前言
前文【从入门到放弃-SpringBoot】SpringBoot源码分析-启动中,我们分析了springboot的启动过程,在refreshContext中调用了onRefresh。在SERVLET类型应用中,实际实例化的应用上下文为ServletWebServerApplicationContext。
其onRefresh中调用了createWebServer。我们在本文中一起分析下是一个web应用是如何启动的。
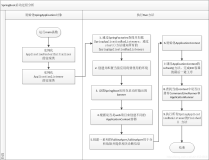
ServletWebServerApplicationContext::createWebServer
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context",
ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
}getWebServerFactory
protected ServletWebServerFactory getWebServerFactory() {
// Use bean names so that we don't consider the hierarchy
String[] beanNames = getBeanFactory()
.getBeanNamesForType(ServletWebServerFactory.class);
if (beanNames.length == 0) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to missing "
+ "ServletWebServerFactory bean.");
}
if (beanNames.length > 1) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to multiple "
+ "ServletWebServerFactory beans : "
+ StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(beanNames));
}
return getBeanFactory().getBean(beanNames[0], ServletWebServerFactory.class);
}- 根据ServletWebServerFactory获取此类型的bean,默认获取的是TomcatServletWebServerFactory,是在ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration中根据条件加载的。
可以通过排除引入Tomcat包等方式切换使用Jetty或Undertow
ServletWebServerApplicationContext::selfInitialize
private void selfInitialize(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
prepareWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
registerApplicationScope(servletContext);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(getBeanFactory(),
servletContext);
for (ServletContextInitializer beans : getServletContextInitializerBeans()) {
beans.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}- 配置servlet启动相关的filter、listener、属性、配置等各项bean。在server启动的时候一起启动
TomcatServletWebServerFactory::getWebServer
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory
: createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
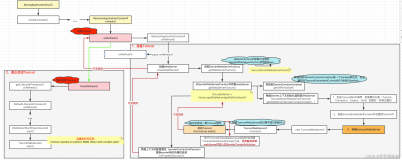
}实际上就是启动了一个Tomcat作为webserver,为了便于理解启动过程,可以先简单了解下Tomcat的架构设计,如下图
Server
tomcat的顶级结构,Tomcat的所有动作都是运行在server中,一个JVM进程中只能启动一个server实例,负责管理整个Service的生命周期。
Service
一个server可以创建多个service,但通常只创建一个。由service对外提供服务
一个service由一个Container和多个Connector构成。通过Connector接收请求交给Container处理
Connector
用于接收请求并封装成request和response的模块。底层用socket进行连接,可以在初始化时,自定义选择使用的协议如http、ajp等
Container
是基础容器接口类,它的子类有Engine、Host、Context和Wrapper,从左到右依次是一对多的父子关系。
Engine
是一个顶级容器,可以包含一个或多个Host,接收到Connector转发的请求后,根据请求头信息找到需要处理的Host,交给它处理
Host
虚拟主机,接收对应host的请求发给context进行处理
Content
web应用上下文,根据请求找到对应的servlet类
Warpper
管理servlet实例,负责其装载、初始化、执行、回收等。一个warpper对应一个servlet实例
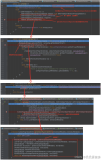
prepareContext
protected void prepareContext(Host host, ServletContextInitializer[] initializers) {
File documentRoot = getValidDocumentRoot();
TomcatEmbeddedContext context = new TomcatEmbeddedContext();
if (documentRoot != null) {
context.setResources(new LoaderHidingResourceRoot(context));
}
context.setName(getContextPath());
context.setDisplayName(getDisplayName());
context.setPath(getContextPath());
File docBase = (documentRoot != null) ? documentRoot
: createTempDir("tomcat-docbase");
context.setDocBase(docBase.getAbsolutePath());
context.addLifecycleListener(new FixContextListener());
context.setParentClassLoader(
(this.resourceLoader != null) ? this.resourceLoader.getClassLoader()
: ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
resetDefaultLocaleMapping(context);
addLocaleMappings(context);
context.setUseRelativeRedirects(false);
configureTldSkipPatterns(context);
WebappLoader loader = new WebappLoader(context.getParentClassLoader());
loader.setLoaderClass(TomcatEmbeddedWebappClassLoader.class.getName());
loader.setDelegate(true);
context.setLoader(loader);
if (isRegisterDefaultServlet()) {
addDefaultServlet(context);
}
if (shouldRegisterJspServlet()) {
addJspServlet(context);
addJasperInitializer(context);
}
context.addLifecycleListener(new StaticResourceConfigurer(context));
ServletContextInitializer[] initializersToUse = mergeInitializers(initializers);
host.addChild(context);
configureContext(context, initializersToUse);
postProcessContext(context);
}- 初始化配置host
- 设置父加载器
- 设置默认的servlet
- 设置jsp的servlet(默认是空)
- 将Content添加至Host
- configureContext:配置Content的默认错误页面、MimeMap、session等内容
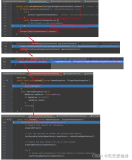
TomcatWebServer::initialize
private void initialize() throws WebServerException {
logger.info("Tomcat initialized with port(s): " + getPortsDescription(false));
synchronized (this.monitor) {
try {
addInstanceIdToEngineName();
Context context = findContext();
context.addLifecycleListener((event) -> {
if (context.equals(event.getSource())
&& Lifecycle.START_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
// Remove service connectors so that protocol binding doesn't
// happen when the service is started.
removeServiceConnectors();
}
});
// Start the server to trigger initialization listeners
this.tomcat.start();
// We can re-throw failure exception directly in the main thread
rethrowDeferredStartupExceptions();
try {
ContextBindings.bindClassLoader(context, context.getNamingToken(),
getClass().getClassLoader());
}
catch (NamingException ex) {
// Naming is not enabled. Continue
}
// Unlike Jetty, all Tomcat threads are daemon threads. We create a
// blocking non-daemon to stop immediate shutdown
startDaemonAwaitThread();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
stopSilently();
throw new WebServerException("Unable to start embedded Tomcat", ex);
}
}
}- 获取service绑定的Connector,保存后删除,这是删除的原因是:在下面start后,Connector就能接收请求了,但还service还未启动,因此先删除Connector达到延后启动的效果
- 启动Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context/Wrapper各级容器
- 之前配置的各项filter、listener等也都在此时启动
TomcatWebServer::startDaemonAwaitThread
private void startDaemonAwaitThread() {
Thread awaitThread = new Thread("container-" + (containerCounter.get())) {
@Override
public void run() {
TomcatWebServer.this.tomcat.getServer().await();
}
};
awaitThread.setContextClassLoader(getClass().getClassLoader());
awaitThread.setDaemon(false);
awaitThread.start();
}
jvm虚拟机在所有的线程都是守护线程时,就会退出。因此需要创建一个用户线程(非守护线程),一直处于监听状态,当接收到关闭信号时,用户线程退出。仅剩下全部守护线程,整个jvm关闭。
public void await() {
// Negative values - don't wait on port - tomcat is embedded or we just don't like ports
if (getPortWithOffset() == -2) {
// undocumented yet - for embedding apps that are around, alive.
return;
}
if (getPortWithOffset() == -1) {
try {
awaitThread = Thread.currentThread();
while(!stopAwait) {
try {
Thread.sleep( 10000 );
} catch( InterruptedException ex ) {
// continue and check the flag
}
}
} finally {
awaitThread = null;
}
return;
}
// Set up a server socket to wait on
try {
awaitSocket = new ServerSocket(getPortWithOffset(), 1,
InetAddress.getByName(address));
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardServer.awaitSocket.fail", address,
String.valueOf(getPortWithOffset()), String.valueOf(getPort()),
String.valueOf(getPortOffset())), e);
return;
}
try {
awaitThread = Thread.currentThread();
// Loop waiting for a connection and a valid command
while (!stopAwait) {
ServerSocket serverSocket = awaitSocket;
if (serverSocket == null) {
break;
}
// Wait for the next connection
Socket socket = null;
StringBuilder command = new StringBuilder();
try {
InputStream stream;
long acceptStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
socket = serverSocket.accept();
socket.setSoTimeout(10 * 1000); // Ten seconds
stream = socket.getInputStream();
} catch (SocketTimeoutException ste) {
// This should never happen but bug 56684 suggests that
// it does.
log.warn(sm.getString("standardServer.accept.timeout",
Long.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis() - acceptStartTime)), ste);
continue;
} catch (AccessControlException ace) {
log.warn(sm.getString("standardServer.accept.security"), ace);
continue;
} catch (IOException e) {
if (stopAwait) {
// Wait was aborted with socket.close()
break;
}
log.error(sm.getString("standardServer.accept.error"), e);
break;
}
// Read a set of characters from the socket
int expected = 1024; // Cut off to avoid DoS attack
while (expected < shutdown.length()) {
if (random == null)
random = new Random();
expected += (random.nextInt() % 1024);
}
while (expected > 0) {
int ch = -1;
try {
ch = stream.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.warn(sm.getString("standardServer.accept.readError"), e);
ch = -1;
}
// Control character or EOF (-1) terminates loop
if (ch < 32 || ch == 127) {
break;
}
command.append((char) ch);
expected--;
}
} finally {
// Close the socket now that we are done with it
try {
if (socket != null) {
socket.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
// Match against our command string
boolean match = command.toString().equals(shutdown);
if (match) {
log.info(sm.getString("standardServer.shutdownViaPort"));
break;
} else
log.warn(sm.getString("standardServer.invalidShutdownCommand", command.toString()));
}
} finally {
ServerSocket serverSocket = awaitSocket;
awaitThread = null;
awaitSocket = null;
// Close the server socket and return
if (serverSocket != null) {
try {
serverSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
}
}- 用户线程创建一个socket,持续监听Tomcat状态,每十秒进行一次检测,如果接收到关闭信号则此线程关闭,整个Tomcat关闭。
TomcatWebServer::start
public void start() throws WebServerException {
synchronized (this.monitor) {
if (this.started) {
return;
}
try {
addPreviouslyRemovedConnectors();
Connector connector = this.tomcat.getConnector();
if (connector != null && this.autoStart) {
performDeferredLoadOnStartup();
}
checkThatConnectorsHaveStarted();
this.started = true;
logger.info("Tomcat started on port(s): " + getPortsDescription(true)
+ " with context path '" + getContextPath() + "'");
}
catch (ConnectorStartFailedException ex) {
stopSilently();
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new WebServerException("Unable to start embedded Tomcat server",
ex);
}
finally {
Context context = findContext();
ContextBindings.unbindClassLoader(context, context.getNamingToken(),
getClass().getClassLoader());
}
}
}- 还记得【从入门到放弃-SpringBoot】SpringBoot源码分析-启动中的finishRefresh吗?
ServletWebServerApplicationContext重写了finishRefresh方法,在里面增加调用了startWebServer。 - 如上将之前删除并保存的connector添加回来并启动。

- 创建socket并绑定监听的端口(默认8080)
- 创建线程池开始接收并处理请求。
总结
至此,springboot中webserver的启动过程我们已经大概清楚了,Tomcat还有很深的内容可以挖,下面可以学习下。