前言:
最近听说thymeleaf好像也挺流行的,还说是spring官方推荐使用,那thymeleaf究竟是什么呢?spring为什么推荐用它呢?怎么用呢?本文将为你揭秘!
一、thymeleaf简介:
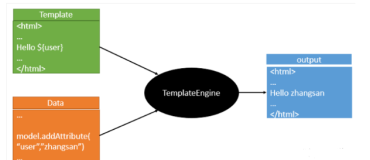
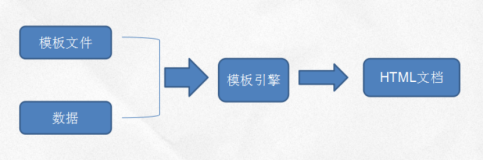
thymeleaf是一种Java模板引擎,那何为模板引擎呢?模板引擎就是为了使用户页面和业务数据相互分离而出现的,将从后台返回的数据生成特定的格式的文档,这里说的特定格式一般都指HTML文档。它能够处理html、xml、js、css甚至纯文本,类似于freemarker。它的优点是语法优雅易懂、原型即页面、遵从web标准。原型即页面是它的特色,所谓原型即页面,就是你写的html,静态的去访问是什么样,动态的去访问还是这样,只不过动态的时候会把数据填充进去。
二、thymeleaf标准方言:
1、变量表达式:${...}
例如前端接收一个user,想取出user的name属性,就可以用变量表达式:
<span th:text="${user.name}">
2、消息表达式:#{...}
也称为文本外部化、国际化或i18n.
<p th:text=" #{header.address.city}" >...</p>
3、选择表达式:*{...}
与变量表达式的区别:选择表达式是在当前选择的对象上执行而不是整个上下文。
<form action="/users" th:action="@{/users}" method="POST" th:object="${userModel.user}">
<input type="hidden" name="id" th:value="*{id}">
</form>
这里id就用了选择表达式,在此处*{id}与${userModel.user.id}效果一样。
4、链接表达式:@{...}
url可以是相对的,也可以是绝对的。
<a th:href="@{.../users/list}">...</a>
<a th:href="@{http://www.baidu.com}">...</a>
5、分段表达式:th:insert 、th:replace 、th:include
就相当插入。这三个的区别:
现有一个片段如下:
<footer th:fragment="copy">
<h1> Hello Thymeleaf </h1>
</footer>
#号分别代表insert、replace、include进行操作:
<div th:#="footer :: copy"></div>
th:insert 的结果:
<div>
<footer th:fragment="copy">
<h1> Hello Thymeleaf </h1>
</footer>
</div>
把footer标签插入到了div标签中。
th:replace的结果:
<footer th:fragment="copy">
<h1> Hello Thymeleaf </h1>
</footer>
把div标签换成了footer标签。
th:include的结果:
<div>
<h1> Hello Thymeleaf </h1>
<div>
把div标签里面的内容换成了footer标签里面的内容。3.X版本后不再推荐使用。
6、字面量:
字面量可以是文本、数字、布尔和null等类型。
7、算术操作:+、-、*、/、%
例如:
<div th:with="isEven=(${user.age} % 2 == 0)">
8、其他运算符:
比较: >、<、>=、<= (gt、lt、ge、le)
等价: ==、!= (eq、ne)
三目运算符:
<tr th:class="${row.even} ? 'even' : 'odd' "></tr>
9、迭代器:th:each
相当于Java的foreach.
<tr th:each="user : ${userList}">
<td th:text="${user.id}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.email}"></td>
</tr>
这样就是遍历userList集合。
迭代器的状态变量有:
index、count、size、current、even/odd、first、last
10、条件语句:th:if、th:unless、switch
<div th:switch="${user.role}">
<p th:case=" 'admin' ">User is admin</p>
<p th:case=" 'guest' ">User is guest</p>
</div>
11、模板布局:th:fragment
比如定义一个公用的页头:
<div th:fragment="header">
<h1>Thymeleaf in action</h1>
<a href="/users" >首页</a>
</div>
在其他页面直接这样引用就行:
<div th:replace="~{fragments/header :: header}"></div>
12、表达式基本对象:
表达式基本对象有:param、session、application、request、servletContext。
三、thymeleaf与springboot集成案例:
本案例使用gradle构建,未涉及数据库,数据保存在ConcurrentMap中。未曾了解gradle的老铁可以参考一下gradle的使用。点我下载本案例源码。
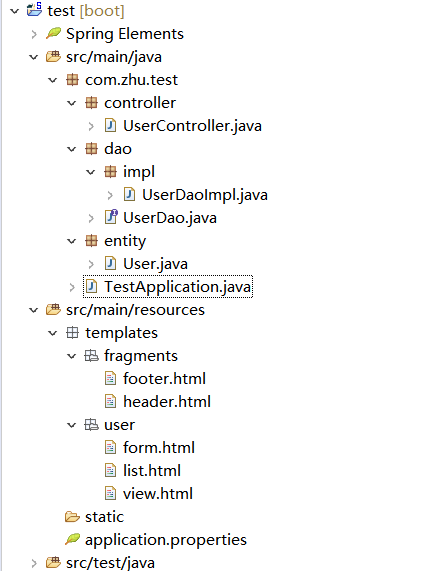
项目结构如下:
1、添加依赖:
dependencies {
compile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web')
testCompile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test')
//thymeleaf的依赖
compile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf')
}
2、application.properties:
#thymeleaf相关配置
spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
spring.thymeleaf.mode=HTML5
3、entity层:
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String email;
}
4、dao层:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.zhu.test.dao.UserDao;
import com.zhu.test.entity.User;
/**
* user dao层实现
* @author zhu
*
*/
@Repository
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
//用来计数的
private static AtomicLong counter = new AtomicLong();
// 用来保存user的map
private final ConcurrentMap<Long, User> userMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
public User saveOrUpdateUser(User user) {
Long id = user.getId();
if(id == null) {//save
id = counter.incrementAndGet();
user.setId(id);
}
this.userMap.put(id, user);
return user;
}
@Override
public void deleteUser(Long id) {
this.userMap.remove(id);
}
@Override
public User getUserById(Long id) {
return this.userMap.get(id);
}
@Override
public List<User> listUsers() {
return new ArrayList<User>(this.userMap.values());
}
}
将user保存在ConcurrentMap中,crud操作其实都是对这个map进行操作。
5、controller层:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
/**
* 查询所有用户
*
* @param model
* @return
*/
@GetMapping
public ModelAndView list(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("userList", userDao.listUsers());
model.addAttribute("title", "用户管理");
return new ModelAndView("user/list", "userModel", model);
}
/**
* 根据id查询用户
*
* @param id
* @param model
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("{id}")
public ModelAndView view(@PathVariable("id") Long id, Model model) {
User user = userDao.getUserById(id);
model.addAttribute("user", user);
model.addAttribute("title", "查看用户");
return new ModelAndView("user/view", "userModel", model);
}
/**
* 获取创建表单页面
*
* @param model
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/form")
public ModelAndView createForm(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("user", new User());
model.addAttribute("title", "创建用户");
return new ModelAndView("user/form", "userModel", model);
}
/**
* 保存或更新用户
*
* @param user
* @return
*/
@PostMapping
public ModelAndView saveOrUpdateUser(User user) {
user = userDao.saveOrUpdateUser(user);
return new ModelAndView("redirect:/users");
}
/**
* 删除用户
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/delete/{id}")
public ModelAndView delete(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
userDao.deleteUser(id);
return new ModelAndView("redirect:/users");// 重定向到list页面
}
/**
* 获取修改用户的界面
*
* @param id
* @param model
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/modify/{id}")
public ModelAndView modify(@PathVariable("id") Long id, Model model) {
User user = userDao.getUserById(id);
model.addAttribute("user", user);
model.addAttribute("title", "修改用户");
return new ModelAndView("user/form", "userModel", model);
}
}
6、前端页面:
注意:要使用thymeleaf,需要在html标签中加上
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
xmlns:layout="http://www.ultraq.net.nz/thymeleaf/layout"
如下页面:
页头:header.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
xmlns:layout="http://www.ultraq.net.nz/thymeleaf/layout">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>thymeleaf in action</title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:fragment="header">
<h1>Thymeleaf in action</h1>
<a href="/users" >首页</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>
页脚:footer.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
xmlns:layout="http://www.ultraq.net.nz/thymeleaf/layout">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>thymeleaf in action</title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:fragment="footer">
<a href="#" >邮箱</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>
form.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
xmlns:layout="http://www.ultraq.net.nz/thymeleaf/layout">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>thymeleaf in action</title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:replace="~{fragments/header :: header}"></div>
<h3 th:text="${userModel.title}">test</h3>
<form action="/users" th:action="@{/users}" method="POST" th:object="${userModel.user}">
<input type="hidden" name="id" th:value="*{id}">
名称:<br>
<input type="text" name="name" th:value="*{name}"><br>
邮箱:<br>
<input type="text" name="email"th:value="*{email}">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
<div th:replace="~{fragments/footer :: footer}"></div>
</body>
</html>
list.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
xmlns:layout="http://www.ultraq.net.nz/thymeleaf/layout">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>thymeleaf in action</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 引用头部信息 -->
<!-- 在fragments下的header文件下有名为header的片段 -->
<div th:replace="~{fragments/header :: header}"></div>
<h3 th:text="${userModel.title}"></h3>
<div>
<a href="/users/form.html" th:href="@{/users/form}">创建用户</a>
</div>
<table border="1">
<thead>
<tr>
<td>ID</td>
<td>Email</td>
<td>Name</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:if="${userModel.userList.size()} eq 0">
<td colspan="3">没有用户信息</td>
</tr>
<tr th:each="user : ${userModel.userList}">
<td th:text="${user.id}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.email}"></td>
<td ><a th:href="@{'/users/'+${user.id}}" th:text="${user.name}"></a></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<div th:replace="~{fragments/footer :: footer}"></div>
</body>
</html>
view.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
xmlns:layout="http://www.ultraq.net.nz/thymeleaf/layout">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>thymeleaf in action</title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:replace="~{fragments/header :: header}"></div>
<h3 th:text="${userModel.title}">test</h3>
<div>
<p><strong>ID:</strong><span th:text="${userModel.user.id}"></span></p>
<p><strong>Name:</strong><span th:text="${userModel.user.name}"></span></p>
<p><strong>Email:</strong><span th:text="${userModel.user.email}"></span></p>
</div>
<div>
<a th:href="@{'/users/delete/'+${userModel.user.id}}">删除</a>
<a th:href="@{'/users/modify/'+${userModel.user.id}}">修改</a>
</div>
<div th:replace="~{fragments/footer :: footer}"></div>
</body>
</html>
以上页面就涉及到了thymeleaf的常用标签,通过这几个页面,理解thymeleaf的用法。
7、测试效果:
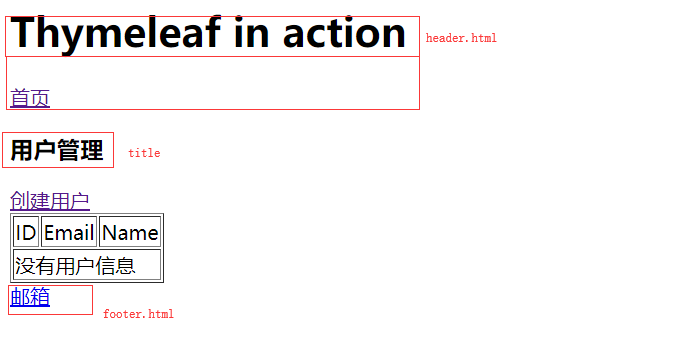
点击“创建用户”:
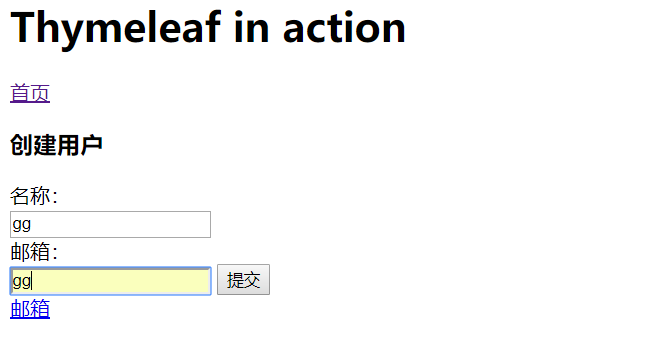
点击“提交”后:

点击name栏可以进入view页面:

这个页面还可以进行删除和修改,这里不再截图。
总结:
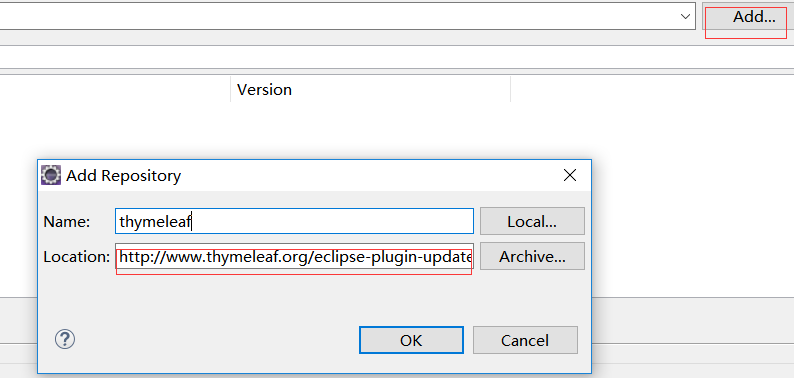
thymeleaf标签看起来很多,其实常用的也不多,且很好理解。主要别忘了在html标签中需要加上xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" xmlns:layout="http://www.ultraq.net.nz/thymeleaf/layout"。如果eclipse写thymeleaf标签时没有提示,安装一下thymeleaf插件重启eclipse即可,点击help --> install new software,地址为:http://www.thymeleaf.org/eclipse-plugin-update-site/.