= [HW,ALSA]
snd-sb8= [HW,ALSA]
snd-sb16= [HW,ALSA]
snd-sbawe= [HW,ALSA]
snd-serial= [HW,ALSA]
snd-sgalaxy= [HW,ALSA]
snd-sonicvibes= [HW,ALSA]
snd-sun-amd7930=
[HW,ALSA]
snd-sun-cs4231= [HW,ALSA]
snd-trident= [HW,ALSA]
snd-usb-audio= [HW,ALSA,USB]
snd-via82xx= [HW,ALSA]
snd-virmidi= [HW,ALSA]
snd-wavefront= [HW,ALSA]
snd-ymfpci= [HW,ALSA]
sonicvibes= [HW,OSS]
Format:
sonycd535= [HW,CD]
Format: [,]
sonypi.*= [HW] Sony Programmable I/O Control Device driver
See Documentation/sonypi.txt
specialix= [HW,SERIAL] Specialix multi-serial port adapter
See Documentation/specialix.txt.
spia_io_base= [HW,MTD]
spia_fio_base=
spia_pedr=
spia_peddr=
sscape= [HW,OSS]
Format: ,,,,
st= [HW,SCSI] SCSI tape parameters (buffers, etc.)
See Documentation/scsi/st.txt.
st0x= [HW,SCSI]
See header of drivers/scsi/seagate.c.
sti= [PARISC,HW]
Format:
Set the STI (builtin display/keyboard on the HP-PARISC
machines) console (graphic card) which should be used
as the initial boot-console.
See also comment in drivers/video/console/sticore.c.
sti_font= [HW]
See comment in drivers/video/console/sticore.c.
stifb= [HW]
Format: bpp:[:[:...]]
swiotlb= [IA-64] Number of I/O TLB slabs
switches= [HW,M68k]
sym53c416= [HW,SCSI]
See header of drivers/scsi/sym53c416.c.
t128= [HW,SCSI]
See header of drivers/scsi/t128.c.
tdfx= [HW,DRM]
thash_entries= [KNL,NET]
Set number of hash buckets for TCP connection
time Show timing data prefixed to each printk message line
tipar.timeout= [HW,PPT]
Set communications timeout in tenths of a second
(default 15).
tipar.delay= [HW,PPT]
Set inter-bit delay in microseconds (default 10).
tmc8xx= [HW,SCSI]
See header of drivers/scsi/seagate.c.
tmscsim= [HW,SCSI]
See comment before function dc390_setup() in
drivers/scsi/tmscsim.c.
tp720= [HW,PS2]
trix= [HW,OSS] MediaTrix AudioTrix Pro
Format:
,,,,,,,,
tsdev.xres= [TS] Horizontal screen resolution.
tsdev.yres= [TS] Vertical screen resolution.
turbografx.map[2|3]= [HW,JOY]
TurboGraFX parallel port interface
Format:
,,,,,,,
See also Documentation/input/joystick-parport.txt
u14-34f= [HW,SCSI] UltraStor 14F/34F SCSI host adapter
See header of drivers/scsi/u14-34f.c.
uart401= [HW,OSS]
Format: ,
uart6850= [HW,OSS]
Format: ,
usbhid.mousepoll=
[USBHID] The interval which mice are to be polled at.
video= [FB] Frame buffer configuration
See Documentation/fb/modedb.txt.
vga= [BOOT,IA-32] Select a particular video mode
See Documentation/i386/boot.txt and
Documentation/svga.txt.
Use vga=ask for menu.
This is actually a boot loader parameter; the value is
passed to the kernel using a special protocol.
vmalloc=nn[KMG] [KNL,BOOT] Forces the vmalloc area to have an exact
size of . This can be used to increase the
minimum size (128MB on x86). It can also be used to
decrease the size and leave more room for directly
mapped kernel RAM.
vmhalt= [KNL,S390]
vmpoff= [KNL,S390]
waveartist= [HW,OSS]
Format: ,,,
wd33c93= [HW,SCSI]
See header of drivers/scsi/wd33c93.c.
wd7000= [HW,SCSI]
See header of drivers/scsi/wd7000.c.
wdt= [WDT] Watchdog
See Documentation/watchdog/watchdog.txt.
xd= [HW,XT] Original XT pre-IDE (RLL encoded) disks.
xd_geo= See header of drivers/block/xd.c.
xirc2ps_cs= [NET,PCMCIA]
Format:
,,,,,[,[,[,]]]