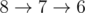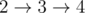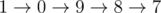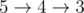下面给出AC代码:
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 char a[1010],b[1010]; 4 int main() 5 { 6 int n; 7 while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF) 8 { 9 cin>>a; 10 cin>>b; 11 int sum=0; 12 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 13 { 14 if(a[i]>=b[i]) 15 sum+=min(a[i]-b[i],b[i]+10-a[i]); 16 else 17 sum+=min(b[i]-a[i],a[i]+10-b[i]); 18 } 19 printf("%d\n",sum); 20 } 21 return 0; 22 }
B. School Marks
Little Vova studies programming in an elite school. Vova and his classmates are supposed to write n progress tests, for each test they will get a mark from 1 to p. Vova is very smart and he can write every test for any mark, but he doesn't want to stand out from the crowd too much. If the sum of his marks for all tests exceeds value x, then his classmates notice how smart he is and start distracting him asking to let them copy his homework. And if the median of his marks will be lower than y points (the definition of a median is given in the notes), then his mom will decide that he gets too many bad marks and forbid him to play computer games.
Vova has already wrote k tests and got marks a1, ..., ak. He doesn't want to get into the first or the second situation described above and now he needs to determine which marks he needs to get for the remaining tests. Help him do that.
The first line contains 5 space-separated integers: n, k, p, x and y (1 ≤ n ≤ 999, n is odd, 0 ≤ k < n, 1 ≤ p ≤ 1000, n ≤ x ≤ n·p, 1 ≤ y ≤ p). Here n is the number of tests that Vova is planned to write, k is the number of tests he has already written, p is the maximum possible mark for a test, x is the maximum total number of points so that the classmates don't yet disturb Vova, y is the minimum median point so that mom still lets him play computer games.
The second line contains k space-separated integers: a1, ..., ak (1 ≤ ai ≤ p) — the marks that Vova got for the tests he has already written.
If Vova cannot achieve the desired result, print "-1".
Otherwise, print n - k space-separated integers — the marks that Vova should get for the remaining tests. If there are multiple possible solutions, print any of them.
5 3 5 18 4
3 5 4
4 1
5 3 5 16 4
5 5 5
-1
The median of sequence a1, ..., an where n is odd (in this problem n is always odd) is the element staying on (n + 1) / 2 position in the sorted list of ai.
In the first sample the sum of marks equals 3 + 5 + 4 + 4 + 1 = 17, what doesn't exceed 18, that means that Vova won't be disturbed by his classmates. And the median point of the sequence {1, 3, 4, 4, 5} equals to 4, that isn't less than 4, so his mom lets him play computer games.
Please note that you do not have to maximize the sum of marks or the median mark. Any of the answers: "4 2", "2 4", "5 1", "1 5", "4 1", "1 4" for the first test is correct.
In the second sample Vova got three '5' marks, so even if he gets two '1' marks, the sum of marks will be 17, that is more than the required value of 16. So, the answer to this test is "-1".
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/540/problem/B
题意:有一个n个元素的序列(n为奇数),现在给出其中的k个元素,让你构造其它的n-k个元素使得该序列的中位数>=y、序列总和<=x、最大元素<=p。输出任意一种可能即可。
分析:由于中位数的区间很小,我们可以去枚举。对于当前的中位数i,我们求出小于i的元素个数l,大于i的元素个数r,等于i的元素个数cnt。除去中位数自身,对于cnt-1(前提cnt!=0),我们贪心的处理,尽可能的放在i的右边,下面就是填数使左右区间元素个数相等。显然左边填1,右边填i就可以保证序列和尽可能小。
下面给出AC代码:
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 typedef long long ll; 4 #define INF 1ll<<60; 5 int main() 6 { 7 int n,k,p,x,y; 8 cin>>n>>k>>p>>x>>y; 9 int sum=0,a; 10 int t1=0;//统计小于y的个数 11 int t2=0;//统计大于等于y的个数 12 int m=n-k;//剩余的标记数 13 for(int i=1;i<=k;i++) 14 { 15 cin>>a; 16 sum+=a; 17 if(a<y) 18 t1++; 19 else t2++; 20 } 21 x-=sum;//剩余的总分 22 if(x<0||t1>n/2||m>x) 23 { 24 cout<<-1<<endl; 25 return 0; 26 } 27 int cnt=(n+1)/2-t2;//判断大于y的个数是否大于总数的一半,(n+1)/2表示向上取整 28 int s=x-(n/2-t1);//最终剩余分数 29 if(cnt>0&&s/cnt<y) 30 { 31 cout<<-1<<endl; 32 return 0; 33 } 34 if(cnt<0) 35 t1=n-k; 36 else t1=(n/2)-t1; 37 for(int i=1;i<=t1;i++) 38 cout<<1<<" "; 39 t2=(n+1)/2-t2; 40 for(int i=1;i<=t2;i++) 41 cout<<y<<" "; 42 return 0; 43 }