转载请注明:@小五义 http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaowuyi
欢迎加入讨论群 64770604
一、本次实验所需器材
1、Arduino板 https://item.taobao.com/item.htm?spm=a1z10.5-c-s.w4002-15820725129.16.AtgoEm&id=545093340395
2、1602液晶板:也叫1602字符型液晶,它是一种专门用来显示字母、数字、符号等的点阵型液晶模块。它由若干个5X7或者5X11等点阵字符位组成,每个点阵字符位都可以显示一个字符,每位之间有一个点距的间隔,每行之间也有间隔,起到了字符间距和行间距的作用,正因为如此所以它不能很好地显示图形。目前,尽管各厂家对其各自产品命名不尽相同,但均提供几乎都同样规格的1602模块或者兼容模块。1602最初采用的LCD控制器是HD44780,在各厂家生产的1602模块中,基本上也都采用了与之兼容的控制IC,所以从特性上基本上是一样的。因此,我们买到的1602模块,在端口标记上可能有所不同,有的从左向右,有的从右向左,但特性上是一样的。本实验中使用的1602板,最里面的孔为1号,最靠近边上的那个为16号。
1602实物图片:
1602的规格情况:
| 显示容量 | 16*2个字符 |
| 芯片工作电压 | 4.5-5.5V |
| 工作电流 | 2,0MA(5.0V) |
| 模块最佳工作电压 | 5.0V |
| 字符尺寸 | 2.95*4.35(WXH)mm |
1602管脚介绍:
第1脚:VSS为电源负极
第2脚:VCC接5V电源正极
第3脚:V0为液晶显示器对比度调整端,接正电源时对比度最弱,接地电源时对比度最高(对比度过高时会产生“鬼影”,使用时可以通过一个10K的电位器调整对比度,本实验使用了一个1KΩ电阻)。
第4脚:RS为寄存器选择,高电平1时选择数据寄存器、低电平0时选择指令寄存器。
第5脚:RW为读写信号线,高电平(1)时进行读操作,低电平(0)时进行写操作。
第6脚:E(或EN)端为使能(enable)端,高电平(1)时读取信息,负跳变时执行指令。
第7~14脚:D0~D7为8位双向数据端。
第15~16脚:背灯电源。15脚背光正极,16脚背光负极。
1602字符集介绍:
1602液晶模块内部的字符发生存储器已经存储了160个不同的点阵字符图形,这些字符有:阿拉伯数字、英文字母的大小写、常用的符号、和日文假名等,每一个字符都有一个固定的代码,比如大写的英文字母“A”的代码是01000001B(41H),显示时模块把地址41H中的点阵字符图形显示出来,我们就能看到字母“A”。
1602的16进制ASCII码表地址可从百度搜索,这里不在列出,只写用法。如:感叹号!的ASCII为0x21,字母B的ASCII为0x42。
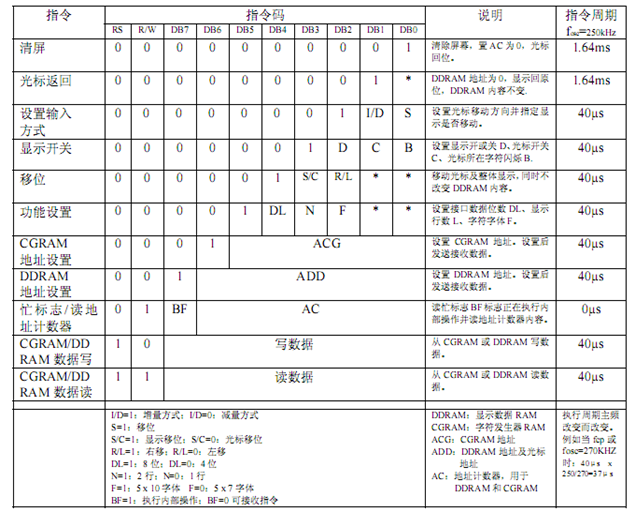
1602指令集:
3、电阻:1KΩ(1个)
4、杜邦线:若干
5、面包板:一个
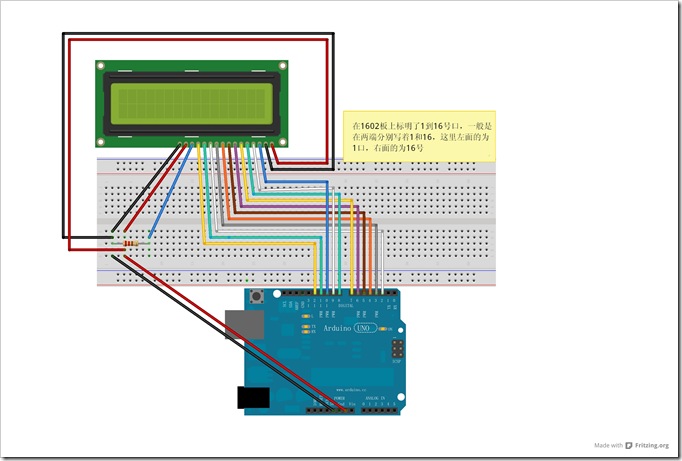
二、8位连接法实验
2、代码:
int DI = 12; int RW = 11; int DB[] = {3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};//使用数组来定义总线需要的管脚 int Enable = 2; void LcdCommandWrite(int value) { // 定义所有引脚 int i = 0; for (i=DB[0]; i <= DI; i++) //总线赋值 { digitalWrite(i,value & 01);//因为1602液晶信号识别是D7-D0(不是D0-D7),这里是用来反转信号。 value >>= 1; } digitalWrite(Enable,LOW); delayMicroseconds(1); digitalWrite(Enable,HIGH); delayMicroseconds(1); // 延时1ms digitalWrite(Enable,LOW); delayMicroseconds(1); // 延时1ms } void LcdDataWrite(int value) { // 定义所有引脚 int i = 0; digitalWrite(DI, HIGH); digitalWrite(RW, LOW); for (i=DB[0]; i <= DB[7]; i++) { digitalWrite(i,value & 01); value >>= 1; } digitalWrite(Enable,LOW); delayMicroseconds(1); digitalWrite(Enable,HIGH); delayMicroseconds(1); digitalWrite(Enable,LOW); delayMicroseconds(1); // 延时1ms } void setup (void) { int i = 0; for (i=Enable; i <= DI; i++) { pinMode(i,OUTPUT); } delay(100); // 短暂的停顿后初始化LCD // 用于LCD控制需要 LcdCommandWrite(0x38); // 设置为8-bit接口,2行显示,5x7文字大小 delay(64); LcdCommandWrite(0x38); // 设置为8-bit接口,2行显示,5x7文字大小 delay(50); LcdCommandWrite(0x38); // 设置为8-bit接口,2行显示,5x7文字大小 delay(20); LcdCommandWrite(0x06); // 输入方式设定 // 自动增量,没有显示移位 delay(20); LcdCommandWrite(0x0E); // 显示设置 // 开启显示屏,光标显示,无闪烁 delay(20); LcdCommandWrite(0x01); // 屏幕清空,光标位置归零 delay(100); LcdCommandWrite(0x80); // 显示设置 // 开启显示屏,光标显示,无闪烁 delay(20); } void loop (void) { LcdCommandWrite(0x01); // 屏幕清空,光标位置归零 delay(10); LcdCommandWrite(0x80+3); delay(10); // 写入欢迎信息 LcdDataWrite('H'); LcdDataWrite('E'); LcdDataWrite('L'); LcdDataWrite('L'); LcdDataWrite('O'); LcdDataWrite(' '); LcdDataWrite('W'); LcdDataWrite('O'); LcdDataWrite('R'); LcdDataWrite('L'); LcdDataWrite('D'); delay(10); LcdCommandWrite(0xc0+2); // 定义光标位置为第二行第二个位置 delay(10); LcdDataWrite('w'); LcdDataWrite('i'); LcdDataWrite('k'); LcdDataWrite('i'); LcdDataWrite('c'); LcdDataWrite('o'); LcdDataWrite('d'); LcdDataWrite('e'); LcdDataWrite('.'); LcdDataWrite('n'); LcdDataWrite('e'); LcdDataWrite('t'); delay(5000); LcdCommandWrite(0x01); // 屏幕清空,光标位置归零 delay(10); LcdDataWrite('I'); LcdDataWrite(' '); LcdDataWrite('a'); LcdDataWrite('m'); LcdDataWrite(' '); LcdDataWrite('x'); LcdDataWrite('i'); LcdDataWrite('a'); LcdDataWrite('o'); LcdDataWrite('w'); LcdDataWrite('u'); LcdDataWrite('y'); LcdDataWrite('i'); delay(3000); LcdCommandWrite(0x02); //设置模式为新文字替换老文字,无新文字的地方显示不变。 delay(10); LcdCommandWrite(0x80+5); //定义光标位置为第一行第6个位置 delay(10); LcdDataWrite('t'); LcdDataWrite('h'); LcdDataWrite('e'); LcdDataWrite(' '); LcdDataWrite('a'); LcdDataWrite('d'); LcdDataWrite('m'); LcdDataWrite('i'); LcdDataWrite('n'); delay(5000); }
3、实验效果
三、四位连接法
4位连接法,可以省出几个数字端口。
1、连接方法
2、代码
int LCD1602_RS=12; int LCD1602_RW=11; int LCD1602_EN=10; int DB[] = { 6, 7, 8, 9}; char str1[]="Welcome to"; char str2[]="wikicode.net"; char str3[]="This is the"; char str4[]="4-bit interface"; void LCD_Command_Write(int command) { int i,temp; digitalWrite( LCD1602_RS,LOW); digitalWrite( LCD1602_RW,LOW); digitalWrite( LCD1602_EN,LOW); temp=command & 0xf0; for (i=DB[0]; i <= 9; i++) { digitalWrite(i,temp & 0x80); temp <<= 1; } digitalWrite( LCD1602_EN,HIGH); delayMicroseconds(1); digitalWrite( LCD1602_EN,LOW); temp=(command & 0x0f)<<4; for (i=DB[0]; i <= 9; i++) { digitalWrite(i,temp & 0x80); temp <<= 1; } digitalWrite( LCD1602_EN,HIGH); delayMicroseconds(1); digitalWrite( LCD1602_EN,LOW); } void LCD_Data_Write(int dat) { int i=0,temp; digitalWrite( LCD1602_RS,HIGH); digitalWrite( LCD1602_RW,LOW); digitalWrite( LCD1602_EN,LOW); temp=dat & 0xf0; for (i=DB[0]; i <= 9; i++) { digitalWrite(i,temp & 0x80); temp <<= 1; } digitalWrite( LCD1602_EN,HIGH); delayMicroseconds(1); digitalWrite( LCD1602_EN,LOW); temp=(dat & 0x0f)<<4; for (i=DB[0]; i <= 9; i++) { digitalWrite(i,temp & 0x80); temp <<= 1; } digitalWrite( LCD1602_EN,HIGH); delayMicroseconds(1); digitalWrite( LCD1602_EN,LOW); } void LCD_SET_XY( int x, int y ) { int address; if (y ==0) address = 0x80 + x; else address = 0xC0 + x; LCD_Command_Write(address); } void LCD_Write_Char( int x,int y,int dat) { LCD_SET_XY( x, y ); LCD_Data_Write(dat); } void LCD_Write_String(int X,int Y,char *s) { LCD_SET_XY( X, Y ); //设置地址 while (*s) //写字符串 { LCD_Data_Write(*s); s ++; } } void setup (void) { int i = 0; for (i=6; i <= 12; i++) { pinMode(i,OUTPUT); } delay(100); LCD_Command_Write(0x28);//4线 2行 5x7 delay(50); LCD_Command_Write(0x06); delay(50); LCD_Command_Write(0x0c); delay(50); LCD_Command_Write(0x80); delay(50); LCD_Command_Write(0x01); delay(50); } void loop (void) { LCD_Command_Write(0x01); delay(50); LCD_Write_String(3,0,str1);//第1行,第4个地址起 delay(50); LCD_Write_String(2,1,str2);//第2行,第2个地址起 delay(5000); LCD_Command_Write(0x01);// delay(50); LCD_Write_String(0,0,str3); delay(50); LCD_Write_String(0,1,str4); delay(5000); }
这里仅做了显示字符串的方法,也可以利用LCD_Write_Char这个过程来显示字符,如:LCD_Write_Char(1,0,0x3a)显示“:”,这里不再举例,在下面的时钟的代码中,会有所利用。
3、实现效果
四、利用Arduino+1602实现时钟
1、硬件连接:采用四位连接法。
2、代码
int LCD1602_RS=12; int LCD1602_RW=11; int LCD1602_EN=10; int DB[] = { 6, 7, 8, 9}; char logtxt[]="Local Time"; char *sec[60]={"00","01","02","03","04","05","06","07","08","09","10","11","12","13","14","15","16","17","18","19","20","21","22","23","24","25","26","27","28","29","30","31","32","33","34","35","36","37","38","39","40","41","42","43","44","45","46","47","48","49","50","51","52","53","54","55","56","57","58","59"}; void LCD_Command_Write(int command) { int i,temp; digitalWrite( LCD1602_RS,LOW); digitalWrite( LCD1602_RW,LOW); digitalWrite( LCD1602_EN,LOW); temp=command & 0xf0; for (i=DB[0]; i <= 9; i++) { digitalWrite(i,temp & 0x80); temp <<= 1; } digitalWrite( LCD1602_EN,HIGH); delayMicroseconds(1); digitalWrite( LCD1602_EN,LOW); temp=(command & 0x0f)<<4; for (i=DB[0]; i <= 9; i++) { digitalWrite(i,temp & 0x80); temp <<= 1; } digitalWrite( LCD1602_EN,HIGH); delayMicroseconds(1); digitalWrite( LCD1602_EN,LOW); } void LCD_Data_Write(int dat) { int i=0,temp; digitalWrite( LCD1602_RS,HIGH); digitalWrite( LCD1602_RW,LOW); digitalWrite( LCD1602_EN,LOW); temp=dat & 0xf0; for (i=DB[0]; i <= 9; i++) { digitalWrite(i,temp & 0x80); temp <<= 1; } digitalWrite( LCD1602_EN,HIGH); delayMicroseconds(1); digitalWrite( LCD1602_EN,LOW); temp=(dat & 0x0f)<<4; for (i=DB[0]; i <= 9; i++) { digitalWrite(i,temp & 0x80); temp <<= 1; } digitalWrite( LCD1602_EN,HIGH); delayMicroseconds(1); digitalWrite( LCD1602_EN,LOW); } void LCD_SET_XY( int x, int y ) { int address; if (y ==0) address = 0x80 + x; else address = 0xC0 + x; LCD_Command_Write(address); } void LCD_Write_Char( int x,int y,int dat) { LCD_SET_XY( x, y ); LCD_Data_Write(dat); } void LCD_Write_String(int X,int Y,char *s) { LCD_SET_XY( X, Y ); //设置地址 while (*s) //写字符串 { LCD_Data_Write(*s); s ++; } } void setup (void) { int i = 0; for (i=6; i <= 12; i++) { pinMode(i,OUTPUT); } delay(100); LCD_Command_Write(0x28);//4线 2行 5x7 delay(50); LCD_Command_Write(0x06); delay(50); LCD_Command_Write(0x0c); delay(50); LCD_Command_Write(0x80); delay(50); LCD_Command_Write(0x01); delay(50); } void loop (void) { for(int index=0,minindex=59,hourindex=12;index<60;index++) //这里来设定现在时间,目前设定为12:59:00
{ LCD_Command_Write(0x01); delay(50); LCD_Write_String(3,0,logtxt); LCD_Write_String(3,1,sec[hourindex]); LCD_Write_Char(6,1,0x3a);//显示: LCD_Write_String(7,1,sec[minindex]); LCD_Write_Char(10,1,0x3a); LCD_Write_String(11,1,sec[index]); delay(950); if (index==59) { index=-1; minindex++; if (minindex==60) { minindex=0; hourindex++; if (hourindex==24) { hourindex=0; } } } } }
3、实现效果