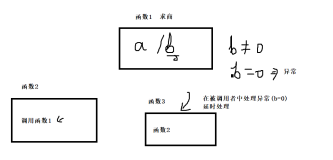
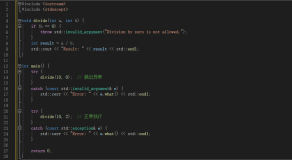
1异常捕获案例1
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
usingnamespacestd;
//标识错误的类型
classwrong{};
intintdiv(inta,intb)
{
try
{
if (b == 0)
{
throw 10;//可以是任何对象 wrong()
}
intc = a /b;
returnc;
}
catch (intdata)
{
cout <<"除法异常已经处理";
return -1;
}
}
intintdivA(inta,intb)
{
returna / b;
}
void main()
{
intx,y;
cin >>x >>y;
try
{
if (y == 0)
{
throw "被除数为0";
}
elseif (x == 0)
{
throw "除数为0";
}
}
//说明捕获的可以使字符串
catch (constchar *s)
{
if (strcmp(s,"被除数为0") == 0)
{
cout <<"被除数为0异常,请重新输入";
cin >>x >>y;
}
elseif (strcmp(s,"除数为0")==0)
{
cout <<"除数为0异常,请重新输入";
cin >>x >>y;
}
}
std::cout << intdiv(x,y);
cin.get();
cin.get();
cin.get();
}
运行结果是:
2.异常处理高级
案例:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
usingnamespacestd;
classbox //正方体
{
public:
box(intdata)
{
std::cout << "开始构造" << std::endl;
if (data == 0)
{
//使用zero抛出异常
zeroz1;
z1.errorcode = 22;
throwz1;
}
elseif (data > 0 &&data < 100)
{
//注意下面是一个(),并非{}
throw small();
}
elseif (data>=100 &&data<=10000)
{
a =data;
}
else
if (data>10000)
{
//使用big抛出异常
throwbig();
}
else
{
//使用wrong抛出异常
throwwrong();
}
}
//用于获得体积
intgettiji()
{
returna *a *a;
}
classzero{
public:
interrorcode;
};
classwrong{};
classbig{};
classsmall{};
private:
inta;//变长
};
voidmain()
{
try
{
//box newbox(0);
//box newbox(99);
//box newbox(100);
//std::cout <<newbox.gettiji() << endl;
boxnewbox(100000);
}
catch (box::zerow)
{
if (w.errorcode == 22)
{
cout <<"大小:错误编码:22:正方体长度不可以为0";
}
else
{
cout <<"错误编码:非22号,错误:正方体长度不可以为0";
}
}
catch (box::wrong)
{
cout <<"正方体长度异常";
}
catch (box::big)
{
cout <<"正方体长度太长";
}
catch (box::small)
{
cout <<"正方体长度太短";
}
cin.get();
}
当代码如下时,运行结果不一样:
//boxnewbox(0);
//boxnewbox(99);
//boxnewbox(100);
//std::cout<< newbox.gettiji() << endl;
boxnewbox(100000);
当前运行结果:
3内存分配异常的处理(std::nothrow)
#include<iostream>
#include<new>
usingnamespacestd;
struct big
{
doubledb[200000];
};
//测试使用异常使得内存异常的时候仍然能够正常使用
voidmain()
{
big *p1, *p2;
//使用std::nothrow让异常不抛出
p1 =new(std::nothrow)big[1000];
p2 =new(std::nothrow)big[1000];
if (p1 ==NULL ||p2 ==NULL)
{
cout <<"内存分配失败";
}
cin.get();
}
4.内存异常
案例:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
usingnamespacestd;
classstudent
{
public:
student()
{
cout <<"构造" << endl;
}
~student()
{
cout <<"析构" << endl;
}
};
classX
{
public:
void *p;//存储地址
charstr[30];
X(void *pt) :p(pt)//这时候pt传递进来的是内存地址
{
}
};//处理异常
boolquit =false;
voidrun()
{
student *p =newstudent;
//delete p;
//p = nullptr;
//异常检测泄露
if (p!=nullptr)
{
quit =true;
if (quit ==true)
{
throwX(reinterpret_cast<void *>(p));//抛出异常,调用构造函数
}
}
}
voidmain()
{
try
{
run();
}
catch (Xe)
{
cout <<"内存异常,内存泄露" << e.p;
}
cin.get();
}
5.异常的虚函数
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
usingnamespacestd;
classbox //正方体
{
public:
box(intdata)
{
cout <<"开始构造";
if (data == 0)
{
zeroz1(22);
z1.seterror(21);
throwz1;
}
elseif (data > 0 &&data<100)
{
throwsmall();
}
else if (data>10000)
{
throwbig();
}
elseif (data > 100 &&data < 10000)
{
a = data;
}
else
{
throwwrong{};
}
}
int gettiji()
{
return a*a*a;
}
classwrong
{
public:
virtualvoidshow()//虚函数
{
cout <<"wrong" <<endl;
}
};
//注意:这里继承了wrong
classbig :publicwrong
{
public:
//实现了虚函数
voidshow()
{
cout <<"big wrong" <<endl;
}
};
//注意:这里继承了wrong
classsmall :publicwrong
{
public:
//实现了虚函数
voidshow()
{
cout <<"small wrong" <<endl;
}
};
classzero :publicsmall //两种错误的处理方式都接受
{
public:
interrorcode;
zero(inti) :errorcode(i)
{
}
void seterror(inti)
{
errorcode =i;
}
};
private:
inta;//变长
};
voidmain()
{
try
{
boxnewbox(11168);
}
catch (box::zerow)
{
if (w.errorcode == 22)
{
cout <<"22号错误正方体长度不可以为0";
}
else
{
cout <<"非22号错误正方体长度不可以为0";
}
}
//虚函数一个接口处理多个错误
//引用是指针实现的,用一个父类的引用
catch (box::wrong &wrong1)
{
wrong1.show();
}
cin.get();
}
运行结果:
6.模板类的异常
#include<iostream>
usingnamespacestd;
//typename会明确类型
//模板的异常,处理通用的数据类型,类中包含一个如果使用
//虚函数,虚函数可以指针,引用来实现
//异常处理机制,一个接口处理通用的异常
template<classT>
classArray
{
public:
classwrong
{
public:
//虚函数
virtualvoidshow()
{
cout <<" wrong " <<typeid(T).name();
}
};
classbig :publicwrong
{
public:
intx;
big(intn) :x(n){}
voidshow()
{
cout <<"big wrong"<<x <<" " <<typeid(T).name();
}
};
classsmall :publicwrong
{
public:
intx;
small(intn) :x(n){}
voidshow()
{
cout <<"small wrong" <<x <<" " <<typeid(T).name();;
}
};
Array(intn)
{
if (n > 0 &&n<10)
{
throwsmall(n);
}
elseif (n>10000)
{
throwbig(n);
}
elseif (n < 0)
{
throwwrong();
}
else
{
p =newT[n];
size = n;
}
}
private:
intsize;
T *p;
};
voidmain()
{
try
{
Array<double>may(1);
}
catch (Array<double>::wrong & wrong1)
{
wrong1.show();
}
cin.get();
}
运行结果: