Overview
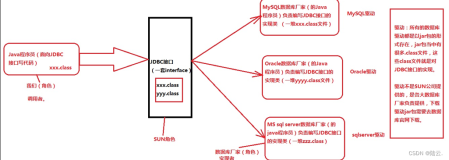
C-JDBC is an open source (LGPL) database cluster middleware that allows any Java application (standalone application, servlet or EJB container, ...) to transparently access a cluster of databases through JDBC(tm). The database is distributed and replicated among several nodes and C-JDBC balances the queries among these nodes. C-JDBC handles node failures and provides support for checkpointing and hot recovery.
Sequoia is a new version of C-JDBC available under an Apache license. You can download Sequoia from the Continuent.org Forge.
| Quick facts |
|---|
|

Wide Database Support
Compatibility is a key aspect of SymmetricDS, which supports 12 major database platforms, making it the perfect choice for heterogenous enterprise environments.
Scale Out
Optimized for performance and scalability, SymmetricDS can replicate thousands of databases asynchronously in near real time.
Flexible Configuration
Configure which tables to sync 1-way or bi-directional. Use horizontal or vertical filtering to subset tables. Combine, filter, or change data with powerful transformations.
Features
- Data Channels - Table synchronizations are grouped into independent channels
- Guaranteed Delivery - Synchronized data is guaranteed to arrive at the target destination. If a synchronization fails, the same batch of data will be retried until it succeeds or manual intervention is taken. All other data synchronization is halted for the failed channel only.
- Transaction Aware - Data updates are recorded and replayed with the same atomicity
- Centralized Configuration - All configuration is downloaded from a central registration server
- Multiple Deployment Options - Standalone engine, web application, embedded software component
- Data Filtering and Rerouting - Allows for localized passwords and sensitive data filtering/routing
- HTTP Transport - Pluggable transport defaults to Representation State Transfer (REST-style) HTTP services
- Payload Compression - Optionally compresses data on transport
- Notification Schemes - Push (trickle-back data) or Pull (trickle-poll data) changes
- Symmetric Data Protocol - A fast streaming data format that is easy to generate, parse, and load
- Plug-In API - Add customizations through extensions and plug-in points
- Two-Way Table Synchronization - The same table can be synchronized both to and from the host system while avoiding update loops
- Database Versioning - Specify data synchronization by version of target database
- Auto Database Creation - Optionally allow creating and upgrading of database schema
- Embeddable - Small enough to embed or bootstrap within another application (i.e. a POS application)
- Multiple Schemas - Supports multiple database schemas naturally through the existence of Data Channels
- Primary Key Updates - Captures the "before" and "after" data being changed, allowing updates to primary key data
- Remote Management - Administration through a Java Management Extensions (JMX) console
- Remote Database Administration - SQL can be delivered and run at remote databases via the synchronization infrastructure
- Initial Data Load - Prepare the satellite database with an initial or recovery load of data
Frequently Asked Questions
What is SymmetricDS?
SymmetricDS is software that replicates relational database tables between multiple databases. It uses a light-weight, web-based protocol to send and receive data, which makes it easy to work with firewalls. Replication is done in the background asynchronously, allowing data changes in offline mode. It supports most commercial and open source database platforms.
How does it work?
Triggers are installed in the database to guarantee that data changes are captured. This means that applications continue to use the database as usual without any special driver software. The triggers are written to be as small and efficient as possible. Routing and syncing of data is done outside of the database in the SymmetricDS process.
Is replication using timestamps?
No, timestamps are not used. Data is captured as it is changed, and each change is given a sequence number. Data changes are grouped together and given a batch number to route through the system. Data changes within a transactional unit are preserved together within a batch.
Can partial tables be replicated?
Yes, subsets of data can be synchronized to other databases. The subset can be: vertical, selecting only some columns to sync; horizontal, selecting only some rows to sync, or both. Different subsets of data can be sent to different databases. For example, a retail store chain can have a central database containing data for all stores, while each retail store database contains just its subset.
Can table names and column names be re-mapped?
Yes, the source table can be mapped to a different table name and different column names at the target database. It is also possible to add new columns and ignore existing columns.
Is there data transformation support?
Data transformation is a built-in core feature. A source table is mapped column by column to a destination table. Data can be transformed using one of several built-in transformers or specifying a Beanshell script. Multiple tables can be mapped together to merge data, and data can be looked up with SQL queries on either the source or target side to supplement data.
Does replication require a fast network connection?
No, the network connection can be slow and even unreliable for periods of time. SymmetricDS makes efficient use of the network with low overhead, batching of data, and data compression. It is designed to withstand periods of network outage by tracking changes that were unsuccessful and retrying.
How quickly are databases replicated?
Asynchronous replication allows the data capture to happen immediately, allowing the source system to continue its activity without waiting. The target system is synchronized in the background separately. The user configures a delay in milliseconds for when the changes are replicated to the target system.
How many replicas are supported?
SymmetricDS is designed to scale to thousands of replicated databases. To scale vertically, configuration properties allow adding more resources to a single node. To scale horizontally, more nodes can be added and configured in cluster mode. A large installation of SymmetricDS at a central database can have multiple instances running together.
Is replication one-way or two-way?
Both one-way and two-way replication configurations are possible. Configuration is at the table level, so table A can be replicated one-way, while table B is replicated two-way. One-way replication, sometimes called primary-backup, means changes are captured at the source system and replicated to the target system. Two-way replication, sometimes called multi-primary, means changes are captured at both source and target systems and replicated to both.
How is data replicated securely?
Data can be encrypted by configuring node addresses to use HTTPS (SSL over HTTP) instead of the default HTTP. By default, connections between instances of SymmetricDS require password authentication. The setup between SymmetricDS instances is called registration, which initiates the password generation and transfer. The registration process can also be customized to use other methods of key exchange.
Can multiple instances be run on the same machine?
Yes, by specifying a different port number for each instance. You can also run multiple nodes in the same instance, which gives each node a different URL to contact.
Can I embed SymmetricDS in my application?
Yes, an application can include SymmetricDS as a library, which allows it to have more control and feedback of replication. This type of application is popular when using a small database system like H2, Apache Derby, or HSQLDB, which gives the overall application a small footprint on memory.
How do I troubleshoot errors?
When an error is encountered during replication, it is written to the log file at the ERROR level with details, using standard Log4J logging. On the source side, the database has an outgoing batch entry with an error status and the captured data that was unable to sync. On the target side, the database has an incoming batch entry with an error status along with the source system's error code and message. Data errors are retried, so if the underlying problem is resolved, such as a missing parent record, then data replication will continue automatically.